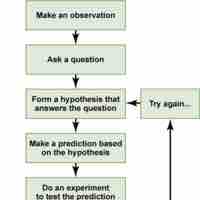
Chapter 2
Researching Psychology
By Boundless

Descriptive research refers to the measurement of behaviors and attributes through observation rather than through experimental testing.
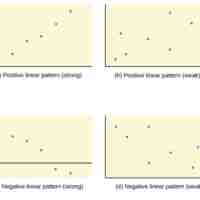
Correlational research can be used to see if two variables are related and to make predictions based on this relationship.
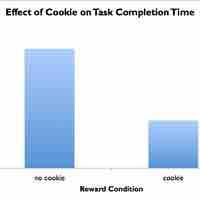
Experimental research tests a hypothesis and establishes causation by using independent and dependent variables in a controlled environment.

Observational studies allow researchers to document behavior in a natural setting and witness events that could not be produced in a lab.
A case study is a method of obtaining in-depth information on a person, group or phenomenon to provide descriptions of specific or rare cases.

Surveys are a low-cost option for gathering a large amount of data, but they are also susceptible to reporting bias.
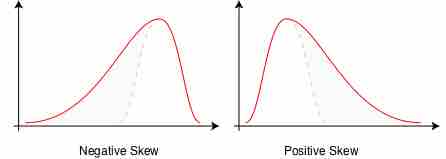
The goal of statistics is to summarize data in a manner that allows for easy descriptions or inferences to be made.
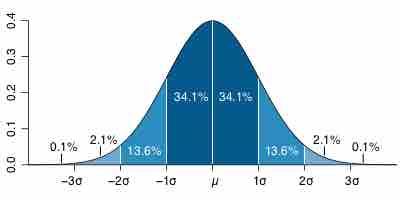
Statistical inference makes claims about a population of individuals or things, using data drawn from a smaller subset of the population known as a sample.

In order to be valid, data must be both accurate and precise.

Ethical guidelines in psychological research serve to minimize harm to participants' mental and physical well-being.
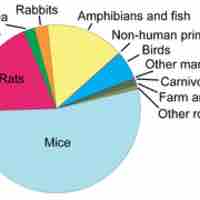
Animal research raises the controversial question of whether it is ethical to harm animals with the aim of improving human lives.

Research studies with small sample sizes, high variability, and sampling bias are usually not representative of the general population.

When interpreting data, a researcher must avoid cognitive bias and be aware of the use of heuristics to avoid drawing incorrect conclusions.