Chapter 20
Nonmetallic Elements
By Boundless
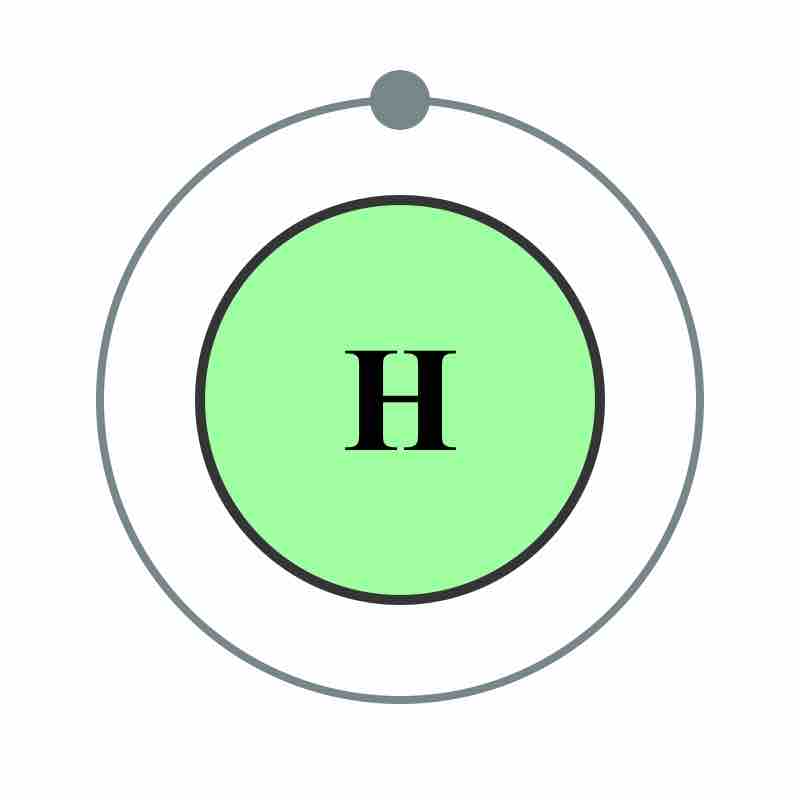
Hydrogen is the smallest element, with one proton and one electron. It is highly abundant and has unique and important chemical properties.
Hydrides are compounds in which one or more hydrogen anions have nucleophilic, reducing, or basic properties.
Hydrogen has three naturally occurring isotopes: protium, deuterium and tritium. Each isotope has different chemical properties.
Hydrogenation reactions, which involve the addition of hydrogen to substrates, have many important applications.

The hydrogen economy refers to using hydrogen as the next important source of fuel.

Boron is produced by cosmic ray spallation, is a metalloid, and is essential to life.
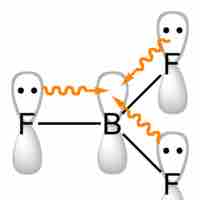
When in a compound with halides, boron has the formal oxidation state +3. Trihalides adopt a planar trigonal structure and are Lewis acids.
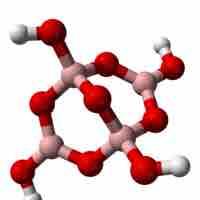
Oxoanions that contain boron are called borates.
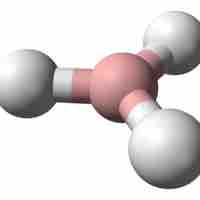
Boranes are chemical compounds of boron and hydrogen with general formula BxHy; many readily oxidize on contact with air.
Carbon has very diverse physical and chemical properties due to the nature of its bonding.

Carbides are a class of compounds composed of carbon and an electropositive atom.
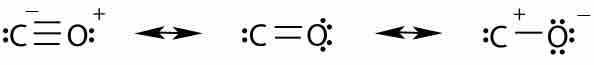
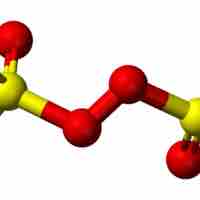
Oxocarbons are compounds containing carbon and oxygen; they exist as carbon oxides and carbonates.
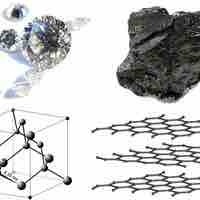
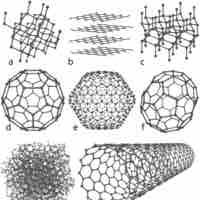
Various allotropes of carbon exhibit different properties and find applications in a variety of fields.
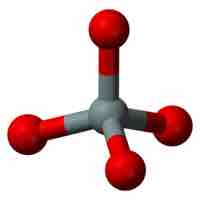
The basic unit of silicate, [SiO4]4- tetrahedron, can form single and double chains and sheets.

Glass is a non-crystalline solid material made of silica, while quartz is a crystalline silicate mineral with piezoelectric properties.

Aluminosilicate minerals are composed of aluminum, silicon, and oxygen.
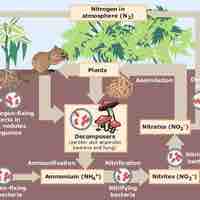
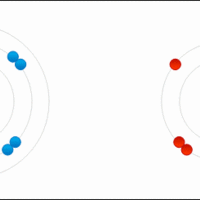
Nitrogen in its elemental form is a non-metallic gas that makes up 78 percent of Earth's atmosphere.

Nitrogen compounds, and especially their oxidized derivatives, are important in biological systems and as explosives.
Phosphorus is found in its elemental form as different allotropes, none of which are stable in the presence of oxygen.
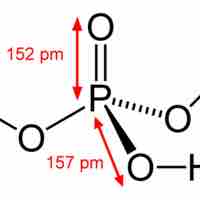
Phosphorus compounds consist mostly of compounds containing strong phosphorus-oxygen bonds. They are important in fertilizers and biology.
Oxygen is a highly reactive nonmetallic element; it is a strong oxidizing agent with high electronegativity and forms O2 at Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP).
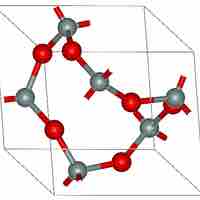
An oxide is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula.

Oxygen is essential for all aerobic organisms; common medical uses include oxygen therapy, hyperbaric medicine, and space suits.
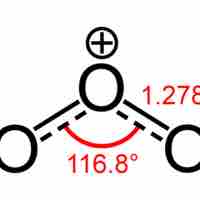
Ozone (O3) is diamagnetic (its electrons are all paired) and is a powerful oxidant.

Halogens (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine) are nonmetal elements that are highly electronegative and reactive.

Halogens are highly reactive and can form hydrogen halides, metal halides, organic halides, interhalogens, and polyhalogenated compounds.
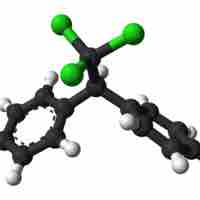
Although halogens and their compounds can be toxic, some are essential for the human body's functioning and are used in everyday products.