The common cold (also known as nasopharyngitis, rhinopharyngitis, acute coryza, or a cold) is a viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract which affects primarily the nose. Symptoms include coughing, sore throat, runny nose, and fever which usually resolve in seven to ten days, with some symptoms lasting up to three weeks. Well over 200 viruses are implicated in the cause of the common cold. The most commonly implicated virus is a rhinovirus (30–80%), a type of picornavirus with 99 known serotypes. A picornavirus is a virus belonging to the family Picornaviridae. Picornaviruses are non-enveloped RNA viruses with an icosahedral capsid. The name is derived from pico, meaning small, and RNA, referring to the ribonucleic acid genome, so "picornavirus" literally means small RNA virus. Others include: coronavirus (10–15%), human parainfluenza viruses, human respiratory syncytial virus, adenoviruses, enteroviruses, and metapneumovirus . Frequently more than one virus is present.
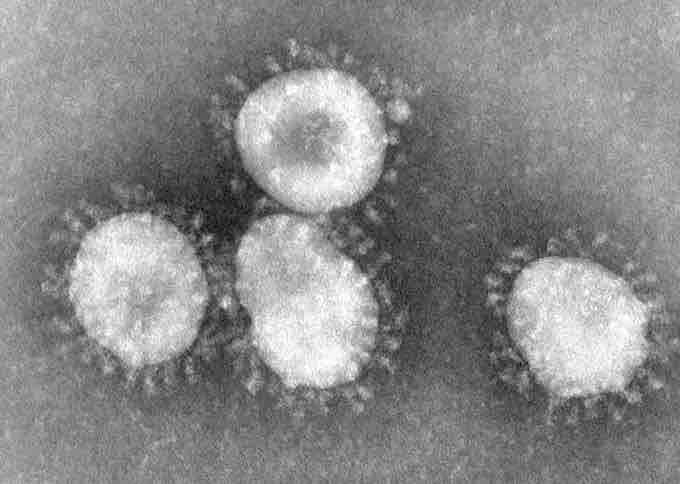
Coronaviruses
Coronaviruses are a group of viruses that have a halo, or crown-like (corona) appearance when viewed under an electron microscope. If you have a cold 10-15% of the time it is caused by a virus like this.
The symptoms of the common cold are believed to be primarily related to the immune response to the virus. The mechanism of this immune response is virus specific. For example, the rhinovirus is typically acquired by direct contact; it binds to human ICAM-1 receptors through unknown mechanisms to trigger the release of inflammatory mediators. These inflammatory mediators then produce the symptoms. It does not generally cause damage to the nasal epithelium. The respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) on the other hand is contracted by both direct contact and air born droplets. It then replicates in the nose and throat before frequently spreading to the lower respiratory tract. RSV does cause epithelium damage. Human parainfluenza virus typically results in inflammation of the nose, throat, and bronchi. In young children when it affects the trachea it may produce the symptoms of croup due to the small size of their airway.
No cure for the common cold exists, but the symptoms can be treated. Antibiotics have no effect against viral infections and thus have no effect against the viruses that cause the common cold. Due to their side effects they cause overall harm; however, they are still frequently prescribed.It is the most frequent infectious disease in humans with the average adult contracting two to three colds a year and the average child contracting between six and twelve. These infections have been with humanity since antiquity.