Group B Streptococcus Colonization
Group B streptococcus (GBS), also called streptococcus agalactiae or simply strep B, is part of the natural genital and intestinal microflora in some people. Studies indicate that as many as 40% of women can be carriers. It is usually harmless but under certain circumstances (in newborns, the elderly, and in people with compromised immune systems) it can cause life-threatening infections. The bacteria is gram-positive streptococcus, and possesses the group B antigen from the Lancefield classification. Its infectivity is due to the presence of a antiphagocytic polysaccharide capsule. If a pregnant woman is a carrier of strep B, the baby can become infected during vaginal delivery.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Healthy adults are usually asymptomatic carriers of the bacteria. Sometimes it can manifest with urinary tract infections (UTIs) in both pregnant and nonpregnant women. In newborns, the first symptoms are breathing difficulties and pneumonia, which can progress to meningitis and sepsis. In elderly people, it can cause pneumonia and/or UTI and is linked to congestive heart failure. A number of different tests are used as diagnostic tools. Screening pregnant women for GBS, usually in the third trimester, is currently routine in many countries. In the cases of positive status, antibiotics are administered during labor to substantially lower the risk of infection for the baby. This strategy has lead to a significant drop in the rates of infant infection in these countries. A very common diagnostic test is the CAMP test named after the three people that discovered it. Sometimes, before plating, enrichment of the gathered probe is performed. This includes sample growth in special medium that will favor its growth over the other bacteria collected with the specimen. The method of enrichment followed by the CAMP tests is currently the gold standard for GBS diagnosis. It lowers significantly the rates of false negatives. However, culturing takes days and is not feasible if labor starts before screening was completed or in cases when it was not performed at all. The best diagnostic tool will allow identification during labor. PCR techniques are faster but they are still complicated and not fast enough to be used widely for diagnostics once labor has started. TreatmentPregnant women who are carriers of GBS are administered penicillin or ampicillin during labor. These antibiotics are the primary choice for GBS therapy in general, since the bacteria are becoming increasingly resistant to many other common antibiotics.
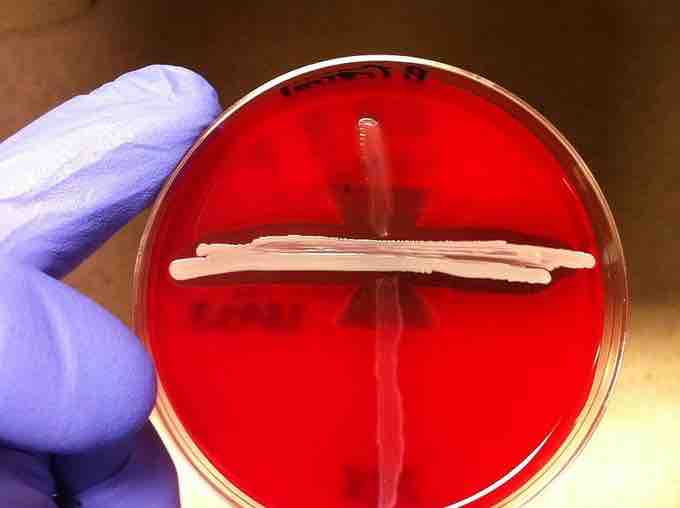
The CAMP Test
The collected sample is streaked on a blood agar plate (vertical streaks) next to staphylococcus aureus culture (horizontal streak). Strep B has weak hemolytic activity, which is enhanced substantially (arrow-like area) when streaked next to s. aureus. The reason for that is the interaction between the CAMP factor from strep B and the s. aureus hemolysin.