关于许可协议
知识共享许可协议做什么
许可协议设计和原理
All Creative Commons licenses have many important features in common. Every license helps creators — we call them licensors if they use our tools — retain copyright while allowing others to copy, distribute, and make some uses of their work — at least non-commercially. Every Creative Commons license also ensures licensors get the credit for their work they deserve. Every Creative Commons license works around the world and lasts as long as applicable copyright lasts (because they are built on copyright). These common features serve as the baseline, on top of which licensors can choose to grant additional permissions when deciding how they want their work to be used.
A Creative Commons licensor answers a few simple questions on the path to choosing a license — first, do I want to allow commercial use or not, and then second, do I want to allow derivative works or not? If a licensor decides to allow derivative works, she may also choose to require that anyone who uses the work — we call them licensees — to make that new work available under the same license terms. We call this idea “ShareAlike” and it is one of the mechanisms that (if chosen) helps the digital commons grow over time. ShareAlike is inspired by the GNU General Public License, used by many free and open source software projects.
Our licenses do not affect freedoms that the law grants to users of creative works otherwise protected by copyright, such as exceptions and limitations to copyright law like fair dealing. Creative Commons licenses require licensees to get permission to do any of the things with a work that the law reserves exclusively to a licensor and that the license does not expressly allow. Licensees must credit the licensor, keep copyright notices intact on all copies of the work, and link to the license from copies of the work. Licensees cannot use technological measures to restrict access to the work by others.
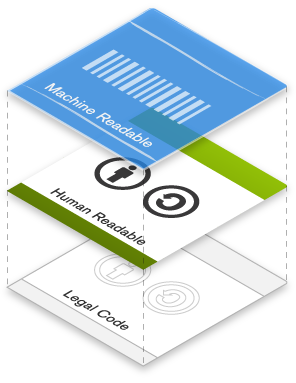
许可协议的三个“层”
计算机可读的
人类可理解的
法律文本
Our public copyright licenses incorporate a unique and innovative “three-layer” design. Each license begins as a traditional legal tool, in the kind of language and text formats that most lawyers know and love. We call this the Legal Code layer of each license.
But since most creators, educators, and scientists are not in fact lawyers, we also make the licenses available in a format that normal people can read — the Commons Deed (also known as the “human readable” version of the license). The Commons Deed is a handy reference for licensors and licensees, summarizing and expressing some of the most important terms and conditions. Think of the Commons Deed as a user-friendly interface to the Legal Code beneath, although the Deed itself is not a license, and its contents are not part of the Legal Code itself.
The final layer of the license design recognizes that software, from search engines to office productivity to music editing, plays an enormous role in the creation, copying, discovery, and distribution of works. In order to make it easy for the Web to know when a work is available under a Creative Commons license, we provide a “machine readable” version of the license — a summary of the key freedoms and obligations written into a format that software systems, search engines, and other kinds of technology can understand. We developed a standardized way to describe licenses that software can understand called CC Rights Expression Language (CC REL) to accomplish this.
Searching for open content is an important function enabled by our approach. You can use Google to search for Creative Commons content, look for pictures at Flickr, albums at Jamendo, and general media at spinxpress. The Wikimedia Commons, the multimedia repository of Wikipedia, is a core user of our licenses as well.
Taken together, these three layers of licenses ensure that the spectrum of rights isn’t just a legal concept. It’s something that the creators of works can understand, their users can understand, and even the Web itself can understand.
许可协议
署名
CC BY
This license lets others distribute, remix, tweak, and build upon your work, even commercially, as long as they credit you for the original creation. This is the most accommodating of licenses offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials.
署名-相同方式共享
CC BY-SA
This license lets others remix, tweak, and build upon your work even for commercial purposes, as long as they credit you and license their new creations under the identical terms. This license is often compared to “copyleft” free and open source software licenses. All new works based on yours will carry the same license, so any derivatives will also allow commercial use. This is the license used by Wikipedia, and is recommended for materials that would benefit from incorporating content from Wikipedia and similarly licensed projects.
We also provide tools that work in the “all rights granted” space of the public domain. Our CC0 tool allows licensors to waive all rights and place a work in the public domain, and our Public Domain Mark allows any web user to “mark” a work as being in the public domain.
Castellano Castellano (España) Català Dansk Deutsch English Esperanto français Galego hrvatski Indonesia Italiano Latviski Lietuvių Magyar Melayu Nederlands Norsk polski Português Português (BR) Português (Portugal) română Suomeksi svenska Türkçe íslenska česky Ελληνικά Беларуская русский українська العربية پارسی 中文 日本語 華語 (台灣) 한국어