Chapter 12
Strategic Management
By Boundless
A strategy is a plan of action designed to achieve a specific goal or series of goals within an organizational framework.
Strategic management is critical to organizational development as it aligns the mission and vision with operations.
Effective strategies must be suitable, feasible, and acceptable to stakeholders.
The effectiveness of a strategy is heavily dependent upon the size of the organization.
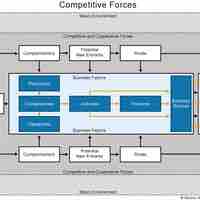
Analysis of both internal factors and external conditions is central to creating effective strategy.
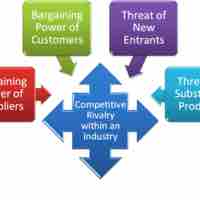
Michael Porter, a leading business analyst and professor, identified five critical external factors that affect strategy in any industry.
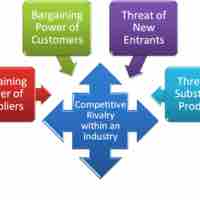
Like most models, Porter's Five Forces has advantages and limitations when applied to strategic planning processes.
PESTEL and SCP frameworks are models for understanding different industry and market factors that impact strategic management.
Crafting an effective strategy requires understanding the competitive dynamics of the space in which the business operates.

A mission statement defines the fundamental purpose of an organization or enterprise.
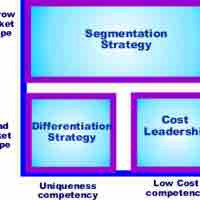
Michael Porter classifies competitive strategies as cost leadership, differentiation, or market segmentation.
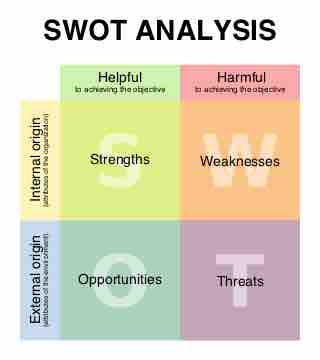
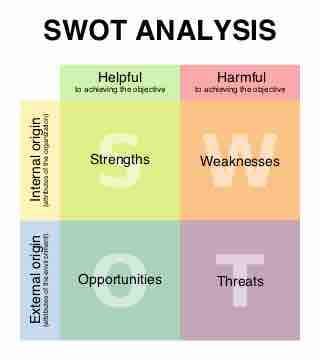
A SWOT analysis allows businesses to assess internal strengths and weaknesses in relation to external opportunities and threats.
Forecasting is the process of making statements about expected future events, based upon evidence, research, and experience.

In the resource-based view (RBV), strategic planning uses organizational resources to generate a viable strategy.
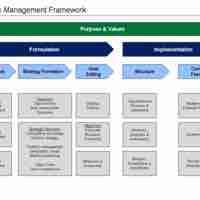
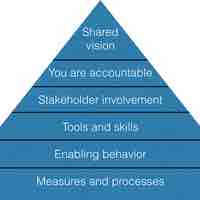
Strategic management entails five steps: analysis, formation, goal setting, structure, and feedback.
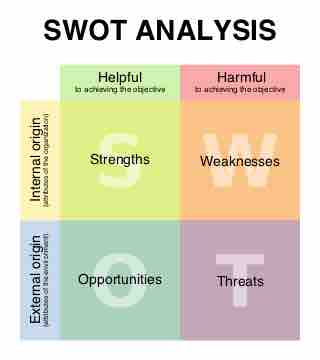
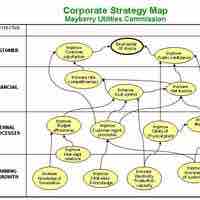
Using combined external and internal analyses, companies are able to generate strategies in pursuit of competitive advantage.
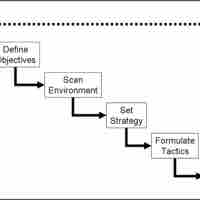
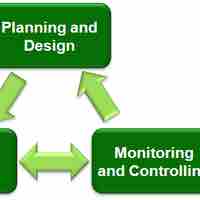
Strategic planning involves managing the implementation process, which translates plans into action.
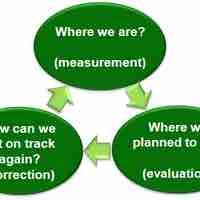
Controlling requires taking an aerial view of operational processes, identifying gaps and weaknesses to improve efficiency.

Growth platforms are specifically named initiatives selected by a business organization to fuel revenue and earnings growth.
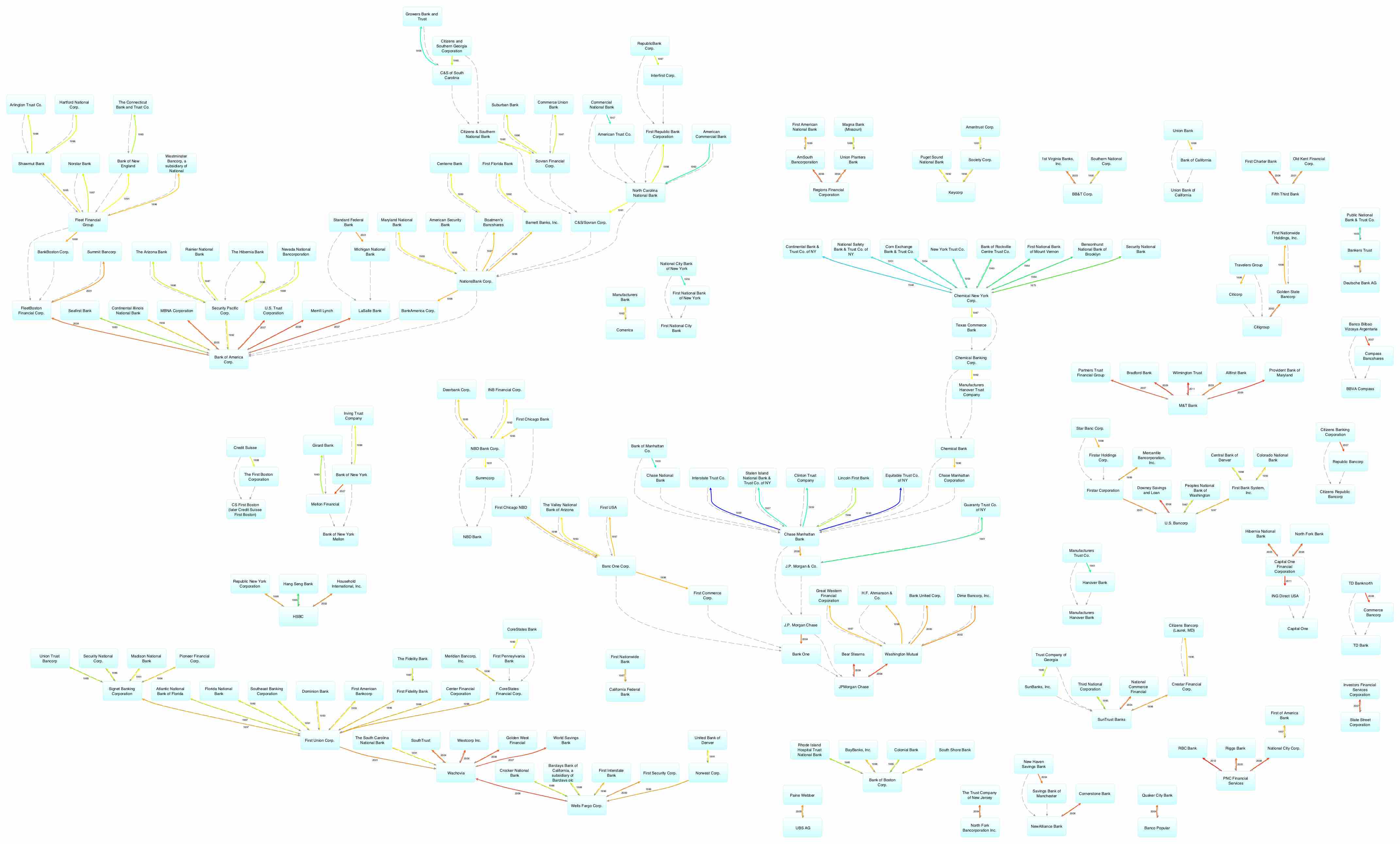
In business, consolidation refers to the mergers and acquisitions of many smaller companies into much larger ones for economic benefit.
_in_us$.jpg)
Global strategy, as defined in business terms, is an organization's strategic guide to pursuing various geographic markets.
A strategic alliance is a cooperation where each member expects the benefit from cooperation will outweigh the cost of individual efforts.

In the emerging global economy, e-business has become an increasingly necessary component of business strategy.
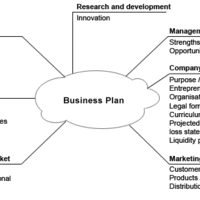
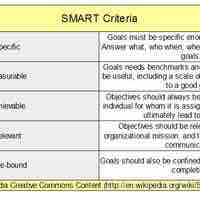
Strategic planning is concerned with defining company goals and determining the resources needed to achieve them.
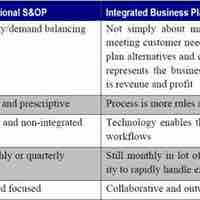
Planning enables companies to achieve efficiency and accuracy by coordinating efforts and managing time effectively.
Strategic plans can take the form of business or marketing plans, and consultants and industry experts are used in their development.
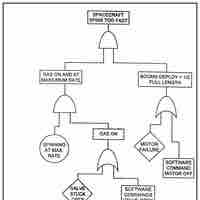
Uncertainty exists when there is more than one possible outcome; it is best managed using scenario-planning tools.