Chapter 19
Social Psychology
By Boundless

Attribution theory explores how individuals attribute, or explain, the causes of their own and others' behaviors.
In psychological terms, attitude is our positive or negative evaluation of a person, an idea, or an object.
In psychology, "prejudice" refers to a usually (but not always) negative evaluation of another person or group based on their perceived characteristics.
Groups influence individual decision-making processes in a variety of ways, such as groupthink, groupshift, and deindividuation.
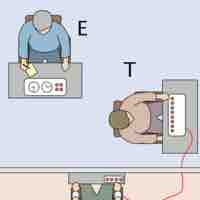
Obedience is a form of social influence that occurs when a person yields to explicit instructions or orders from an authority figure.
"Compliance" refers to a response, specifically a submission, made in reaction to an implicit or explicit request.
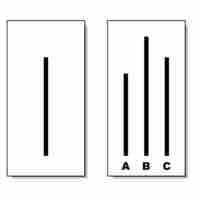
In psychology, conformity is defined as the act of matching attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors to group norms.
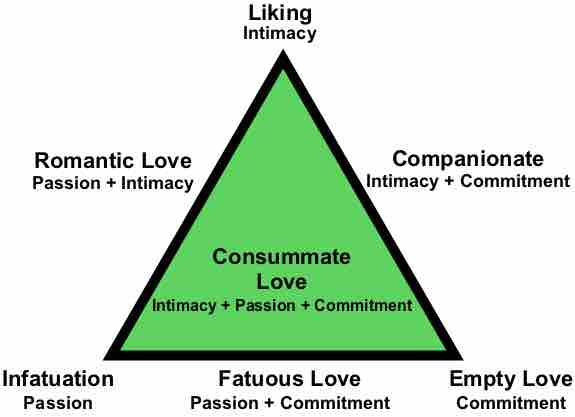
Numerous factors influence the multifaceted ways in which love and attraction are felt and expressed.
"Aggression" describes a range of behaviors that are intended to cause harm to others; aggression may be physical, mental, or verbal, and varies according to cultural factors.
Altruism, often referred to as selflessness, is the principle or practice of concern for the welfare of others.