Chapter 12
The Presidency
By Boundless
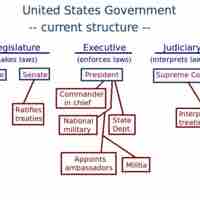
The expressed powers of the President are those expressed in the Constitution of the United States.

The delegated powers are a list of items found in the U.S. Constitution that set forth the authoritative capacity of Congress.
Inherent powers are assumed powers of the president not specifically listed in the Constitution.
The president of the United States, as head of the executive branch, has the authority to declare a federal state of emergency.

In the United States, an executive order is an order or directive issued by the head of the executive branch at some level of government.
Executive privilege is the power claimed by the President to resist subpoenas and other interventions by other branches of government.

Presidential power has shifted over time, which has resulted in claims that the modern presidency has become too powerful.

The Executive Office of the President is comprised of a Chief of Staff, Counsel, Press Secretary, and other members assisting the President of the United States.

The Cabinet of the United States is composed of the most senior appointed officers of the executive branch of the federal government.
Constitutionally, the Vice President is indirectly elected by the people through the Electoral College to a four-year term of office.

The First Lady of the United States is the hostess of the White House, traditionally filled by the wife of the president.

Chief Executive is a term commonly used to refer to Presidential powers given by the Constitution.

A commander-in-chief is the person exercising supreme command authority of a nation's military forces; in the US, this person is the president.

The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States.
The appointment power of the President allows him or her to appoint and receive ambassadors around the world.

As chief legislator, the president may suggest, request, and insist that Congress enact laws he believes are needed.

The president is largely responsible for dictating the legislative agenda of his political party.