The ABC analysis is a business term used to define an inventory categorization technique often used in material management. It is also known as "Selective Inventory Control. " Policies based on ABC analysis:
- A ITEMS: very tight control and accurate records
- B ITEMS: less tightly controlled and good records
- C ITEMS: simplest controls possible and minimal records
The ABC analysis provides a mechanism for identifying items that will have a significant impact on overall inventory cost, while also providing a mechanism for identifying different categories of stock that will require different management and controls.
The ABC analysis suggests that inventories of an organization are not of equal value. Thus, the inventory is grouped into three categories (A, B, and C) in order of their estimated importance.
A items are very important for an organization. Because of the high value of these A items, frequent value analysis is required. In addition to that, an organization needs to choose an appropriate order pattern (e.g., "Just- in- time") to avoid excess capacity.
B items are important, but of course less important, than A items and more important than C items. Therefore, B items are intergroup items.
C items are marginally important.
The following is an example of the Application of Weighed Operation based on ABC class in the electronics manufacturing company with 4,051 active parts.
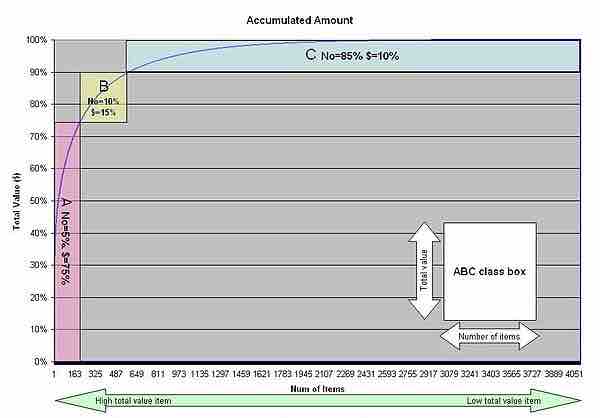
ABC analysis
Actual distribution of ABC class in the electronics manufacturing company with 4051 active parts.
Using this distribution of ABC class and change total number of the parts to 4,000.
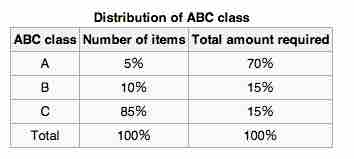
ABC techniques
Distribution of ABC class
- Uniform Purchase: When you apply equal purchasing policy to all 4,000 components, example weekly delivery and re-order point (safety stock) of two-week supply assuming that there are no lot size constraints, the factory will have a 16,000 delivery in four weeks and the average inventory will be 2.5 weeks supply.
- Weighed Purchase: In comparison, when weighed purchasing policy applied based on ABC class, example C class monthly (every four weeks) delivery with re-order point of three-week supply, B class Bi-weekly delivery with re-order point of two-week supply, A class weekly delivery with re-order point of one-week supply, total number of delivery in four weeks will be (A 200x4=800)+(B 400 x2=800) + (C 3400x1=3400)=5000 and average inventory will be (A 75%x1.5weeks)+(B 15%x3weeks)+ (C 10%x3.5weeks)= 1.925 week supply.
By applying weighed control based on ABC classification, required man hours and inventory level are drastically reduced.