Chapter 18
Treating Psychological Disorders
By Boundless
"Psychotherapy" is an umbrella term that describes the use of psychological methods to help a client overcome distressing thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
Biomedical therapies involve the use of medication and/or medical procedures to treat psychological disorders.
Cultural and gender norms significantly shape how mental illness as well as therapy and various other treatment methods are perceived.
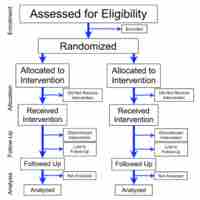
Several research methods can be used to evaluate which therapeutic approaches are the most beneficial under which circumstances.
The primary focus of psychodynamic therapy is to uncover the unconscious content of a client's psyche in order to alleviate psychic tension.
Behavior therapy is based on the idea that maladaptive behavior is learned, and thus adaptive behavior can also be learned.
Cognitive and cognitive-behavioral therapies address the interplay between dysfunctional emotions, maladaptive behaviors, and biased cognitions.
Humanistic therapy helps individuals access and understand their feelings, gain a sense of meaning in life, and reach self-actualization.
Body-oriented psychotherapies focus on the importance of working with the body in the treatment of mental health issues.
Group therapy is a form of psychotherapy in which one or more therapists treat a small group of clients together at the same time.
Expressive therapies use the creative arts as a form of therapy; systemic therapies emphasize the treatment of a system rather than an individual.
Biological therapies include four classes of psychiatric medications: antipsychotics, antidepressants, anti-cycling agents, and hypnoanxiolytics.
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a treatment method sometimes used for psychiatric disorders that do not respond to other forms of treatment.
Psychosurgery, a group of procedures aimed at disrupting neural pathways, has declined over the years due to better psychiatric medications.