Section 1
Entry into the Host
By Boundless
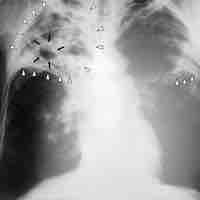
Microbes gain access to human tissues via mucosal surfaces within the body or epithelial surfaces on the outside of the body.
Infection begins when an organism successfully colonizes a host by entering the host's body, growing and multiplying from there.
Pathogenicity islands (PAIs) are a distinct class of genomic islands acquired by microorganisms through horizontal gene transfer.
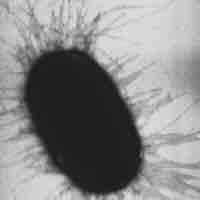
Adhesins are cell-surface components or appendages of bacteria that facilitate bacterial adhesion to other cells or to inanimate surfaces.
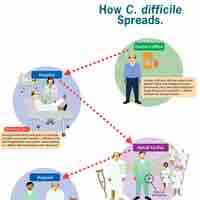
Individuals who are weak, sick, malnourished, have cancer, or are diabetic have increased susceptibility to chronic or persistent infections.
Several barriers protect organisms from infection including mechanical, chemical, and biological barriers.