Chapter 19
Nuclear Chemistry
By Boundless

Becquerel accidentally found that a uranium-rich mineral emitted invisible, penetrating rays that could darken a photographic plate.
Radioactive decay occurs when an unstable atomic nucleus emits particles or light waves.
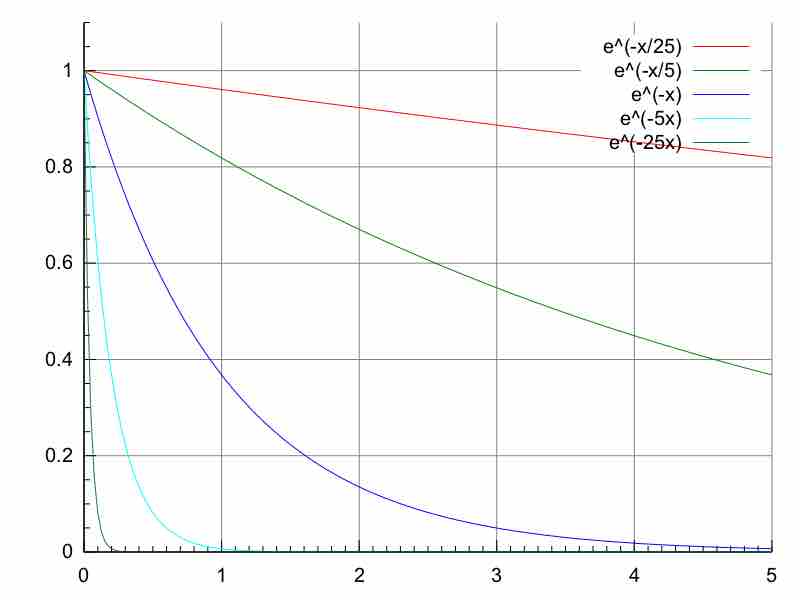
Radioactive decay rate is exponential and is characterized by constants, such as half-life, as well the activity and number of particles.

The half-life is a parameter for the rate of decay that is related to the decay constant by:
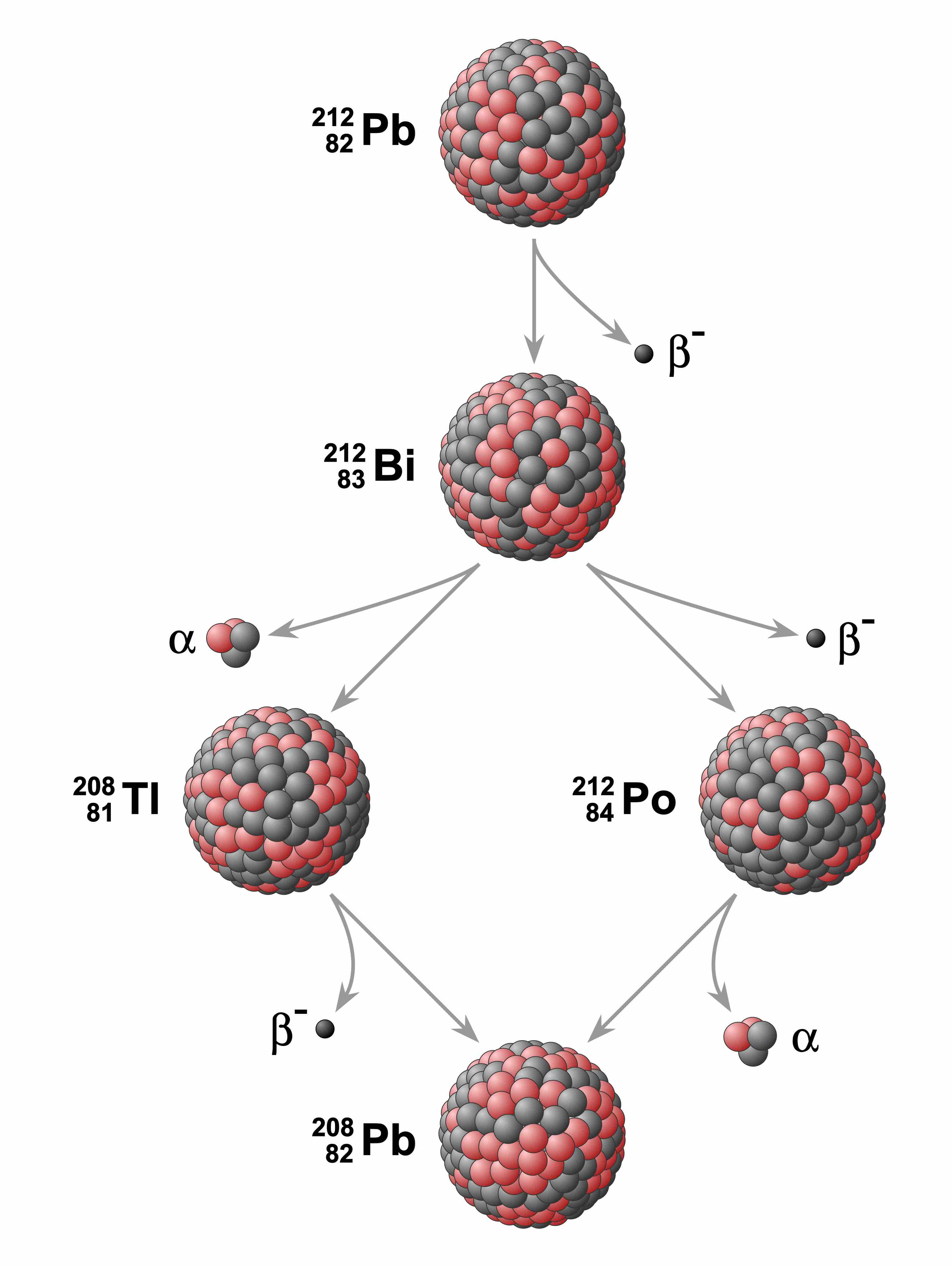
Radiometric dating is used to date materials using the decay rate of a radioactive isotope.
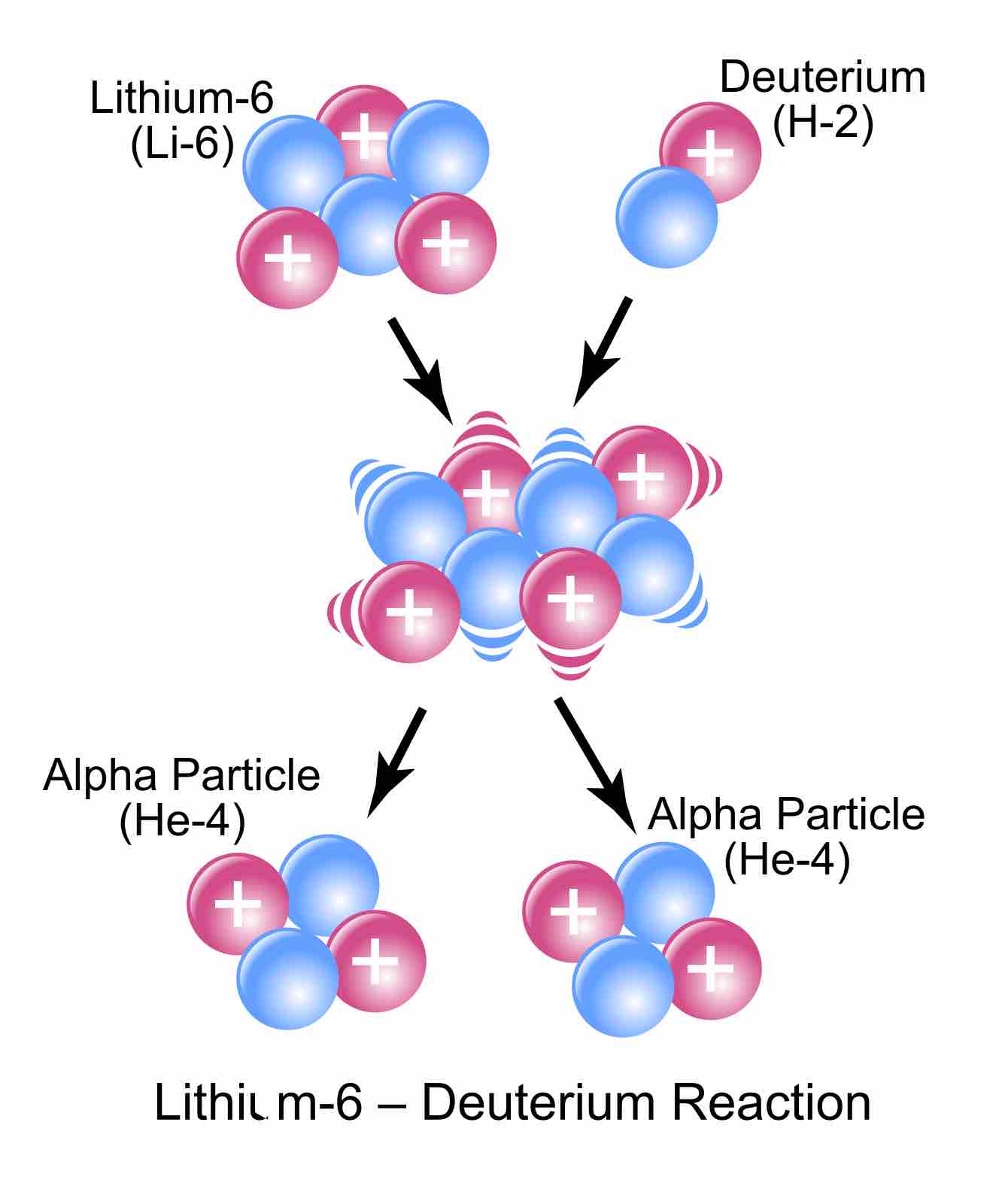
To balance a nuclear equation, the mass number and atomic numbers of all particles on either side of the arrow must be equal.
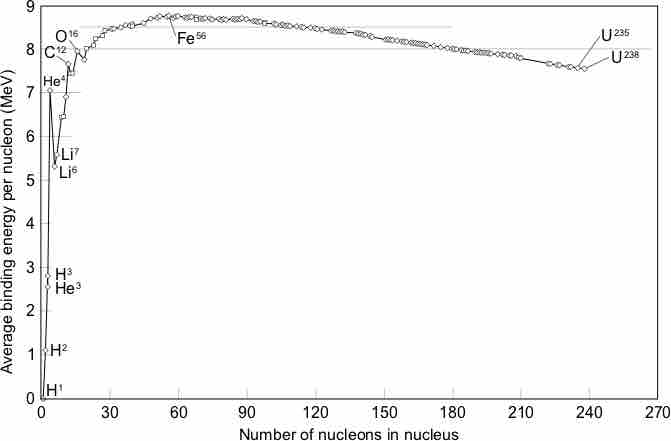
A nucleus weighs less than its sum of nucleons, a quantity known as the mass defect, caused by release of energy when the nucleus formed.
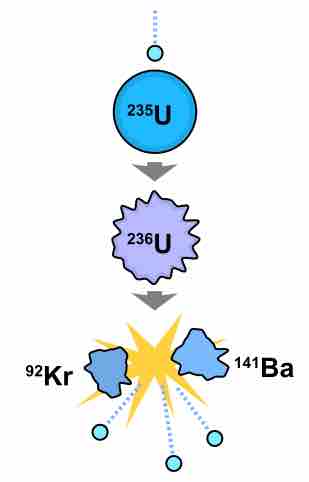
Nuclear fission occurs when an atom splits into two or more smaller atoms, most often the as the result of neutron bombardment.
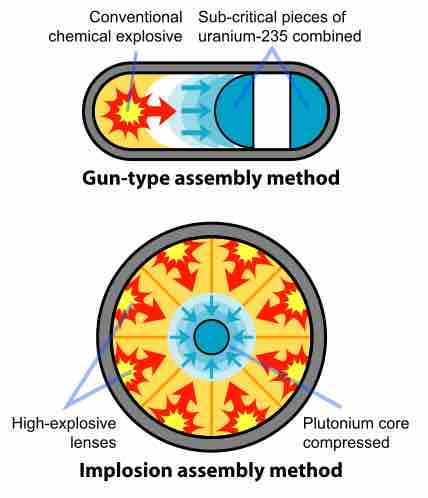
Atomic bombs are nuclear weapons that use the energetic output of nuclear fission to produce massive explosions.
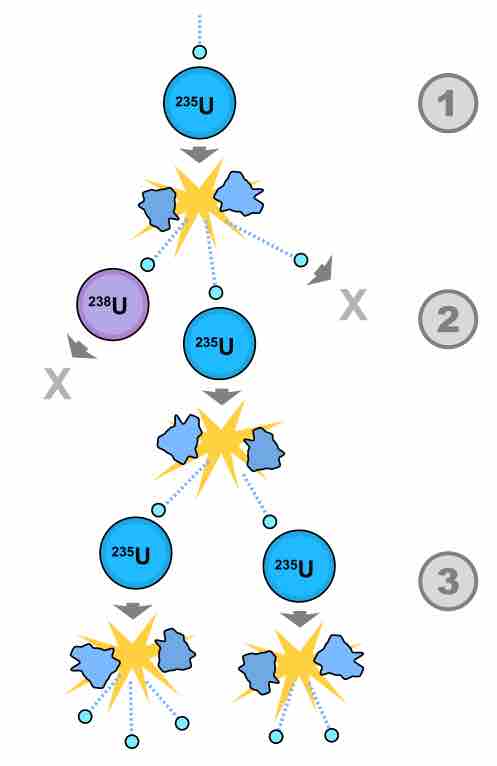
A nuclear reactor is a piece of equipment in which nuclear chain reactions can be harnessed to produce energy in a controlled way.
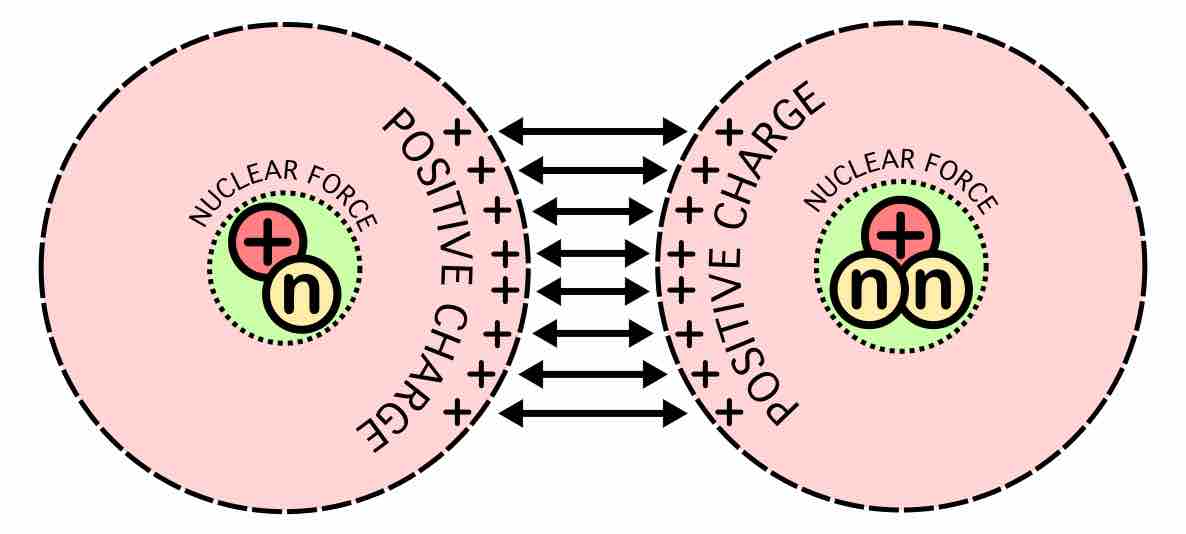
Nuclear fusion is the process by which two or more atomic nuclei join together to form a single heavier nucleus and large amounts of energy.
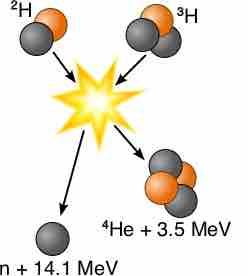
A fusion reactor is designed to use the thermal energy from nuclear fusion to produce electricity.
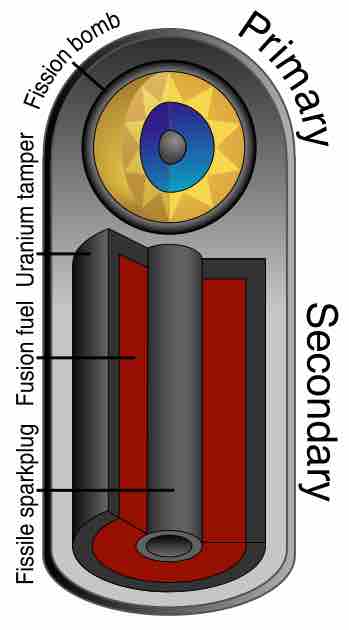
The hydrogen bomb is a nuclear weapon that uses a mixture of fission and fusion to produce a massive explosion.
Structural determination using isotopes is often performed using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and mass spectrometry.
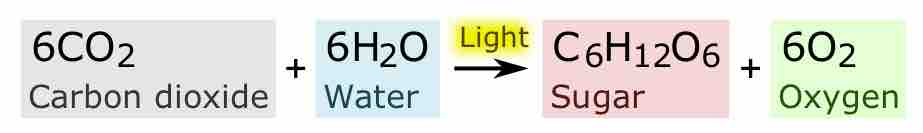
Mass spectrometry has been used to study the ratio of carbon isotopes in various plants to understand the mechanisms of photosynthesis.
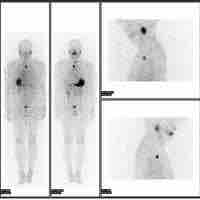
Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that involves the application of radioactive substances to diagnose or treat disease.

Acute radiation syndrome or damage describes health effects present within 24 hours of exposure to high amounts of ionizing radiation.
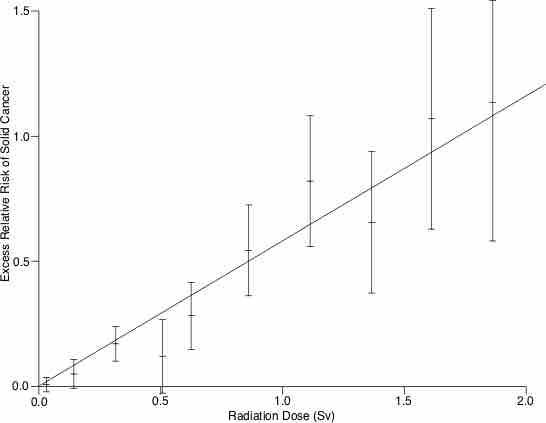
Up to 10 percent of invasive cancers are related to radiation exposure, including both ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation.
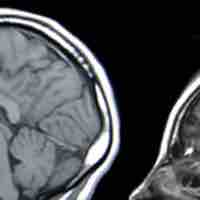
Ionizing radiation from fallout can cause genetic effects, birth defects, cancer, cataracts, and other organ and tissue defects.

Radiation dosimetry is the measurement and calculation of the absorbed dose from exposure to indirect and direct ionizing radiation.