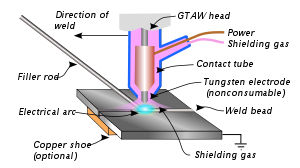
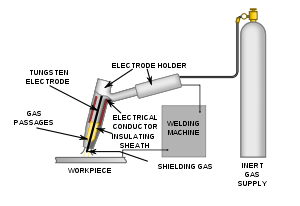
Gas tungsten arc welding
Background to the schools Wikipedia
SOS Children has tried to make Wikipedia content more accessible by this schools selection. Sponsoring children helps children in the developing world to learn too.
Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), also known as tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding, is an arc welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. The weld area is protected from atmospheric contamination by an inert shielding gas (argon or helium), and a filler metal is normally used, though some welds, known as autogenous welds, do not require it. A constant-current welding power supply produces energy which is conducted across the arc through a column of highly ionized gas and metal vapors known as a plasma.
GTAW is most commonly used to weld thin sections of stainless steel and non-ferrous metals such as aluminium, magnesium, and copper alloys. The process grants the operator greater control over the weld than competing processes such as shielded metal arc welding and gas metal arc welding, allowing for stronger, higher quality welds. However, GTAW is comparatively more complex and difficult to master, and furthermore, it is significantly slower than most other welding techniques. A related process, plasma arc welding, uses a slightly different welding torch to create a more focused welding arc and as a result is often automated.
Development
After the discovery of the electric arc in 1800 by Humphry Davy, arc welding developed slowly. C. L. Coffin had the idea of welding in an inert gas atmosphere in 1890, but even in the early 20th century, welding non-ferrous materials like aluminium and magnesium remained difficult, because these metals reacted rapidly with the air, resulting in porous and dross-filled welds. Processes using flux-covered electrodes did not satisfactorily protect the weld area from contamination. To solve the problem, bottled inert gases were used in the beginning of the 1930s. A few years later, a direct current, gas-shielded welding process emerged in the aircraft industry for welding magnesium.
This process was perfected in 1941, and became known as heliarc or tungsten inert gas welding, because it utilized a tungsten electrode and helium as a shielding gas. Initially, the electrode overheated quickly, and in spite of tungsten's high melting temperature, particles of tungsten were transferred to the weld. To address this problem, the polarity of the electrode was changed from positive to negative, but this made it unsuitable for welding many non-ferrous materials. Finally, the development of alternating current units made it possible to stabilize the arc and produce high quality aluminium and magnesium welds.
Developments continued during the following decades. Linde Air Products developed water-cooled torches that helped to prevent overheating when welding with high currents. Additionally, during the 1950s, as the process continued to gain popularity, some users turned to carbon dioxide as an alternative to the more expensive welding atmospheres consisting of argon and helium. However, this proved unacceptable for welding aluminium and magnesium because it reduced weld quality, and as a result, it is rarely used with GTAW today.
In 1953, a new process based on GTAW was developed, called plasma arc welding. It affords greater control and improves weld quality by using a nozzle to focus the electric arc, but is largely limited to automated systems, whereas GTAW remains primarily a manual, hand-held method. Development within the GTAW process has continued as well, and today a number of variations exist. Among the most popular are the pulsed-current, manual programmed, hot-wire, dabber, and increased penetration GTAW methods.
Operation
Manual gas tungsten arc welding is often considered the most difficult of all the welding processes commonly used in industry. Because the welder must maintain a short arc length, great care and skill are required to prevent contact between the electrode and the workpiece. Similar to torch welding, GTAW normally requires two hands, since most applications require that the welder manually feed a filler metal into the weld area with one hand while manipulating the welding torch in the other. However, some welds combining thin materials (known as autogenous or fusion welds) can be accomplished without filler metal; most notably edge, corner, and butt joints.
To strike the welding arc, a high frequency generator (similar to a Tesla coil) provides an electric spark; this spark is a conductive path for the welding current through the shielding gas and allows the arc to be initiated while the electrode and the workpiece are separated, typically about 1.5–3 mm (0.06–0.12 in) apart. This high voltage, high frequency burst can be damaging to some vehicle electrical systems and electronics, because induced voltages on vehicle wiring can also cause small conductive sparks in the vehicle wiring or within semiconductor packaging. Vehicle 12V power may conduct across these ionized paths, driven by the high-current 12V vehicle battery. These currents can be sufficiently destructive as to disable the vehicle; thus the warning to disconnect the vehicle battery power from both +12 and ground before using welding equipment on vehicles.
An alternate way to initiate the arc is the "scratch start". Scratching the electrode against the work with the power on also serves to strike an arc, in the same way as SMAW ("stick") arc welding. However, scratch starting can cause contamination of the weld and electrode. Some GTAW equipment is capable of a mode called "touch start" or "lift arc"; here the equipment reduces the voltage on the electrode to only a few volts, with a current limit of one or two amps (well below the limit that causes metal to transfer and contamination of the weld or electrode). When the GTAW equipment detects that the electrode has left the surface and a spark is present, it immediately (within microseconds) increases power, converting the spark to a full arc.
Once the arc is struck, the welder moves the torch in a small circle to create a welding pool, the size of which depends on the size of the electrode and the amount of current. While maintaining a constant separation between the electrode and the workpiece, the operator then moves the torch back slightly and tilts it backward about 10–15 degrees from vertical. Filler metal is added manually to the front end of the weld pool as it is needed.
Welders often develop a technique of rapidly alternating between moving the torch forward (to advance the weld pool) and adding filler metal. The filler rod is withdrawn from the weld pool each time the electrode advances, but it is never removed from the gas shield to prevent oxidation of its surface and contamination of the weld. Filler rods composed of metals with low melting temperature, such as aluminium, require that the operator maintain some distance from the arc while staying inside the gas shield. If held too close to the arc, the filler rod can melt before it makes contact with the weld puddle. As the weld nears completion, the arc current is often gradually reduced to allow the weld crater to solidify and prevent the formation of crater cracks at the end of the weld.
Safety
Like other arc welding processes, GTAW can be dangerous if proper precautions are not taken. Welders wear protective clothing, including heavy leather gloves and protective long sleeve jackets, to avoid exposure to extreme heat and flames. Due to the absence of smoke in GTAW, the electric arc can seem brighter than in shielded metal arc welding, making operators especially susceptible to arc eye and skin irritations not unlike sunburn. Helmets with dark face plates are worn to prevent this exposure to ultraviolet light, and in recent years, new helmets often feature a liquid crystal-type face plate that self-darkens upon exposure to high amounts of UV light. Transparent welding curtains, made of a polyvinyl chloride plastic film, are often used to shield nearby workers and bystanders from exposure to the UV light from the electric arc.
Welders are also often exposed to dangerous gases and particulate matter. While smoke is not produced, the brightness of the arc in GTAW can cause surrounding air to break down and form ozone. Similarly, the brightness and heat can cause poisonous fumes to form from cleaning and degreasing materials. Cleaning operations using these agents should not be performed near the site of welding, and proper ventilation is necessary to protect the welder.
Applications
While the aerospace industry is one of the primary users of gas tungsten arc welding, the process is used in a number of other areas. Many industries use GTAW for welding thin workpieces, especially nonferrous metals. It is used extensively in the manufacture of space vehicles, and is also frequently employed to weld small-diameter, thin-wall tubing such as those used in the bicycle industry. In addition, GTAW is often used to make root or first pass welds for piping of various sizes. In maintenance and repair work, the process is commonly used to repair tools and dies, especially components made of aluminum and magnesium. Because the weld metal is not transferred directly across the electric arc like most open arc welding processes, a vast assortment of welding filler metal is available to the welding engineer. In fact, no other welding process permits the welding of so many alloys in so many product configurations. Filler metal alloys, such as elemental aluminium and chromium, can be lost through the electric arc from volatilization. This loss does not occur with the GTAW process. Because the resulting welds have the same chemical integrity as the original base metal or match the base metals more closely, GTAW welds are highly resistant to corrosion and cracking over long time periods, GTAW is the welding procedure of choice for critical welding operations like sealing spent nuclear fuel canisters before burial.
Quality
Gas tungsten arc welding, because it affords greater control over the weld area than other welding processes, can produce high-quality welds when performed by skilled operators. Maximum weld quality is assured by maintaining cleanliness—all equipment and materials used must be free from oil, moisture, dirt and other impurities, as these cause weld porosity and consequently a decrease in weld strength and quality. To remove oil and grease, alcohol or similar commercial solvents may be used, while a stainless steel wire brush or chemical process can remove oxides from the surfaces of metals like aluminium. Rust on steels can be removed by first grit blasting the surface and then using a wire brush to remove any embedded grit. These steps are especially important when negative polarity direct current is used, because such a power supply provides no cleaning during the welding process, unlike positive polarity direct current or alternating current. To maintain a clean weld pool during welding, the shielding gas flow should be sufficient and consistent so that the gas covers the weld and blocks impurities in the atmosphere. GTAW in windy or drafty environments increases the amount of shielding gas necessary to protect the weld, increasing the cost and making the process unpopular outdoors.
The level of heat input also affects weld quality. Low heat input, caused by low welding current or high welding speed, can limit penetration and cause the weld bead to lift away from the surface being welded. If there is too much heat input, however, the weld bead grows in width while the likelihood of excessive penetration and spatter increase. Additionally, if the welding torch is too far from the workpiece the shielding gas becomes ineffective causing porosity within the weld. This results in a weld with pinholes, which is weaker than a typical weld.
If the amount of current used exceeds the capability of the electrode, tungsten inclusions in the weld may result. Known as tungsten spitting, it can be identified with radiography and prevented by changing the type of electrode or increasing the electrode diameter. In addition, if the electrode is not well protected by the gas shield or the operator accidentally allows it to contact the molten metal, it can become dirty or contaminated. This often causes the welding arc to become unstable, requiring that electrode be ground with a diamond abrasive to remove the impurity.
Equipment
The equipment required for the gas tungsten arc welding operation includes a welding torch utilizing a non-consumable tungsten electrode, a constant-current welding power supply, and a shielding gas source.
Welding torch
GTAW welding torches are designed for either automatic or manual operation and are equipped with cooling systems using air or water. The automatic and manual torches are similar in construction, but the manual torch has a handle while the automatic torch normally comes with a mounting rack. The angle between the centerline of the handle and the centerline of the tungsten electrode, known as the head angle, can be varied on some manual torches according to the preference of the operator. Air cooling systems are most often used for low-current operations (up to about 200 A), while water cooling is required for high-current welding (up to about 600 A). The torches are connected with cables to the power supply and with hoses to the shielding gas source and where used, the water supply.
The internal metal parts of a torch are made of hard alloys of copper or brass in order to transmit current and heat effectively. The tungsten electrode must be held firmly in the centre of the torch with an appropriately sized collet, and ports around the electrode provide a constant flow of shielding gas. Collets are sized according to the diameter of the tungsten electrode they hold. The body of the torch is made of heat-resistant, insulating plastics covering the metal components, providing insulation from heat and electricity to protect the welder.
The size of the welding torch nozzle depends on the amount of shielded area desired. The size of the gas nozzle will depend upon the diameter of the electrode, the joint configuration, and the availability of access to the joint by the welder. The inside diameter of the nozzle is preferably at least three times the diameter of the electrode, but there are no hard rules. The welder will judge the effectiveness of the shielding and increase the nozzle size to increase the area protected by the external gas shield as needed. The nozzle must be heat resistant and thus is normally made of alumina or a ceramic material, but fused quartz, a glass-like substance, offers greater visibility. Devices can be inserted into the nozzle for special applications, such as gas lenses or valves to improve the control shielding gas flow to reduce turbulence and introduction of contaminated atmosphere into the shielded area. Hand switches to control welding current can be added to the manual GTAW torches.
Power supply
Gas tungsten arc welding uses a constant current power source, meaning that the current (and thus the heat) remains relatively constant, even if the arc distance and voltage change. This is important because most applications of GTAW are manual or semiautomatic, requiring that an operator hold the torch. Maintaining a suitably steady arc distance is difficult if a constant voltage power source is used instead, since it can cause dramatic heat variations and make welding more difficult.
The preferred polarity of the GTAW system depends largely on the type of metal being welded. Direct current with a negatively charged electrode (DCEN) is often employed when welding steels, nickel, titanium, and other metals. It can also be used in automatic GTAW of aluminium or magnesium when helium is used as a shielding gas. The negatively charged electrode generates heat by emitting electrons which travel across the arc, causing thermal ionization of the shielding gas and increasing the temperature of the base material. The ionized shielding gas flows toward the electrode, not the base material, and this can allow oxides to build on the surface of the weld. Direct current with a positively charged electrode (DCEP) is less common, and is used primarily for shallow welds since less heat is generated in the base material. Instead of flowing from the electrode to the base material, as in DCEN, electrons go the other direction, causing the electrode to reach very high temperatures. To help it maintain its shape and prevent softening, a larger electrode is often used. As the electrons flow toward the electrode, ionized shielding gas flows back toward the base material, cleaning the weld by removing oxides and other impurities and thereby improving its quality and appearance.
Alternating current, commonly used when welding aluminium and magnesium manually or semi-automatically, combines the two direct currents by making the electrode and base material alternate between positive and negative charge. This causes the electron flow to switch directions constantly, preventing the tungsten electrode from overheating while maintaining the heat in the base material. Surface oxides are still removed during the electrode-positive portion of the cycle and the base metal is heated more deeply during the electrode-negative portion of the cycle. Some power supplies enable operators to use an unbalanced alternating current wave by modifying the exact percentage of time that the current spends in each state of polarity, giving them more control over the amount of heat and cleaning action supplied by the power source. In addition, operators must be wary of rectification, in which the arc fails to reignite as it passes from straight polarity (negative electrode) to reverse polarity (positive electrode). To remedy the problem, a square wave power supply can be used, as can high-frequency voltage to encourage ignition.
Electrode
| ISO Class |
ISO Colour |
AWS Class |
AWS Colour |
Alloy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WP | Green | EWP | Green | None |
| WC20 | Gray | EWCe-2 | Orange | ~2% CeO2 |
| WL10 | Black | EWLa-1 | Black | ~1% La2O3 |
| WL15 | Gold | EWLa-1.5 | Gold | ~1.5% La2O3 |
| WL20 | Sky-blue | EWLa-2 | Blue | ~2% La2O3 |
| WT10 | Yellow | EWTh-1 | Yellow | ~1% ThO2 |
| WT20 | Red | EWTh-2 | Red | ~2% ThO2 |
| WT30 | Violet | ~3% ThO2 | ||
| WT40 | Orange | ~4% ThO2 | ||
| WY20 | Blue | ~2% Y2O3 | ||
| WZ3 | Brown | EWZr-1 | Brown | ~0.3% ZrO2 |
| WZ8 | White | ~0.8% ZrO2 |
The electrode used in GTAW is made of tungsten or a tungsten alloy, because tungsten has the highest melting temperature among pure metals, at 3,422 °C (6,192 °F). As a result, the electrode is not consumed during welding, though some erosion (called burn-off) can occur. Electrodes can have either a clean finish or a ground finish—clean finish electrodes have been chemically cleaned, while ground finish electrodes have been ground to a uniform size and have a polished surface, making them optimal for heat conduction. The diameter of the electrode can vary between 0.5 and 6.4 millimetres (0.02 and 0.25 in), and their length can range from 75 to 610 millimetres (3.0 to 24 in).
A number of tungsten alloys have been standardized by the International Organization for Standardization and the American Welding Society in ISO 6848 and AWS A5.12, respectively, for use in GTAW electrodes, and are summarized in the adjacent table.
- Pure tungsten electrodes (classified as WP or EWP) are general purpose and low cost electrodes. They have poor heat resistance and electron emission. They find limited use in AC welding of e.g. magnesium and aluminium.
- Cerium oxide (or ceria) as an alloying element improves arc stability and ease of starting while decreasing burn-off. Cerium addition is not as effective as thorium but works well, and cerium is not radioactive.
- Using an alloy of lanthanum oxide (or lanthana) has a similar effect. Addition of 1% lanthanum has the same effect as 2% of cerium.
- Thorium oxide (or thoria) alloy electrodes were designed for DC applications and can withstand somewhat higher temperatures while providing many of the benefits of other alloys. However, it is somewhat radioactive. Inhalation of the thorium grinding dust during preparation of the electrode is hazardous to one's health. As a replacement to thoriated electrodes, electrodes with larger concentrations of lanthanum oxide can be used. Larger additions than 0.6% do not have additional improving effect on arc starting, but they help with electron emission. Higher percentage of thorium also makes tungsten more resistant to contamination.
- Electrodes containing zirconium oxide (or zirconia) increase the current capacity while improving arc stability and starting and increasing electrode life. Zirconium-tungsten electrodes melt easier than thorium-tungsten.
- In addition, electrode manufacturers may create alternative tungsten alloys with specified metal additions, and these are designated with the classification EWG under the AWS system.
Filler metals are also used in nearly all applications of GTAW, the major exception being the welding of thin materials. Filler metals are available with different diameters and are made of a variety of materials. In most cases, the filler metal in the form of a rod is added to the weld pool manually, but some applications call for an automatically fed filler metal, which often is stored on spools or coils.
Shielding gas
As with other welding processes such as gas metal arc welding, shielding gases are necessary in GTAW to protect the welding area from atmospheric gases such as nitrogen and oxygen, which can cause fusion defects, porosity, and weld metal embrittlement if they come in contact with the electrode, the arc, or the welding metal. The gas also transfers heat from the tungsten electrode to the metal, and it helps start and maintain a stable arc.
The selection of a shielding gas depends on several factors, including the type of material being welded, joint design, and desired final weld appearance. Argon is the most commonly used shielding gas for GTAW, since it helps prevent defects due to a varying arc length. When used with alternating current, the use of argon results in high weld quality and good appearance. Another common shielding gas, helium, is most often used to increase the weld penetration in a joint, to increase the welding speed, and to weld metals with high heat conductivity, such as copper and aluminium. A significant disadvantage is the difficulty of striking an arc with helium gas, and the decreased weld quality associated with a varying arc length.
Argon-helium mixtures are also frequently utilized in GTAW, since they can increase control of the heat input while maintaining the benefits of using argon. Normally, the mixtures are made with primarily helium (often about 75% or higher) and a balance of argon. These mixtures increase the speed and quality of the AC welding of aluminium, and also make it easier to strike an arc. Another shielding gas mixture, argon-hydrogen, is used in the mechanized welding of light gauge stainless steel, but because hydrogen can cause porosity, its uses are limited. Similarly, nitrogen can sometimes be added to argon to help stabilize the austenite in austentitic stainless steels and increase penetration when welding copper. Due to porosity problems in ferritic steels and limited benefits, however, it is not a popular shielding gas additive.
Materials
Gas tungsten arc welding is most commonly used to weld stainless steel and nonferrous materials, such as aluminium and magnesium, but it can be applied to nearly all metals, with a notable exception being zinc and its alloys. Its applications involving carbon steels are limited not because of process restrictions, but because of the existence of more economical steel welding techniques, such as gas metal arc welding and shielded metal arc welding. Furthermore, GTAW can be performed in a variety of other-than-flat positions, depending on the skill of the welder and the materials being welded.
Aluminium and magnesium
Aluminum and magnesium are most often welded using alternating current, but the use of direct current is also possible, depending on the properties desired. Before welding, the work area should be cleaned and may be preheated to 175 to 200 °C (347 to 392 °F) for aluminium or to a maximum of 150 °C (302 °F) for thick magnesium workpieces to improve penetration and increase travel speed. AC current can provide a self-cleaning effect, removing the thin, refractory aluminium oxide ( sapphire) layer that forms on aluminium metal within minutes of exposure to air. This oxide layer must be removed for welding to occur. When alternating current is used, pure tungsten electrodes or zirconiated tungsten electrodes are preferred over thoriated electrodes, as the latter are more likely to "spit" electrode particles across the welding arc into the weld. Blunt electrode tips are preferred, and pure argon shielding gas should be employed for thin workpieces. Introducing helium allows for greater penetration in thicker workpieces, but can make arc starting difficult.
Direct current of either polarity, positive or negative, can be used to weld aluminum and magnesium as well. Direct current with a negatively charged electrode (DCEN) allows for high penetration. Argon is commonly used as a shielding gas for DCEN welding of aluminum. Shielding gases with high helium contents are often used for higher penetration in thicker materials. Thoriated electrodes are suitable for use in DCEN welding of aluminium. Direct current with a positively charged electrode (DCEP) is used primarily for shallow welds, especially those with a joint thickness of less than 1.6 mm (0.063 in). A thoriated tungsten electrode is commonly used, along with a pure argon shielding gas.
Steels
For GTAW of carbon and stainless steels, the selection of a filler material is important to prevent excessive porosity. Oxides on the filler material and workpieces must be removed before welding to prevent contamination, and immediately prior to welding, alcohol or acetone should be used to clean the surface. Preheating is generally not necessary for mild steels less than one inch thick, but low alloy steels may require preheating to slow the cooling process and prevent the formation of martensite in the heat-affected zone. Tool steels should also be preheated to prevent cracking in the heat-affected zone. Austenitic stainless steels do not require preheating, but martensitic and ferritic chromium stainless steels do. A DCEN power source is normally used, and thoriated electrodes, tapered to a sharp point, are recommended. Pure argon is used for thin workpieces, but helium can be introduced as thickness increases.
Dissimilar metals
Welding dissimilar metals often introduces new difficulties to GTAW welding, because most materials do not easily fuse to form a strong bond. However, welds of dissimilar materials have numerous applications in manufacturing, repair work, and the prevention of corrosion and oxidation. In some joints, a compatible filler metal is chosen to help form the bond, and this filler metal can be the same as one of the base materials (for example, using a stainless steel filler metal with stainless steel and carbon steel as base materials), or a different metal (such as the use of a nickel filler metal for joining steel and cast iron). Very different materials may be coated or "buttered" with a material compatible with a particular filler metal, and then welded. In addition, GTAW can be used in cladding or overlaying dissimilar materials.
When welding dissimilar metals, the joint must have an accurate fit, with proper gap dimensions and bevel angles. Care should be taken to avoid melting excessive base material. Pulsed current is particularly useful for these applications, as it helps limit the heat input. The filler metal should be added quickly, and a large weld pool should be avoided to prevent dilution of the base materials.
Welding Parameters
Regardless of the technology, efficiency or variability, these are the list of parameters that affect the quality and outcome of the weld. When these parameters are improperly configured or out of range for the equipment or materials, this can lead to a variety of problems.
Current
Too much current can lead to splatter and workpiece damage. In thin materials, it can lead to a widening of the material gap. Too little current can lead to sticking of the filler wire. This can also lead to heat damage and a much larger weld affected area, as high temperatures must be applied for much longer periods of time in order to deposit the same amount of filling materials. Current limiting helps to prevent splatter when the tungsten tip accidentally comes too close or in contact with the workpiece. Fixed current mode will vary the voltage in order to maintain a constant arc current.
Welding Voltage
This can be fixed or adjustable depending on the equipment. Some metals require a specific voltage range to be able to work
A high initial voltage allows for easy arc initiation and allows for a greater range of working tip distance. Too large a voltage, however, can lead to greater variability in workpiece quality (depending on the workpiece distance and a greater variation in power and heat delivered to the workarea.
Pulsed-current, frequency & waveform
In the pulsed-current mode, the welding current rapidly alternates between two levels. The higher current state is known as the pulse current, while the lower current level is called the background current. During the period of pulse current, the weld area is heated and fusion occurs. Upon dropping to the background current, the weld area is allowed to cool and solidify. Pulsed-current has a number of advantages, including lower heat input and consequently a reduction in distortion and warpage in thin workpieces. In addition, it allows for greater control of the weld pool, and can increase weld penetration, welding speed, and quality. A similar method, 'manual programmed' allows the operator to program a specific rate and magnitude of current variations, making it useful for specialized applications.
Gas Flow and Composition
Various welding or shielding gasses are available including mixtures of argon, carbon dioxide, oxygen, nitrogen, helium, hydrogen, nitric oxide, sulfur hexafluoride and dichlorodifluoromethane. The choice of gas is specific to the working metals and affects the production costs, electrode life, weld temperature, arc stability, welder control complexity, molten weld fluidity, weld speed, splatter. Most importantly it also affects the finished weld penetration depth and subsurface profile, surface profile, composition, porosity, corrosion resistance, strength, ductility, hardness and brittleness.
Welding techniques
Dabbing
The dabber variation is used to precisely place weld metal on thin edges. The automatic process replicates the motions of manual welding by feeding a cold filler wire into the weld area and dabbing (or oscillating) it into the welding arc. It can be used in conjunction with pulsed current, and is used to weld a variety of alloys, including titanium, nickel, and tool steels. Common applications include rebuilding seals in jet engines and building up saw blades, milling cutters, drill bits, and mower blades.
Vacuum welding
For industrial applications, superior results can be achieved by eliminating the effects of absorbed gasses at the weld. This can lead to reduced oxidation, reduced workpiece heat carried by convection and stronger materials due to dissolved or reacted gases such as oxygen, nitrogen and hydrogen.