Strategic planning is an organization's process of defining its strategy and making decisions on how to allocate resources to pursue that strategy. To determine the direction of the organization, it is necessary to understand its current position and the possible avenues through which it can pursue a particular course of action. Strategic planning generally deals with at least one of three key questions:
- What do we do?
- For whom do we do it?
- How do we excel?
In many organizations, this is viewed as a process for determining where the organization is going over the next year or, more typically, three to five years, although some extend their vision to 20 years. The last question—how do we excel?—is critical to achieving competitive advantage, and it should be answered clearly and practically in the planning process prior to extensive investment in resources.
Components of a Strategic Plan
Planning is concerned with defining goals for a company's future direction and determining the resources required to achieve those goals. To meet the goals, managers will develop marketing and operational plans inclusive of key organizational values (vision, mission, culture, etc.).
Common components of a business plan include external and internal analyses, marketing and branding, investments, debt, resource allocation, suppliers, production processes, competition, and research and development. While different business models include different components in their planning, based on unique organizational or industry needs, the central theme is that all aspects of the strategy should be researched and discussed prior to incurring the costs of operations.
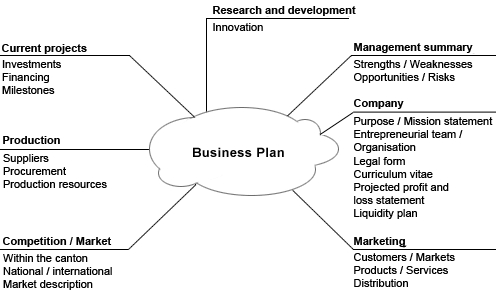
Business plan
This image summarizes some of the factors that should be considered in the creation of a business plan, such as a company's mission and purpose, personnel, financial resources, market and customer base, competition, and strengths and weaknesses.
Planning Process
There are many approaches to strategic planning, but typically one of the following approaches is used.
Situation-Target-Proposal
This method involves the following steps:
- Situation: Evaluate the current situation and how it came about.
- Target: Define goals and objectives (sometimes called ideal state).
- Proposal: Map a possible route to the goals and objectives.
Draw-See-Think-Plan
This method involves addressing the following questions:
- Draw: What is the ideal state or the desired end state?
- See: What is today's situation? What is the gap between today's situation and the ideal state, and why?
- Think: What specific actions must be taken to close the gap between today's situation and the ideal state?
- Plan: What resources are required to execute these specific actions?