Adhesins are cell-surface components or appendages of bacteria that facilitate bacterial adhesion or adherence to other cells or to inanimate surfaces. Adhesins are a type of virulence factor. Adherence is an essential step in bacterial pathogenesis or infection, required for colonizing a new host. For example, nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae expresses the adhesins Hia, Hap, Oap, and a hemagglutinating pili.
Fimbriae are fine filaments of protein, just 3–10 nanometers in diameter and up to several micrometers in length. They are distributed over the surface of the cell, and resemble fine hairs when seen under the electron microscope. Fimbriae are believed to be involved in attachment to solid surfaces or to other cells, and are essential for the virulence of some bacterial pathogens. Most fimbriae of Gram-negative bacteria function as adhesins, but in many cases the actual adhesin is a minor subunit protein at the tip of the fimbriae. In Gram-positive bacteria, a protein or polysaccharide surface layer serves as the specific adhesin. To effectively achieve adherence to host surfaces, many bacteria produce multiple adherence factors called adhesins.
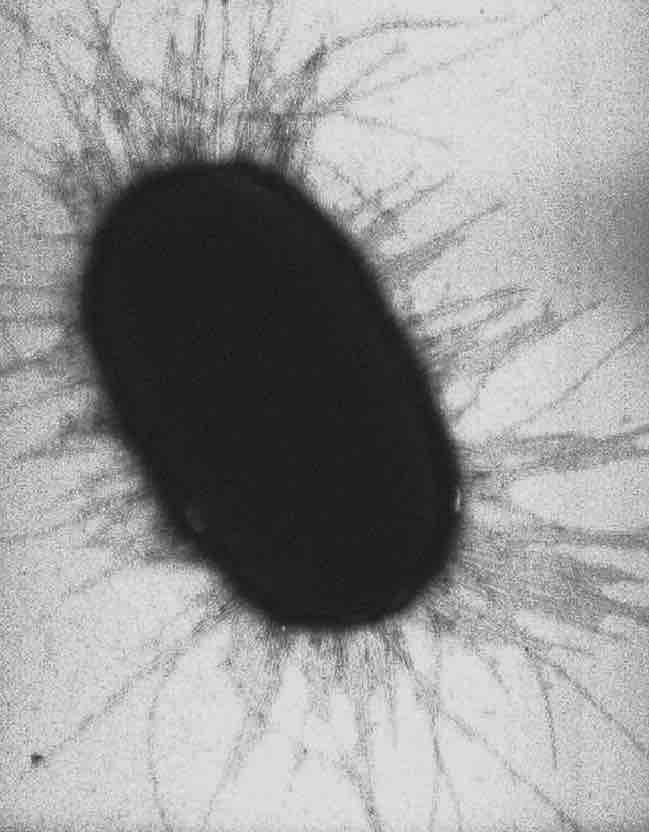
E. coli fimbriae
In bacteriology, a fimbria (plural fimbriae; abbreviated FIM) is an appendage composed of curlin proteins that can be found on many Gram-negative and some Gram-positive bacteria that is thinner and shorter than a flagellum. This appendage ranges from 3-10 nanometers in diameter and can be up to several micrometers long.
The Dr family of adhesins bind to the Dr blood group antigen component of decay-accelerating factor (DAF). These proteins contain both fimbriated and afimbriated adherence structures and mediate adherence of uropathogenic Escherichia coli to the urinary tract. They do so by inducing the development of long cellular extensions that wrap around the bacteria. They also confer the mannose-resistant hemagglutination phenotype, which can be inhibited by chloramphenicol. The N-terminal portion of the mature protein is thought to be responsible for chloramphenicol sensitivity. Also, they induce activation of several signal transduction cascades, including activation of PI-3 kinase. The Dr family of adhesins are particularly associated with cystitis and pregnancy-associated pyelonephritis.
Adhesins are attractive vaccine candidates because they are often essential to infection and are surface-located, making them readily accessible to antibodies. The effectiveness of anti-adhesin antibodies is illustrated by studies with FimH, the adhesin of uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC). In animal models, passive immunization with anti FimH-antibodies and vaccination with the protein significantly reduced colonization by UPEC. Moreover, the Bordetella pertussis adhesins FHA and pertactin are components of 3 of the 4 acellular pertussis vaccines currently licensed for use in the U.S.