Strategic management analyzes the major initiatives, involving resources and performance in external environments, that a company's top management takes on behalf of owners. It entails specifying the organization's mission, vision, and objectives, as well as developing policies and plans which allocate resources to drive growth and profitability. Strategy, in short, is the overarching methodology behind the business operations.
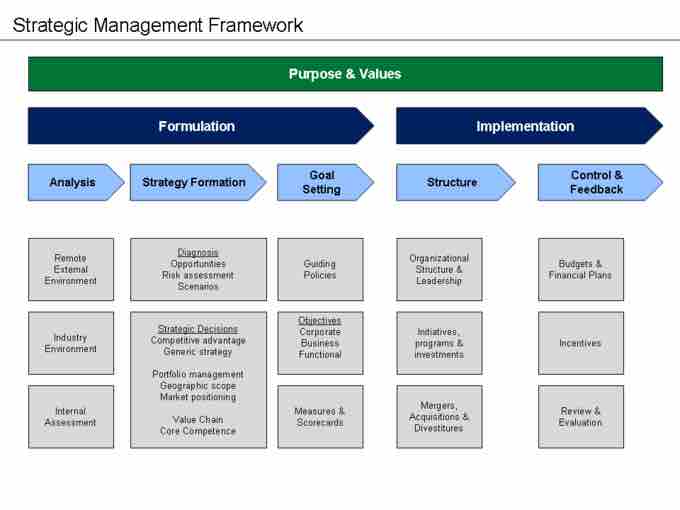
Strategic management framework
The above model is a summary of what is involved in each of the five steps of management: 1. analysis (internal and external), 2. strategy formation (diagnosis and decision-making), 3. goal setting (objectives and measurement), 4. structure (leadership and initiatives), and 5. control and feedback (budgets and incentives).
Five Steps of Strategic Management
As strategic management is a large, complex, and ever-evolving endeavor, it is useful to divide it into a series of concrete steps to illustrate the process of strategic management. While many management models pertaining to strategy derivation are in use, most general frameworks include five steps embedded in two general stages:
Formulation
- Analysis – Strategic analysis is a time-consuming process, involving comprehensive market research on the external and competitive environments as well as extensive internal assessments. The process involves conducting Porter's Five Forces, SWOT, PESTEL, and value chain analyses and gathering experts in each industry relating to the strategy.
- Strategy Formation – Following the analysis phase, the organization selects a generic strategy (for example, low-cost, differentiation, etc.) based upon the value-chain implications for core competence and potential competitive advantage. Risk assessments and contingency plans are also developed based upon external forecasting. Brand positioning and image should be solidified.
- Goal Setting – With the defined strategy in mind, management identifies and communicates goals and objectives that correlate to the predicted outcomes, strengths, and opportunities. These objectives include quantitative ways to measure the success or failure of the goals, along with corresponding organizational policy. Goal setting is the final phase before implementation begins.
Implementation
- Structure – The implementation phase begins with the strategy in place, and the business solidifies its organizational structure and leadership (making changes if necessary). Leaders allocate resources to specific projects and enact any necessary strategic partnerships.
- Feedback – During the final stage of strategy, all budgetary figures are submitted for evaluation. Financial ratios should be calculated and performance reviews delivered to relevant personnel and departments. This information will be used to restart the planning process, or reinforce the success of the previous strategy.