Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an inflammation of the uterus, fallopian tubes and/or the ovaries. It is most often caused by a sexually transmitted infection (STI) but there are other predisposing conditions (e.g., postpartum period, the use of intrauterine device). It should be treated promptly to avoid serious complications like scarring and adhesions which can cause infertility, ectopic pregnancy and chronic pelvic pain.
Symptoms and diagnosis
PID can be asymptomatic or present with acute symptoms. About two thirds of patients whose laparoscopies indicated a previous PID were unaware of it. Asymptomatic infections should be treated as well, since they can still cause permanent damage to the reproductive tract.
Symptoms include fever, lower abdominal pain, unusual discharge, irregular menstrual bleeding, painful intercourse.
Different tests can be used for diagnosis such as pelvic ultrasound and laboratory tests for STIs. Usually, more than one test is needed for proper diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to limit the spread of the infection to the lower part of the tract and to avoid long term consequences.
Infectious agents
PID can be caused by many different infectious agents like viruses, fungi or bacteria. The most common infectious agents are Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae which are sexually transmitted.
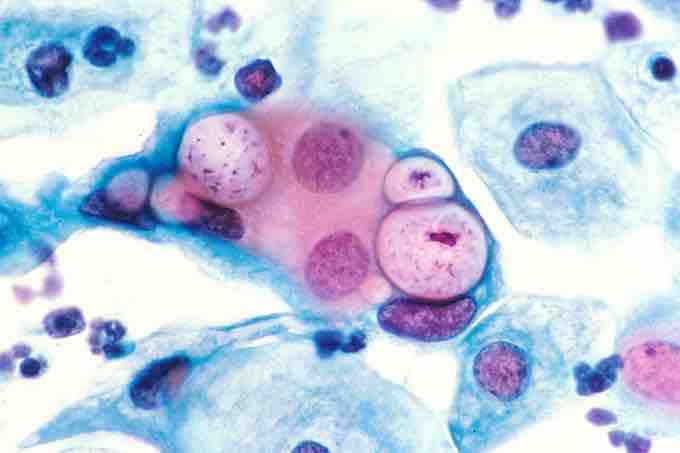
Pap smear with Chlamydia
Cells of Chlamydia are visible in the vacuoles. Magnification 500x, stained with hematoxylin and eosin stain (HE)
The normal vaginal flora can also cause PID under certain circumstances. Co-infection with multiple species is also possible.
Treatment
The primary mode of therapy is an antibiotic regimen. In serious cases, intravenous administration of drugs may be necessary. Usually, improvement of symptoms should be noticed within a few days.
Sexual partners of patients with PID should be treated as well. Some of the most commonly used antibiotics and combinations of antibiotics are: cefoxitin or cefotetan plus doxycycline, cefoxitin plus doxycycline, clindamycin plus gentamycin, ampicillin and sublactam plus doxycycline.