Chapter 18
Working Capital Management
By Boundless

The main reason a business maintains cash on hand is to meet financial obligations.
The cash flow cycle measures how long it takes for a firm to recover cash that it invests in ongoing operations.
Cash flow cycle = # days between disbursing cash and collecting cash in connection with undertaking a discrete unit of operations.
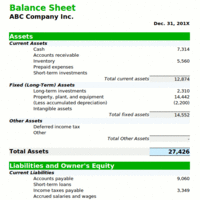
The cash budget includes the beginning balance, detail on payments and receipts, and an ending balance.

Float is the term used to represent duplicate money present between the time a deposit is made and when the deposit clears the bank.

A company must balance its need for quick cash collections with the needs and desires of its customers.

How a company manages various disbursements and current assets can have a significant impact on its cash flows.
Accounts receivable represents money owed by entities to the firm on the sale of products or services on credit.
To establish a credit policy, a company must establish credit standards, credit terms, and a collection policy.

Terms of trade credit include the amount of time allowable for payment to be received, including any potential discounts.

Companies use different methods to collect their outstanding receivables, like sending out reminders or employing a collection agency.
Most manufacturing organizations usually divide their inventory into raw materials, work in process, finished goods, and goods for sales.

FIFO, LIFO, and average cost methods are accounting techniques used in managing inventory.
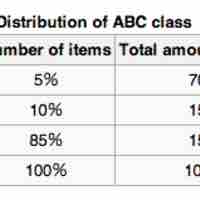
The ABC analysis is an inventory categorization technique often used in material management wherein accuracy and control decreases from A to C.
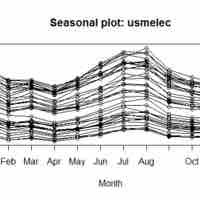
Seasonal trends and internal projections of consumption in certain goods can have a significant impact on opportunity cost and potential profit for an organization.
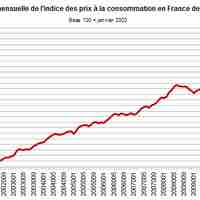
High inflation encourages companies to keep a high level of inventories.

Inventory costs depends on methods used, which include Specific Identification, Weighted Average Cost, Moving-Average Cost, FIFO, and LIFO.
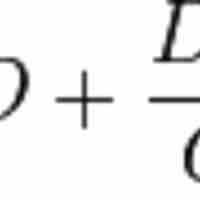
Economic order quantity is the order quantity that minimizes total inventory holding costs and ordering costs:
Just in time (JIT) is a production strategy that strives to reduce in-process inventory and carrying costs in a manufacturing system.

Improved inventory management can lead to increased revenue, lower handling and holding costs, and improved cash flows.
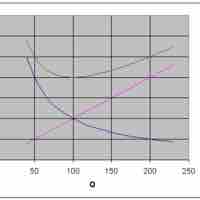
Excessive inventory means idle funds which earn no profits; inadequate inventory means lost sales.
- Working Capital
- Approaches to Working Capital Financing
- Overview of the Working Capital Financing Decision