The complement system or "complements" the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear pathogens from an organism. The complement system consists of a number of small proteins found in the blood, generally synthesized by the liver as a part of the acute phase reaction during systemic inflammation (from TNF-alpha release). When stimulated by one of several triggers, proteases in the system cleave specific proteins to release cytokines and initiate an amplifying cascade of further cleavages. The end result of this activation cascade is massive amplification of the response and activation of the cell-killing membrane attack complex (also called MAC). There are three different pathways by which the complement system may occur.
Classical Complement Pathway
The classical complement pathway is the main pathway by which the complement system occurs. It is comprised of a cascade of many steps with complement proteins cleaving one another in a sequential order:
- The antibody binds to an antigen on the surface of a pathogen, activating the C1 complement protein.
- C1 acts a protease and cleaves C2 and C4 to form C4b2b.
- C42b converts C3 into C3a and C3b, which forms a C5 convertase.
- C5 convertase cleaves C5 into C5a and C5b.
- C5b forms a complex with C6, C7, and then C8, and C9, which becomes the membrane attack complex that lyses the pathogen.
Note that C5a has a number of other functions in the immune system, such as causing vasodilation during inflammation and stimulating neutrophil chemotaxis. Additionally, the body's cells express a glycoprotein called decay accelerating factor, which decays C3 and C5 convertase on the body's cells. This factor prevents membrane attack complexes from forming on the body's cells under normal conditions.
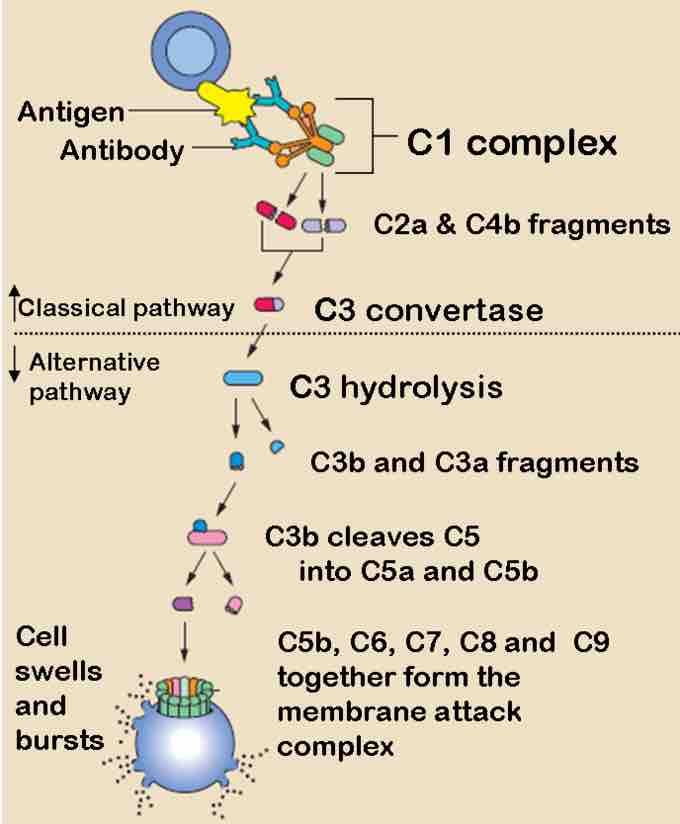
The Classical and Alternative Complement Pathways
The classical and alternative complement pathways start off differently, but end in the same cascade of complement proteins that combine to form a membrane attack complex.
The Alternative Complement Pathway
The alternative pathway may be a leftover evolutionary precursor to the classical pathway. Unlike the classical pathway, the alternative pathway is generally activated by microbial inflammatory mediators instead of antibodies. For example, lipopolysaccharide, the toxin of gram-negative bacteria, may activate this pathway. The steps for the alternative pathway are:
- The pathogenic antigen (such as LPS) activates C3 so it creates a C3B complex
- Factor D cleaves the C3B complex so that C3bBb is created.
- C3bBb is a C3 convertase, which converts more C3 into C3a and C3b.
- Similarly to the classical pathway, C3b forms a C42b complex, and the rest of the steps are essentially the same as the classical pathway, ending with C5b forming a membrane attack complex with C6, C7, C8, and C9.
Lectin Pathway
The lectin pathway is not caused by antibody binding, but by a carbohydrate-binding-protein called mannan-binding-lectin (MBL). It is an acute phase reactant produced in the liver and binds to the carbohydrates on the surfaces of many pathogens. The steps for the lectin pathway are:
- MBL binds to the carbohydrates on a pathogen.
- Proteases bound on the other side of the MBL cleaves C4 into C4a and C4b.
- C4b creates C3 convertase, and the rest of the steps happen identically to the classical pathway from the C3 convertase step.
Problems with the Complement System
The complement system might play a role in diseases with an immune component, such as Barraquer-Simons Syndrome, asthma, lupus erythematosus, glomerulonephritis, various forms of arthritis, autoimmune heart disease, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, ischemia-reperfusion injuries, and rejection of transplanted organs. The complement system is also becoming increasingly implicated in diseases of the central nervous system such as Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative conditions such as spinal cord injuries. Additionally, deficiencies in complement proteins produced in the liver can lead to a form of primary (congenital) immunodeficiency, in which the body is more susceptible to disease, particularly autoimmune diseases and severe bacterial infections.