Chapter 18
Electrochemistry
By Boundless
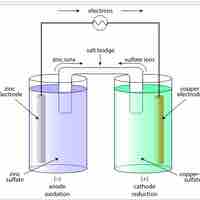
A voltaic cell is a device that produces an electric current from energy released by a spontaneous redox reaction in two half-cells.
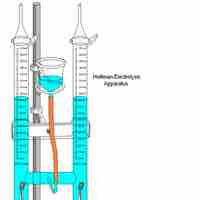
Electrolysis uses electrical energy to induce a chemical reaction, which then takes place in an electrolytic cell.
Cell notation is shorthand that expresses a certain reaction in an electrochemical cell.
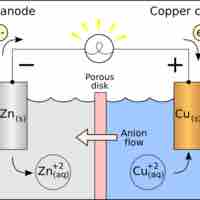
Standard reduction potentials provide a systematic measurement for different molecules' tendency to be reduced.
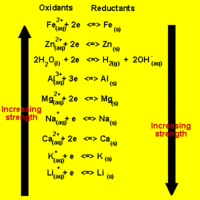
The direction of a redox reaction depends on the relative strengths of the oxidants and reductants in a solution.
A metal is soluble in acid if it displaces H2 from solution, which is determined by the metal's standard reduction potential.

The thermodynamics of redox reactions can be determined using their standard reduction potentials and the Nernst equation.
In electrochemistry, the Nernst equation can be used to determine the reduction potential of an electrochemical cell.

Walther Nernst proposed a mathematical model to determine the effect of reactant concentration on the electrochemical cell potential.
In a galvanic cell, where a spontaneous redox reaction drives the cell to produce an electric potential, the change in Gibbs free energy must be negative.
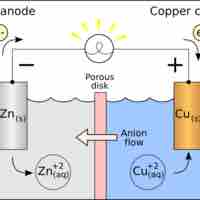
The equilibrium constant K can be calculated using the Nernst equation.
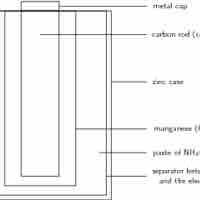
A dry-cell battery uses an immobilized electrolyte that minimizes moisture and allows for superior portability.
Mercury batteries were a common electrochemical battery that were phased out of mainstream use in the U.S. by the 1996 Battery Act.
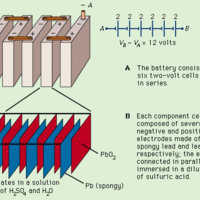
Lead-acid batteries provide high currents and store charge for long periods of time, making them essential for vehicles.
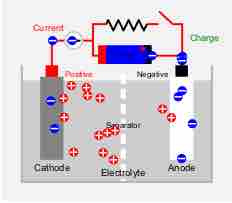
The demand for many varieties of rechargeable batteries is due to their lower cost and lower environmental impact.

Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable batteries commonly used in consumer electronics; they rely on Li+ migration.
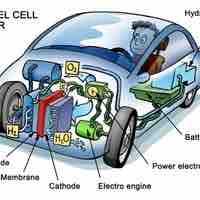
Fuel cells are a compelling alternative to batteries, but they are still in the early stages of development.
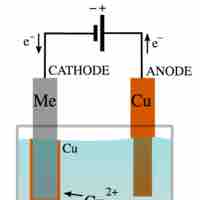
Electrolysis is a way of separating a compound by passing an electric current through it; the products are the compound's component ions.
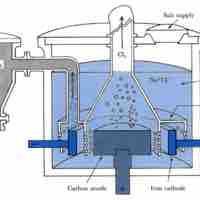
Two commonly used methods of electrolysis involve molten sodium chloride and aqueous sodium chloride, which give different products.
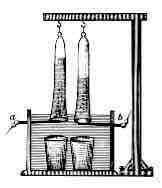
Pure water cannot undergo significant electrolysis without an electrolyte, such as an acid or a base.
The amount of chemical change that occurs in electrolysis is stoichiometrically related to the amount of electrons that pass through the cell.
