Chapter 17
Electric Charge and Field
By Boundless
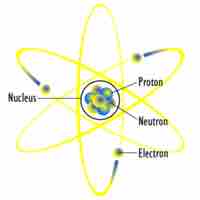
Atoms contain negatively charged electrons and positively charged protons; the number of each determines the atom's net charge.

Electric charge is a fundamental physical property of matter that has many parallels to mass.

Charge separation, often referred to as static electricity, is the building of space between particles of opposite charges.
Dielectric polarization is the phenomenon that arises when positive and negative charges in a material are separated.

Electric charge is a physical property that is perpetually conserved in amount; it can build up in matter, which creates static electricity.

Based on the ability to conduct current, materials are divided into conductors and insulators.
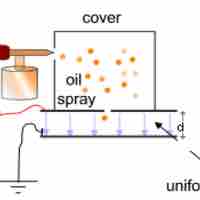
In 1911, using charged droplets of oil, Robert Millikan was able to determine the charge of an electron.
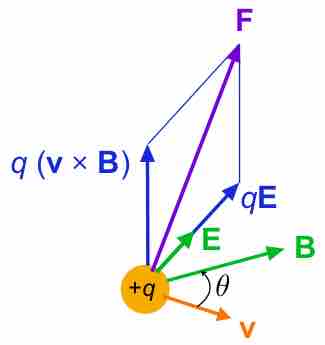
The superposition principle (superposition property) states that for all linear forces the total force is a vector sum of individual forces.
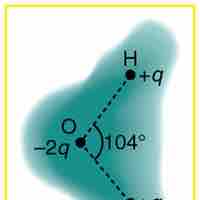
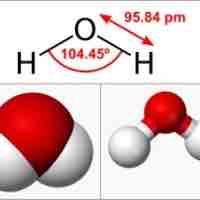
The charge distribution around a molecule is spherical in nature, and creates a sort of electrostatic "cloud" around the molecule.
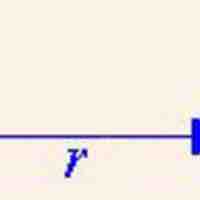
Coulomb's Law, which calculates the electric force between charged particles, can be written in vector notation as
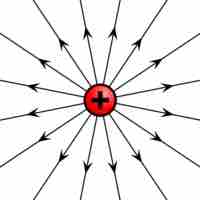
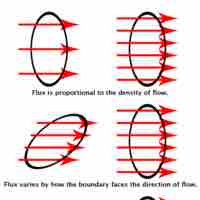
A point charge creates an electric field that can be calculated using Coulomb's law.
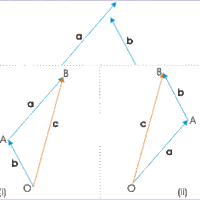
The resultant of multiple electric fields acting on the same point is the sum of the strength of each field's applied force at that point.
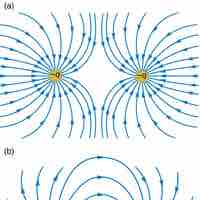
Electric fields created by multiple charges interact as do any other type of vector field; their forces can be summed.
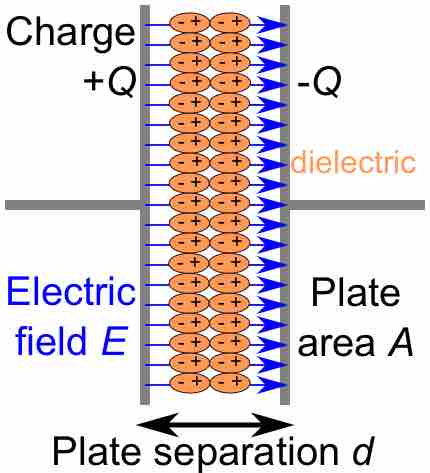
A parallel-plate capacitor is an electrical component used to store energy in an electric field between two charged, flat surfaces.
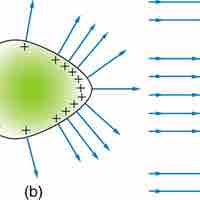
Electric fields in the presence of conductors have several unique and not necessarily intuitive properties.
In the presence of charge or an electric field, the charges in a conductor will redistribute until they reach static equilibrium.
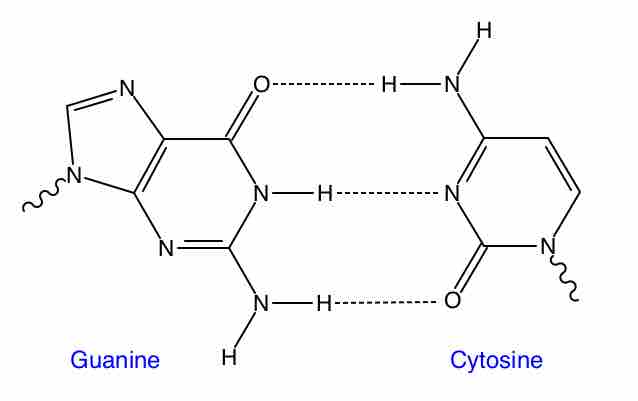
Hydrogen bonding, brought on by electrostatic interactions, is critical to holding together strands of DNA.
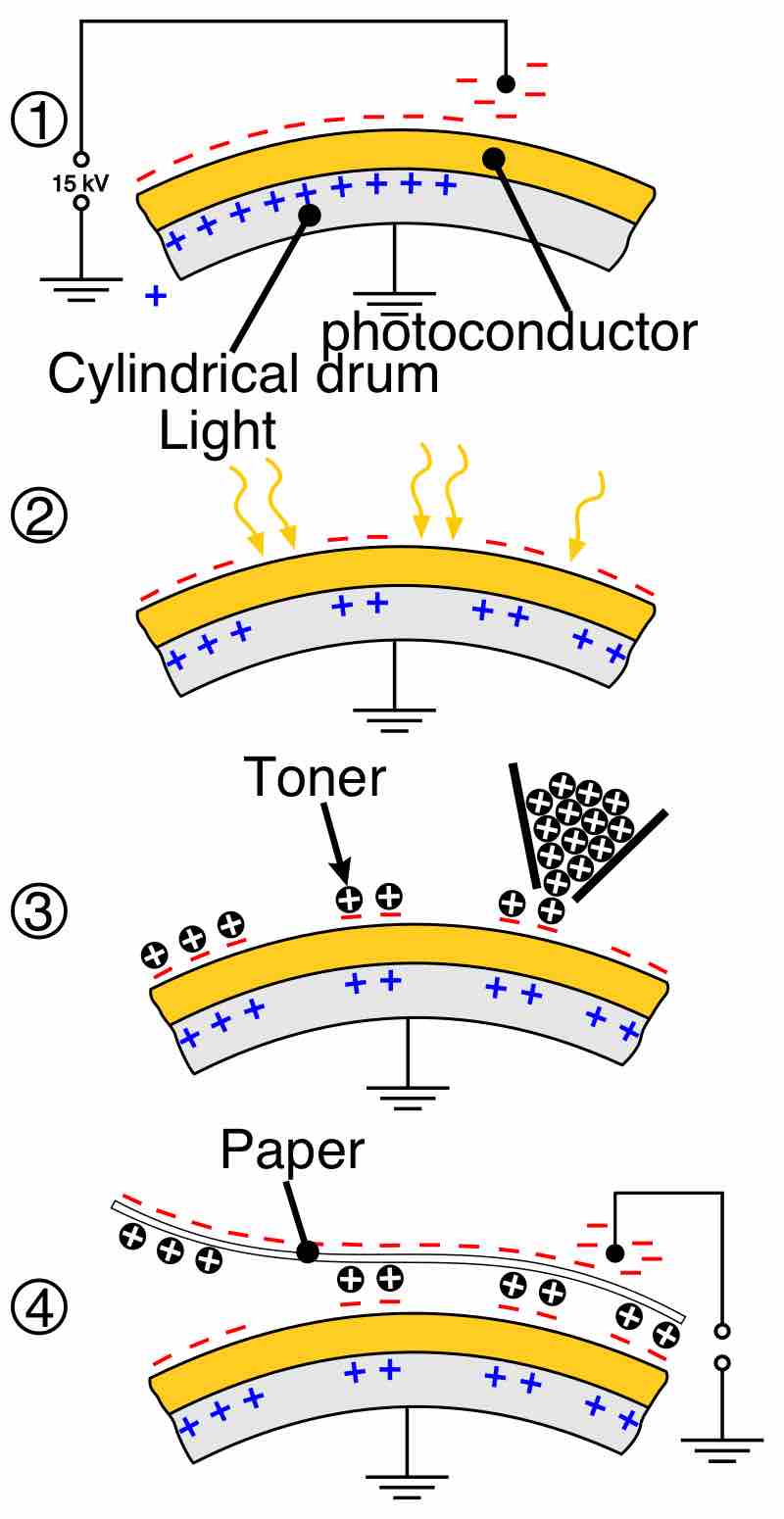
Photocopiers use xerography, a process that uses principles of electrostatics, to copy images.
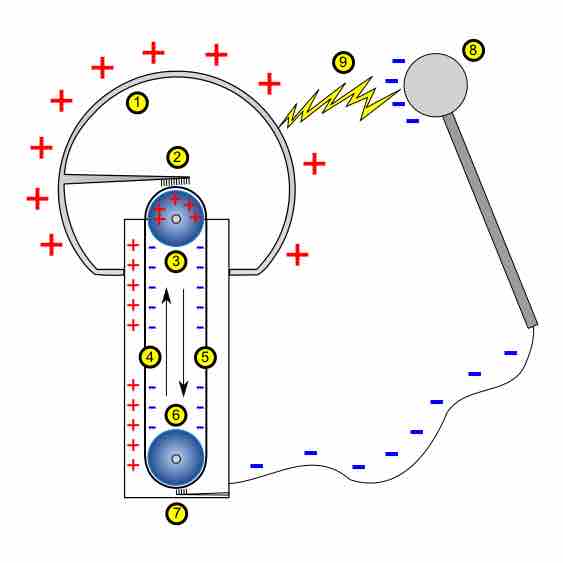
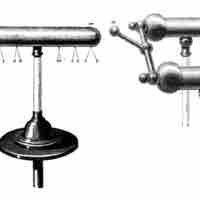
A Van de Graaff generator is a device that can be used to separate charges and create potential differences in the range of megavolts.