Chapter 14
Thermodynamics
By Boundless
Work performed by a closed system is the energy transferred to another system that is measured by mechanical constraints on the system.
Zeroth law justifies the use of thermodynamic temperature, defined as the shared temperature of three designated systems at equilibrium.
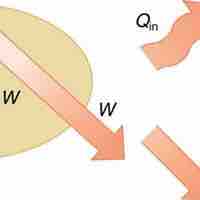
The 1st law of thermodynamics states that internal energy change of a system equals net heat transfer minus net work done by the system.
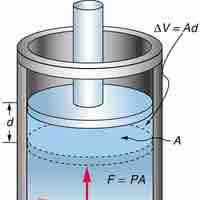
Isobaric process is one in which a gas does work at constant pressure, while an isochoric process is one in which volume is kept constant.
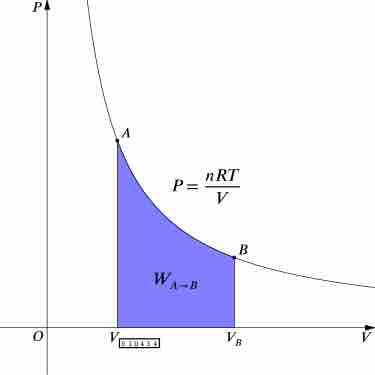
An isothermal process is a change of a thermodynamic system, in which the temperature remains constant.
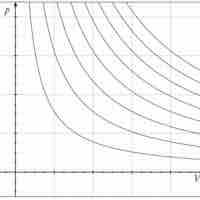
An adiabatic process is any process occurring without gain or loss of heat within a system.
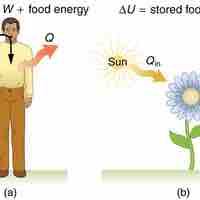
The 1st law of thermodynamics explains human metabolism: the conversion of food into energy that is used by the body to perform activities.
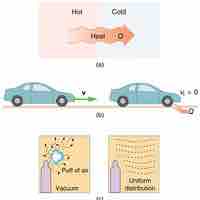
The second law of thermodynamics states that heat transfer occurs spontaneously only from higher to lower temperature bodies.
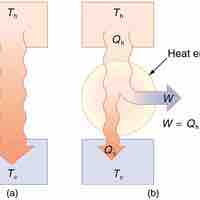
In thermodynamics, a heat engine is a system that performs the conversion of heat or thermal energy to mechanical work.
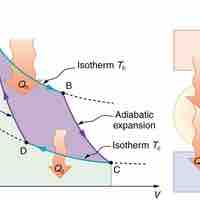
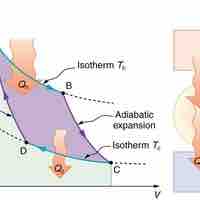
The Carnot cycle is the most efficient cyclical process possible and uses only reversible processes through its cycle.
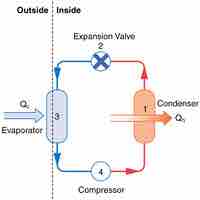
A heat pump is a device that transfers heat energy from a heat source to a heat sink against a temperature gradient.
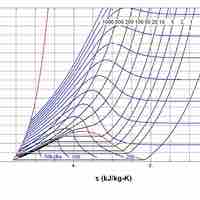
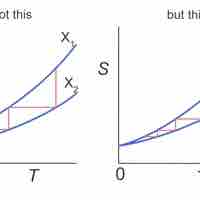
The entropy of a system is a measure of its disorder and of the unavailability of energy to do work.
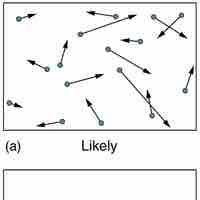
According the second law of thermodynamics, disorder is vastly more likely than order.
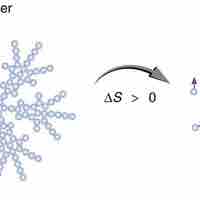
Entropy is a measure of disorder, so increased entropy means more disorder in the system.
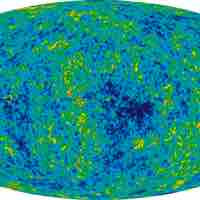
The entropy of the universe is constantly increasing and is destined for thermodynamic equilibrium, called the heat death of the universe.
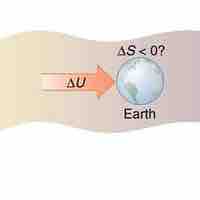
It is possible for the entropy of one part of the universe to decrease, provided the total change in entropy of the universe increases.
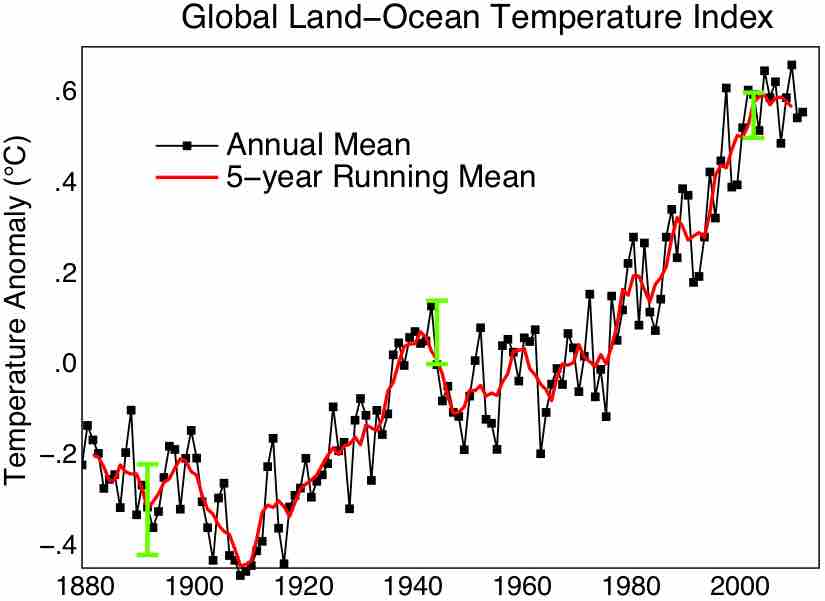
The Second Law of Thermodynamics may help provide explanation for the global warming over the last 250 years.

Thermal pollution is the degradation of water quality by any process that changes ambient water temperature.
- Introduction
- Specific Heat
- Phase Change and Latent Heat
- Methods of Heat Transfer
- Global Warming