Chapter 15
Diseases
By Boundless
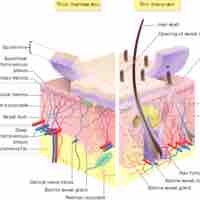
The epidermis includes five main layers: the stratum corneum, stratum lucidium, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum germinativum.
The skin flora, more properly referred to as the skin microbiome or skin microbiota, are the microorganisms that reside on the skin.
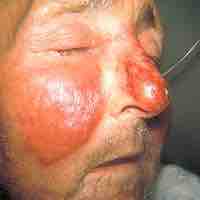
Bacterial skin infections include impetigo, erysipelas, and cellulitis.
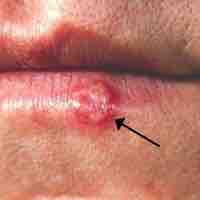
Virus-related cutaneous conditions include cold sores, shingles, and warts.
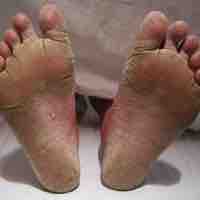
Common fungal skin diseases include athlete's foot, jock itch, and ringworm.

Parasites can cause skin infections and common examples include creeping eruption, lice, and scabies.
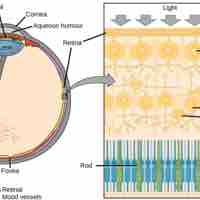
Many structures in the human eye, such as the cornea and fovea, process light so it can be deciphered by rods and cones in the retina.
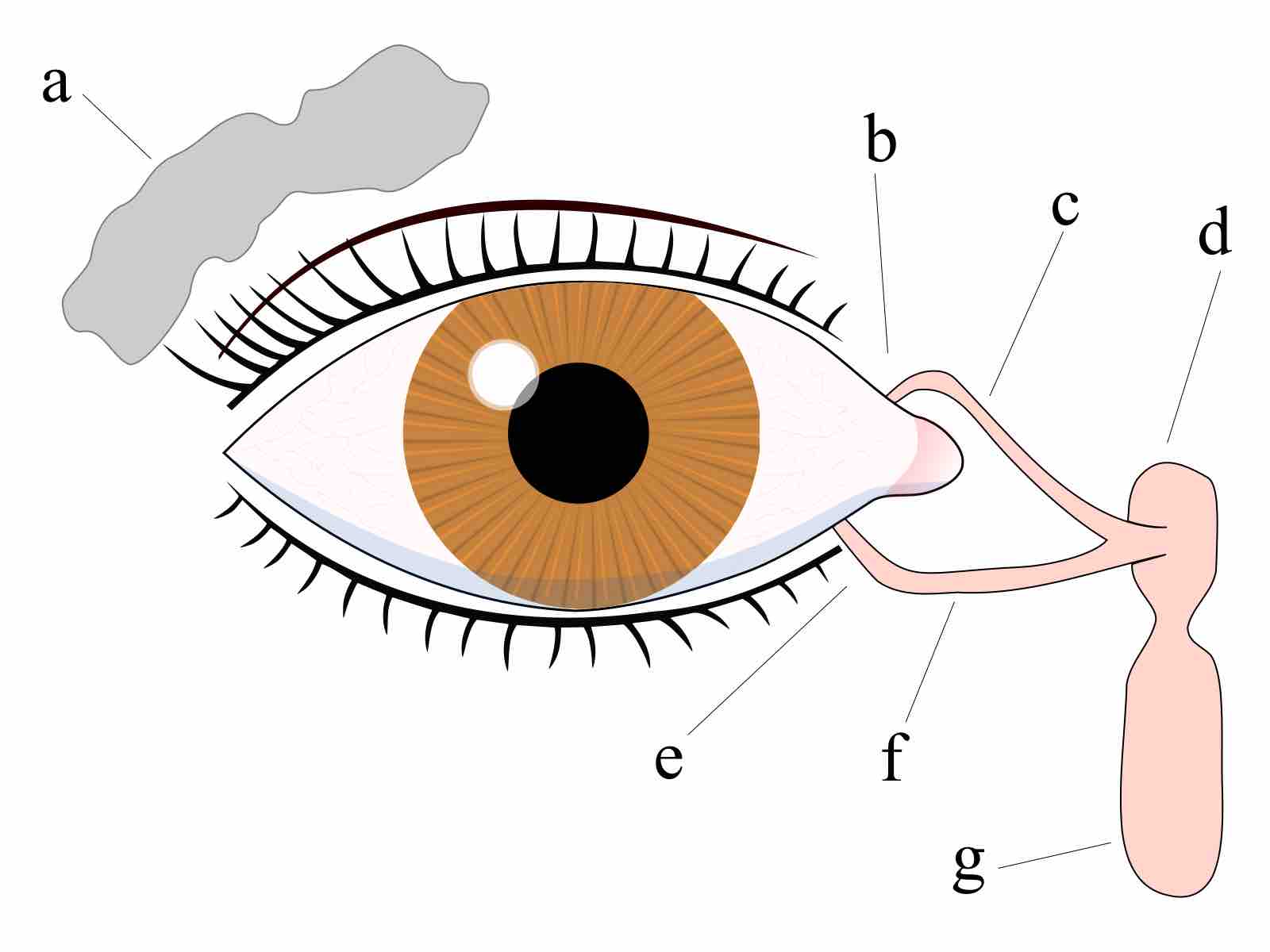
A small number of bacteria are normally present in the conjunctiva.
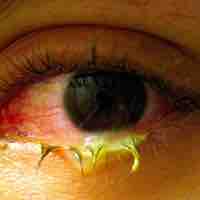
Conjunctivitis is inflammation of the conjunctiva, most commonly due to an infection.
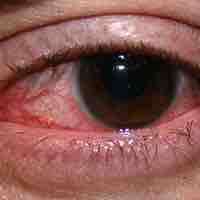
Fungi and viruses such as herpes simplex can cause eye infections.
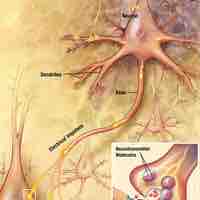
The primary function of the nervous system is to coordinate and control the various functions of our body.
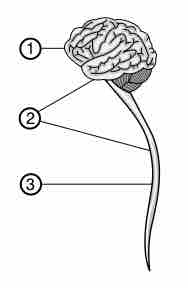
The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS is a network of nerves linking the body to the brain and spinal cord.
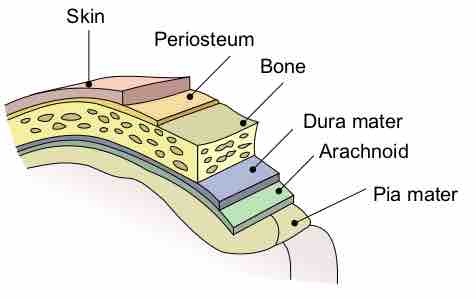
Meningitis is inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, known collectively as the meninges.
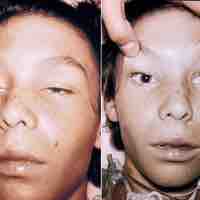
Botulism is a rare but sometimes fatal paralytic illness caused by botulinum toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum.
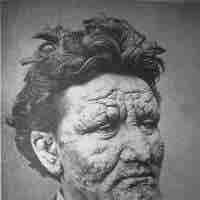
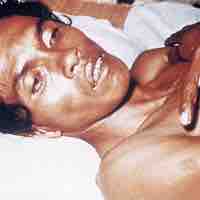
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease, is a chronic bacterial disease caused by Mycobacterium leprae and Mycobacterium lepromatosis.

Tetanus is a medical condition characterized by a prolonged contraction of skeletal muscle fibers.
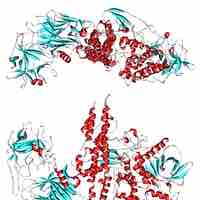
Botulinum toxin is a protein and neurotoxin, which blocks neuromuscular transmission through decreased acetylcholine release.

Rabies is a viral disease that causes acute encephalitis in warm-blooded animals.

Poliomyelitis is an infection by the polio virus that affects the motor neurons of the central nervous system.
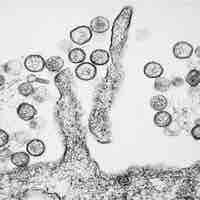
Hantaviruses are negative-sense RNA viruses that sometimes lead to hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in humans.

Arboviral encephalitis (acute swelling in the brain) is caused by a group of arthropod-transmitted viruses.
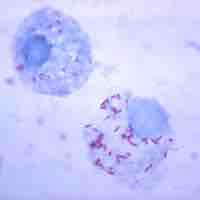
Rickettsia is a genus of bacteria that can be transmitted by arthropod vectors to humans, causing diseases.
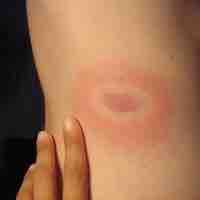
Lyme disease is caused by bacteria from the Borrelia genus.
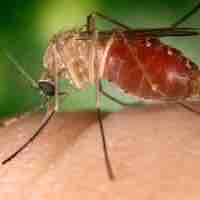
West Nile virus is a mosquito-borne arbovirus found in temperate and tropical regions of the world.

The plague is an infectious disease caused by the Gram-negative rod-shaped bacteria Yersinia pestis.
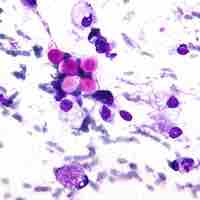
Cryptococcosis is a disease caused by fungi that can be fatal.
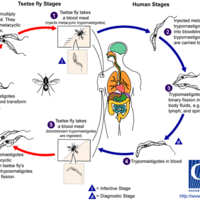
Sleeping sickness is caused by a protozoa transmitted by the tsetse fly.
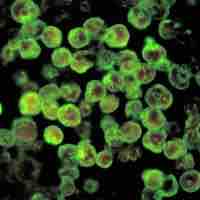
Amoebic meningoencephalitis is an often-fatal central nervous system infection caused by Naegleria fowleri.

Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) is a fatal neurodegenerative disease in cows.
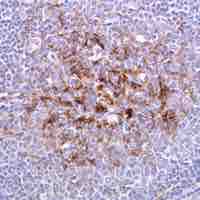
Variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease (vCJD) is a fatal neurological disorder which is caused by prions.

Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) is the most common persistent fatigue syndrome that affects people.
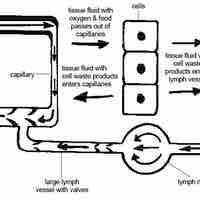
The lymphatic system plays a prominent role in immune function, fatty acid absorption, and removal of interstitial fluid from tissues.
Both the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system are susceptible to diseases caused by microorganisms.
The lymphatic system consists of lymphatic vessels and associated lymphoid organs.
The circulatory system has a defence against microbial invaders in the form of the lymphatic system.
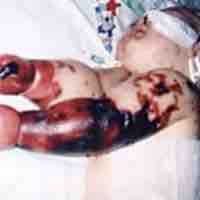
Septic shock occurs when a body's response to an infection (sepsis) leads to life-threatening low blood pressure.
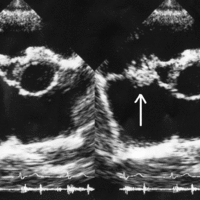
Bacterial endocarditis is an infection of the inner surface of the heart or heart valves caused by the presence of bacteria in the blood.
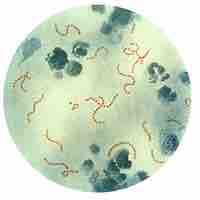
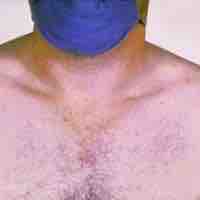
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that can develop as a complication of inadequately treated strep throat.
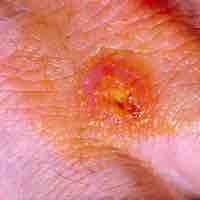
Tularemia is an infection caused by the Gram-negative bacteria Francisella tularensis.
Brucellosis is an infectious disease that occurs from contact with animals carrying Brucella bacteria.
Anthrax is a rare, infectious disease caused by Bacillus anthracis that can spread from animals to humans.

Gangrene is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that arises when a considerable mass of body tissue dies.
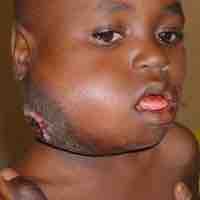
Burkitt's lymphoma is a very fast growing form of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, a cancer in the lymphatic system.
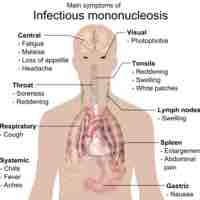
Mononucleosis is an infectious disease caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and results in flu-like symptoms.
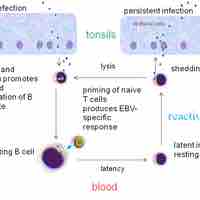
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a member of the herpesvirus family and is best known as the cause of infectious mononucleosis.
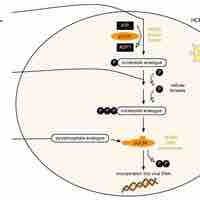
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a type of herpesvirus that largely affects infants and the immunocompromised.

Chikungunya (CHIKV) is a mosquito-borne viral disease which causes fever and severe joint pain.
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a group of illnesses that are caused by several distinct families of RNA viruses.
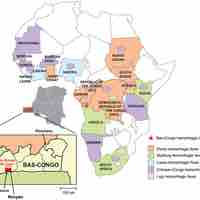
As human habitation expands, new viral hemorrhagic fevers are infecting humans.
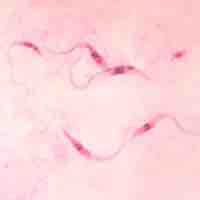
Chagas disease is caused by the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma cruzi and transmitted via the reduviid bug.
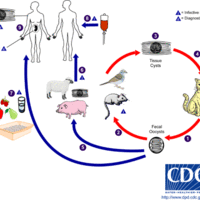
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by the protozoan Toxoplasma gondii and its life cycle mandates a definitive host which are cats.
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals caused by various species of the protist Plasmodium.
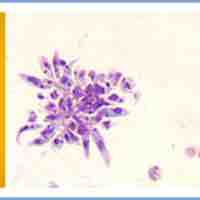
Leishmaniasis is caused by the protozoan parasite Leishmania and presents itself in two forms: cutaneous or visceral leishmaniasis.
Babesiosis is a malaria-like parasitic disease caused by infection with Babesia, a parasite transmitted to human hosts by ticks.
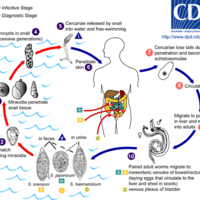
Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease caused by various species of trematodes or "flukes," which are of the genus Schistosoma.
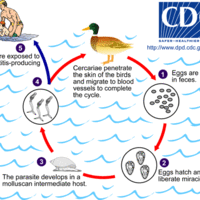
Swimmer's itch is a result of an immune reaction in response to the penetration of the skin by a schistosome.
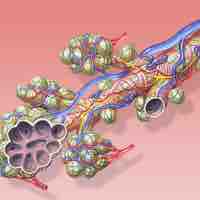
The respiratory system include lungs, airways and respiratory muscles. Ventilation is the rate at which gas enters or leaves the lung.
Airborne diseases are characterized by diseases that are transmitted through the air via the presence of a pathogen.
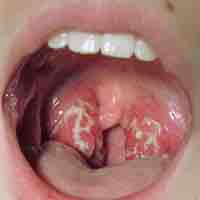
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the throat that has many causes, some of which are bacterial infections.
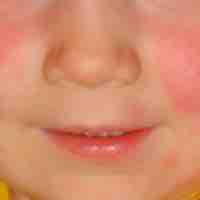
Scarlet fever is caused by a bacteriophage that infects Streptococcus pyogenes.
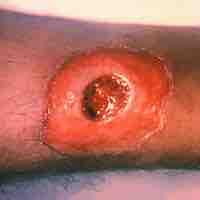
Diphtheria is an upper respiratory infection that is largely benign unless left untreated, at which point very harmful toxins are produced.
Otitis media, or earache, is the inflammation of the middle ear and is often due to bacterial infections.

Pertussis, more commonly known as whooping cough, is a bacterial infection of the upper respiratory system.
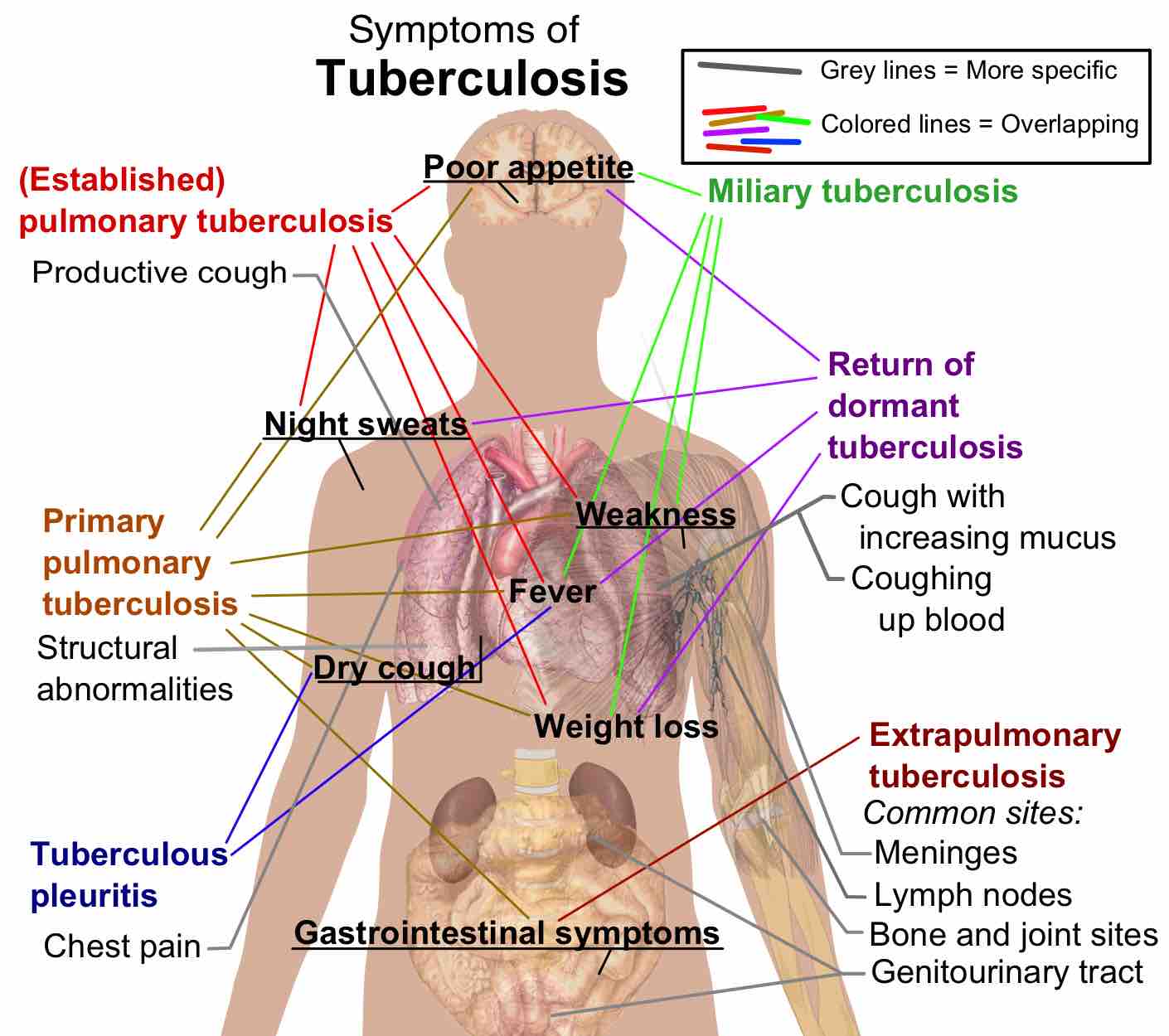
Tuberculosis is a common, and in many cases lethal, infectious bacterial disease that mainly affects the lungs.
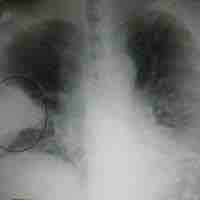
Pneumonia is an inflammatory lung disease that can lead to problems with breathing, often caused by bacterial infections.
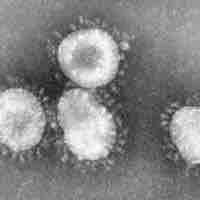
The common cold is caused by several different viruses and is the most common human viral infection.
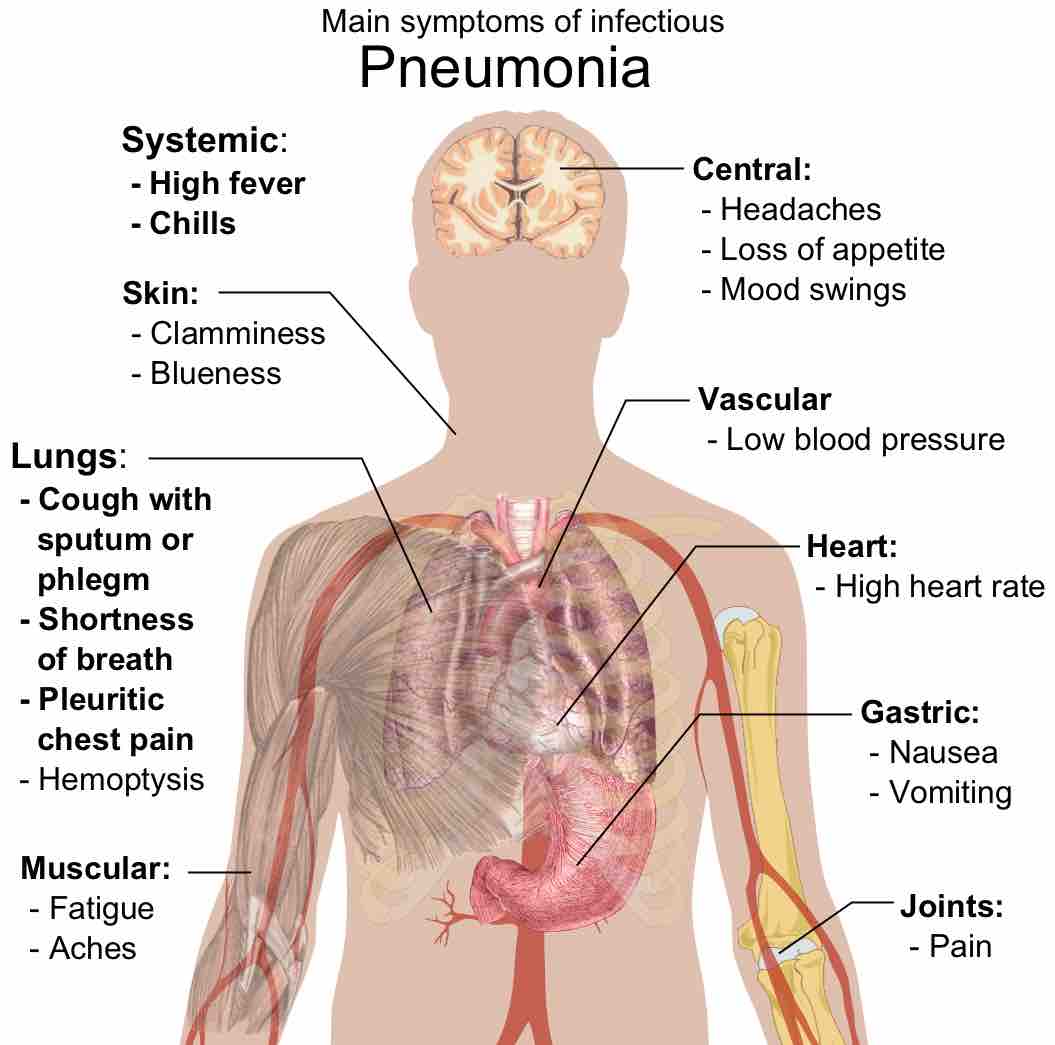
Viral pneumonia, one of the two leading causes of pneumonia, more commonly affects children.
Human respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes respiratory tract infections in humans.
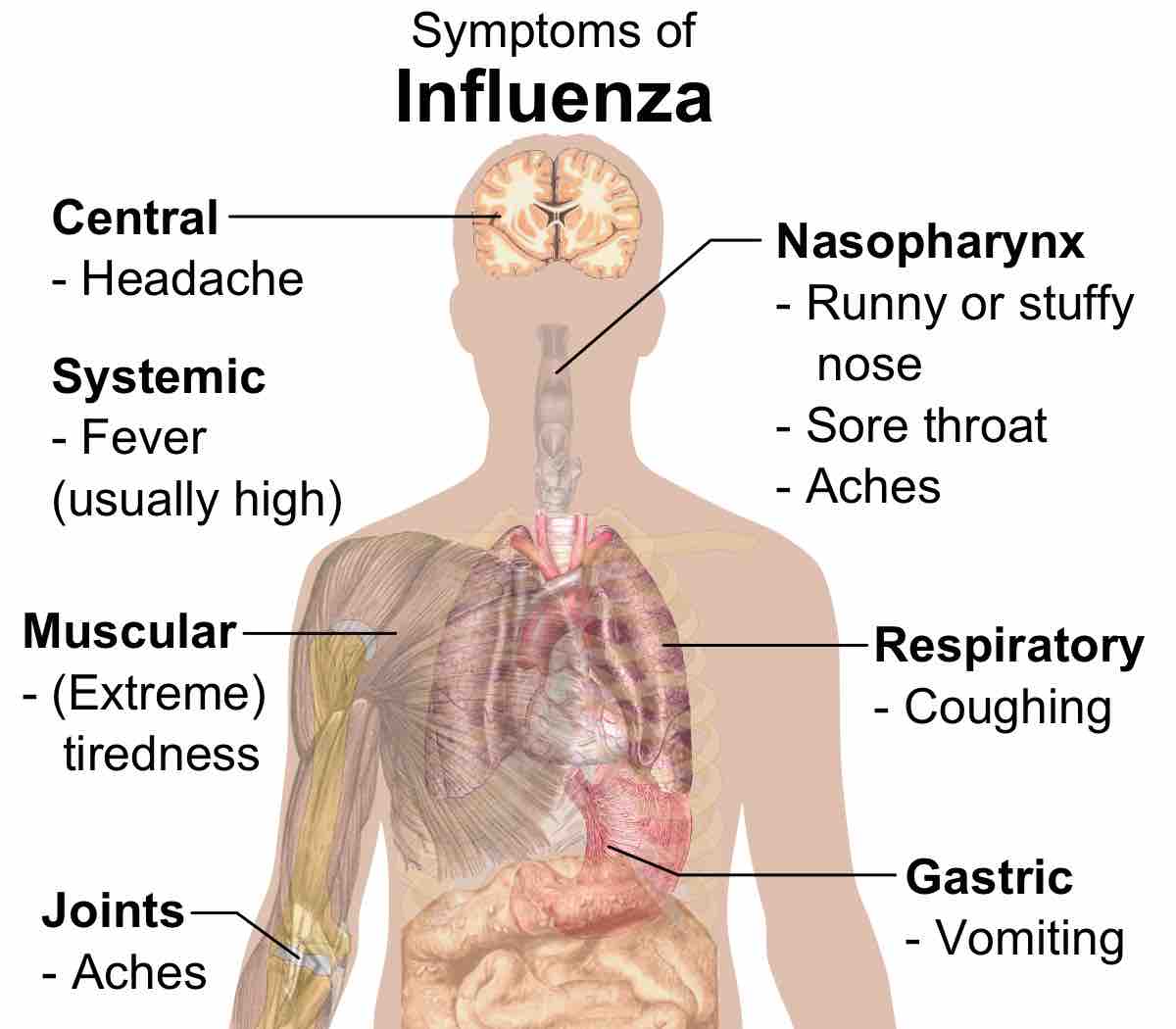
Influenza is an infectious disease caused by RNA viruses of the family Orthomyxoviridae that affects birds and mammals.
Histoplasmosis is a disease caused by the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum.

Coccidioidomycosis is a fungal disease caused by Coccidioides immitis or C. posadasii.
Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) or pneumocystosis is a form of pneumonia, caused by the yeast-like fungus Pneumocystis jirovecii.
Blastomycosis is a fungal infection caused by the organism Blastomyces dermatitidis.
Sporotrichosis is a disease caused by the fungus Sporothrix schenckii.
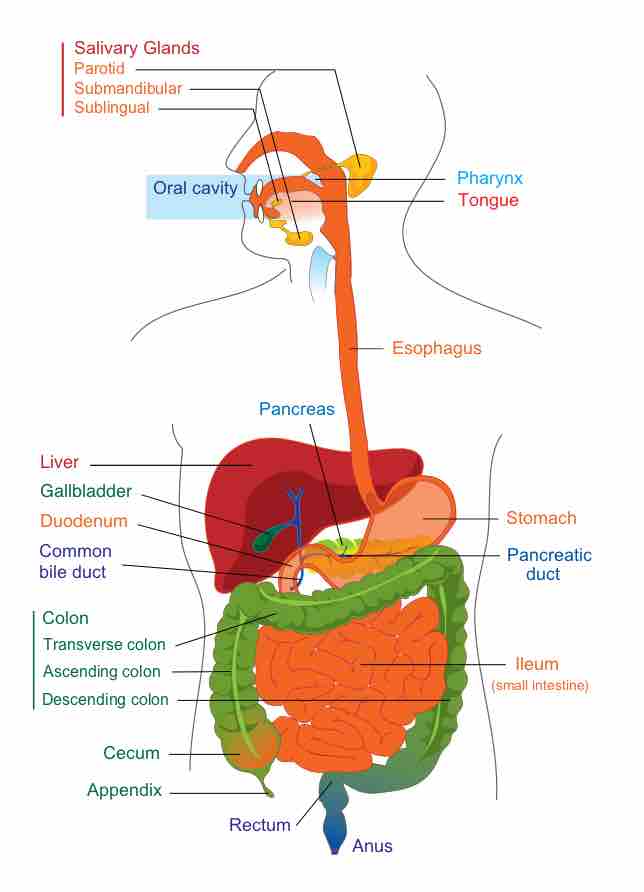
The human gastrointestinal tract refers to the stomach and intestine, and sometimes to all the structures from the mouth to the anus.
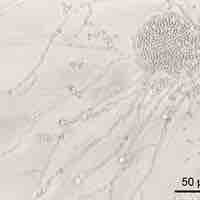
Gut flora consist of microorganisms that live in the digestive tracts of animals and are the largest reservoir of human flora.
The mouth contains a wide variety of oral bacteria, but only a few specific species of bacteria are believed to cause tooth and gum infections.
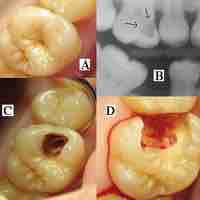
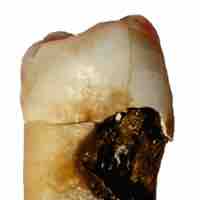
Dental caries cause demineralization of the hard tissues and destruction of the organic matter of the tooth.

Plaque-induced inflammatory lesions make up the vast majority of periodontal diseases, which are divided into peridontitis or gingivitis.
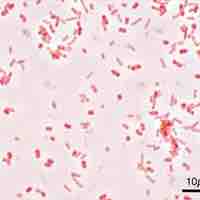
Gastroenteritis is characterized by inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract that involves both the stomach and the small intestine.
Staphylococcal toxins are a common cause of food poisoning, as they can be produced in improperly-stored food.
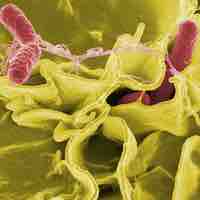
Salmonellosis is an infection by the Salmonella bacteria that results in diarrhea, fever, vomiting, and abdominal cramps.
Typhoid fever is a common, worldwide bacterial disease transmitted by Salmonella typhi, serotype Typhi.
Cholera is an infection in the small intestine caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae.
Vibrio is a Gram-negative bacteria possessing a curved rod shape (comma shape), several species of which can cause foodborne infection.
Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes are pathogenic and can cause serious food poisoning in humans and other species.
Campylobacter (meaning 'twisted bacteria') is a genus of bacteria that are Gram-negative, spiral, and microaerophilic.
A peptic ulcer, also known as peptic ulcer disease, is an erosion in the wall of the stomach, duodenum, or esophagus.

Listeriosis is a bacterial infection caused by a Gram-positive, motile bacterium called Listeria monocytogenes.
Mumps was a common childhood viral disease, but widespread vaccination has now made it rare in developed countries.
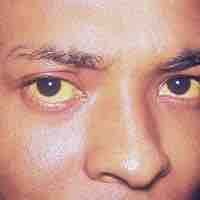
Hepatitis is the inflammation of the liver. Causes include viruses, bacterial infections, alcohol, autoimmune disorders, drugs, and toxins.
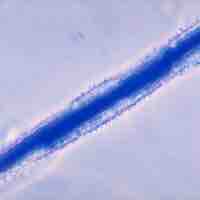
Gastroenteritis is caused by two different virus types in adults and children.

Ergot poisoning is caused by ingestion of the alkaloids produced by the ergot fungi.
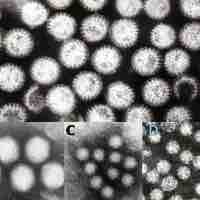
Aflatoxin poisoning is a result of ingestion of aflatoxins produced by Aspergillus that have contaminated a food source.

Giardiasis, sometimes referred to as beaver fever, is caused by the protozoan Giardia lamblia and results in diarrheal illness.
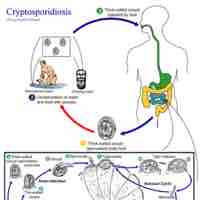
Cryptosporidiosis is a type of parasitic disease caused by Cryptosporidium that infects the gastrointestinal system.
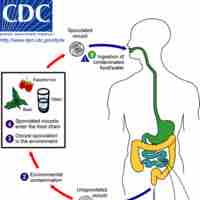
Cyclospora diarrheal infection is commonly referred to as traveler's diarrhea and is caused by the parasite Cyclospora cayetanensis.
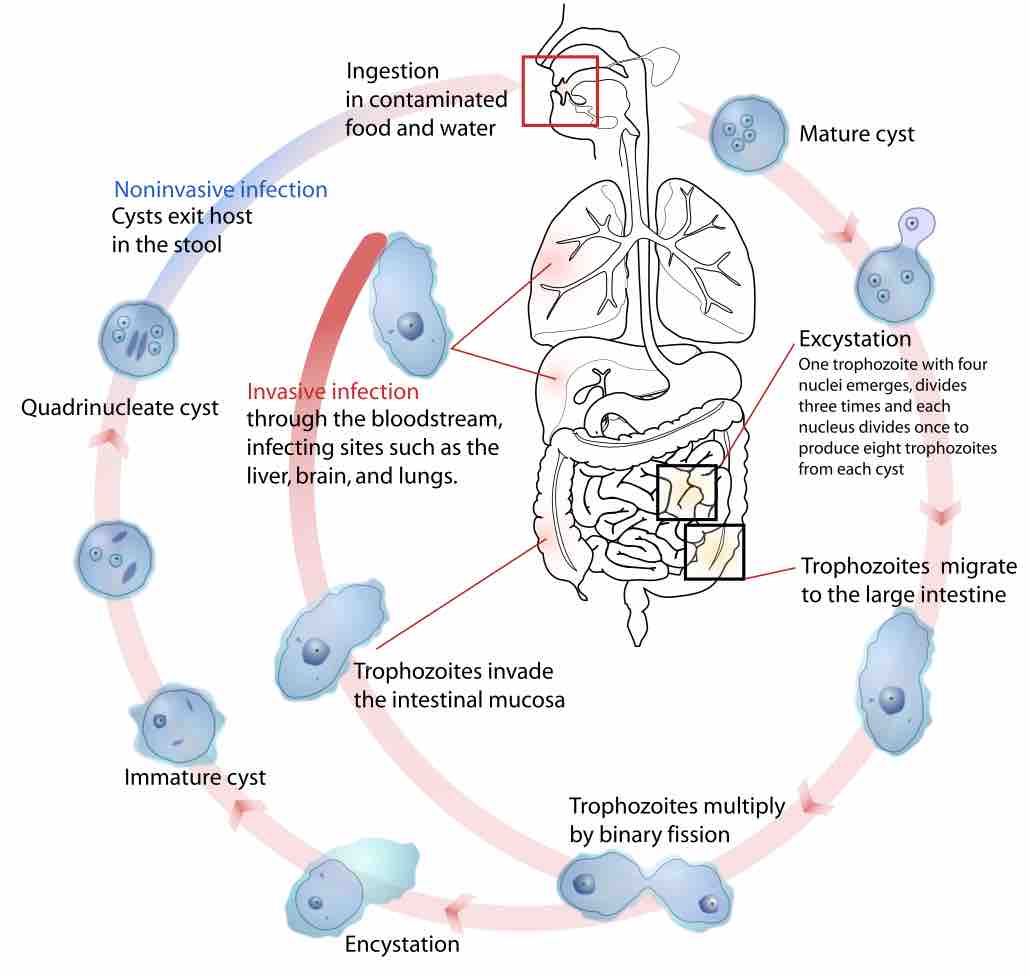
Amoebic dysentery is caused by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica and infected individuals suffer from severe diarrhea, cramps, and fever.

Legionellosis is most commonly caused by the Gram-negative bacteria Legionella pneumophila which is an aquatic organism.

Tapeworms are helminths capable of targeting the digestive system, but require various hosts for successful growth and transmission.
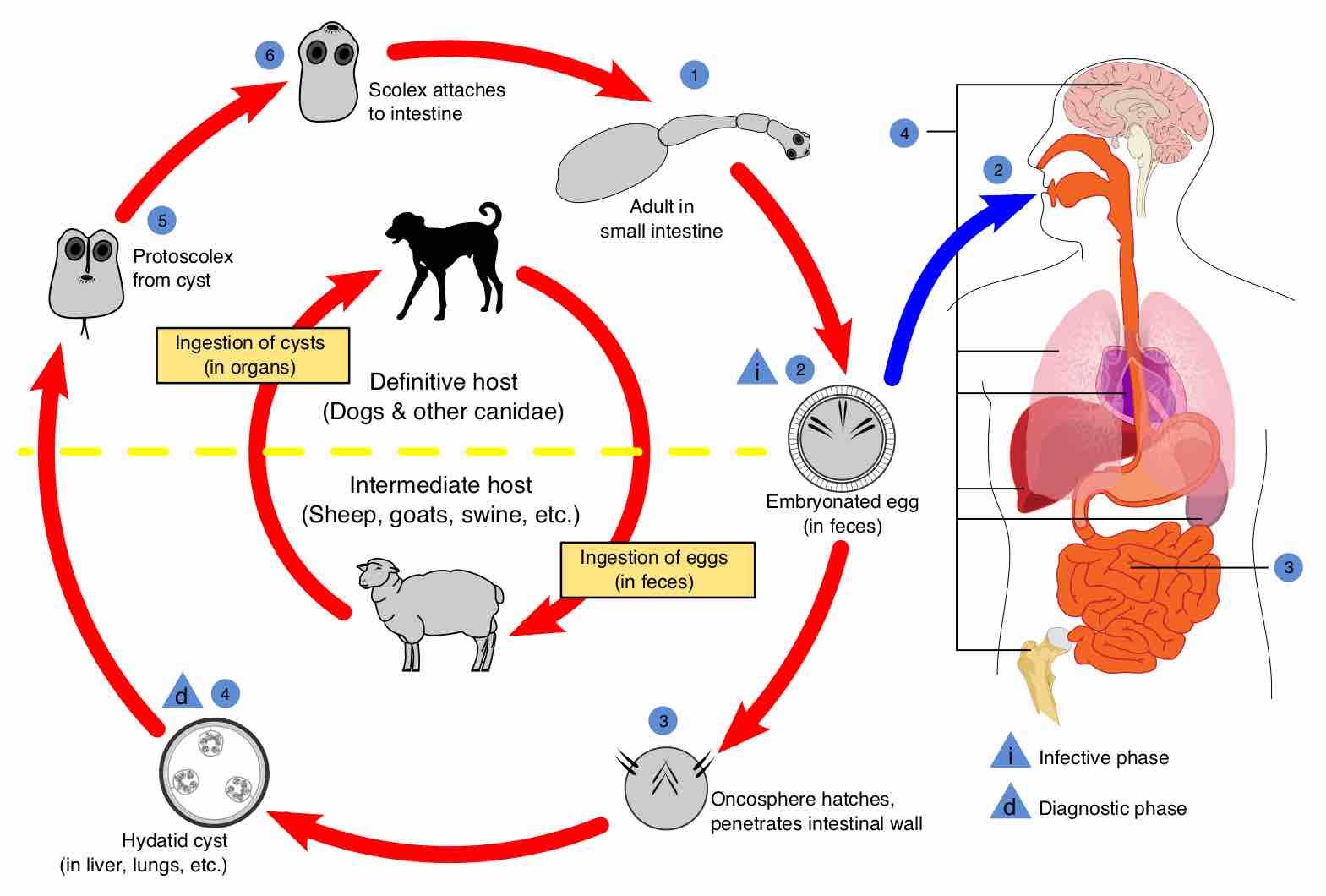
Hydatid disease, also referred to as cystic echinococcosis, is characterized by the slow growth of large cysts within various organs.
Nematodes, or roundworms, are capable of exhibiting parasitic behavior.
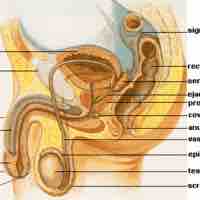
The human reproductive system functions to produce human offspring, with the male providing sperm and the female providing the ovum.
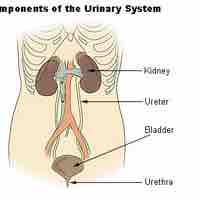
The urinary system maintains blood homeostasis by filtering out excess fluid and other substances from the bloodstream and secreting waste.
The vaginal microflora consist mostly of various lactobacillus species.
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection affecting the urinary tract; about 150 million people develop UTIs each year.
Cystitis is a urinary bladder inflammation that is most commonly caused by a bacterial infection of the lower urinary tract infection.
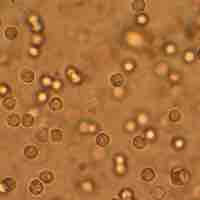
Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the kidney tissue and surrounding area, commonly caused by a bacterial infection ascending up the upper urinary tract.
Leptospirosis is a rare and severe infection caused by Leptospira bacteria and usually transmitted to people from animals.
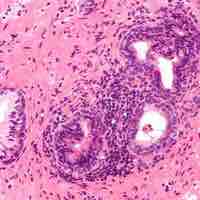
Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate which can be caused by bacteria.

Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate which can be caused by bacteria.
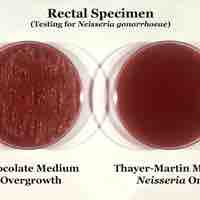
Gonorrhea (also colloquially known as the clap) is a common human sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Nongonococcal urethritis (NGU) is an urethral inflammation that is not caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
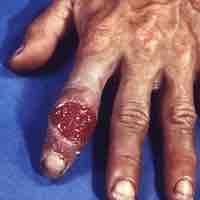
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an inflammation of the female reproductive organs that is most often caused by infection.
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum.
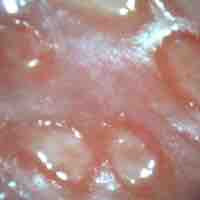
Genital ulcers are skin ulcers on the genital area caused by sexually transmitted diseases or noninfectious conditions.
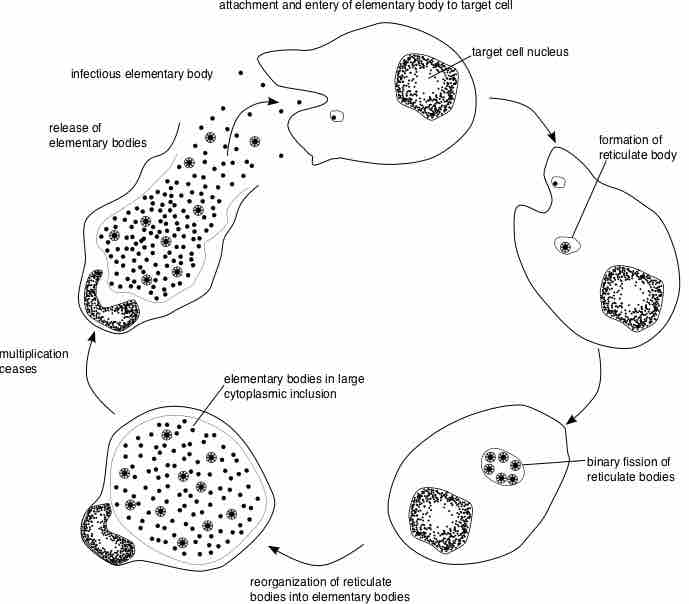
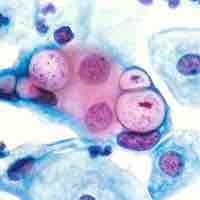
Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) is a sexually transmitted disease which causes an infection of the lymph nodes.
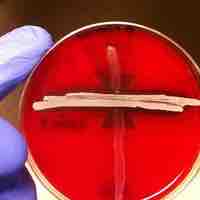
Group B streptococcus is part of the natural microflora in some people, but can sometimes cause life-threatening infections.
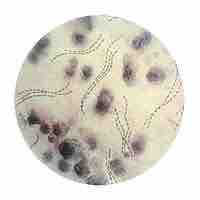
Chancroid is a sexually transmitted disease caused by Haemophilus ducreyi.
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a condition of disrupted balance of the vaginal microflora.
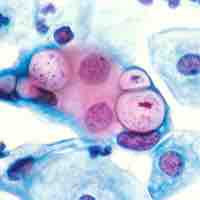
Chlamydia infection is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) in humans caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis.
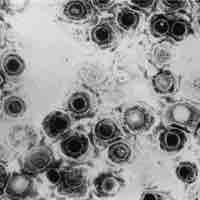
Herpes genitalis (or genital herpes) refers to a genital infection by Herpes simplex virus.
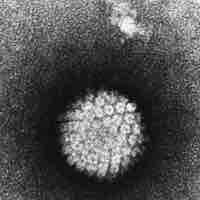
Genital warts is a highly contagious sexually transmitted disease caused by some sub-types of human papillomavirus (HPV).
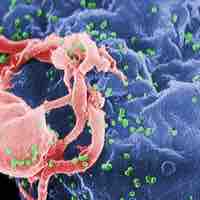
Human immunodeficiency virus infection/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is a disease of the human immune system caused by HIV.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a virus from the papillomavirus family that is capable of infecting humans.
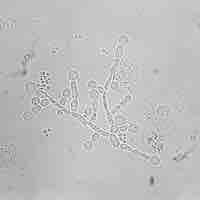
Candidal vulvovaginitis is an infection of the vagina's mucous membranes caused by Candida albicans.
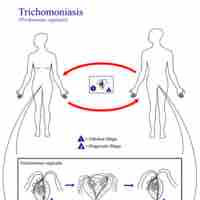
Trichomoniasis is primarily an infection of the urogenital tract; the most common site of infection is the urethra and the vagina in women.
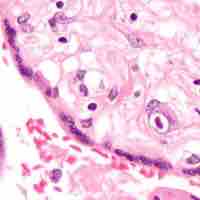
TORCH infections are a group of viral, bacterial, and protozoan infections that gain access to the fetal bloodstream from the mother.