Chapter 11
Congress
By Boundless

The United States House of Representatives is one of the two houses of the United States Congress.

The Senate is composed of two senators from each state who are granted exclusive powers to confirm appointments and place holds on laws.
The US Congress is composed of the House of Representatives and the Senate, which differ in representation, term length, power, and prestige.

The House and Senate are equal partners in the legislative process; legislation cannot be enacted without the consent of both chambers.

A compromise plan was adopted where representatives were chosen by the population and two senators were chosen by state governments.
A major role for members of Congress is providing services to constituents.

The United States Congress has oversight of the Executive Branch and other U.S. federal agencies.

The Library of Congress provides public information and educates the public about legislation among other general information.

Both the Senate and the House have a conflict-resolution procedure before a bill is passed as a piece of legislation.

Party leaders and whips of the U.S. House of Representatives are elected by their respective parties in a closed-door caucus.
The party leadership of the Senate refers to the officials elected by the Senate Democratic Caucus and the Senate Republican Conference.

Bicameralism is the practice of having two legislative or parliamentary chambers.

An agenda is a list of meeting activities in the order in which they are to be taken up in the legislature.
A congressional committee is a legislative sub-organization in Congress that handles a specific duty.

Congressional staff are employees of the United States Congress or individual members of Congress.

A caucus is a meeting of supporters or members of a political party or movement.
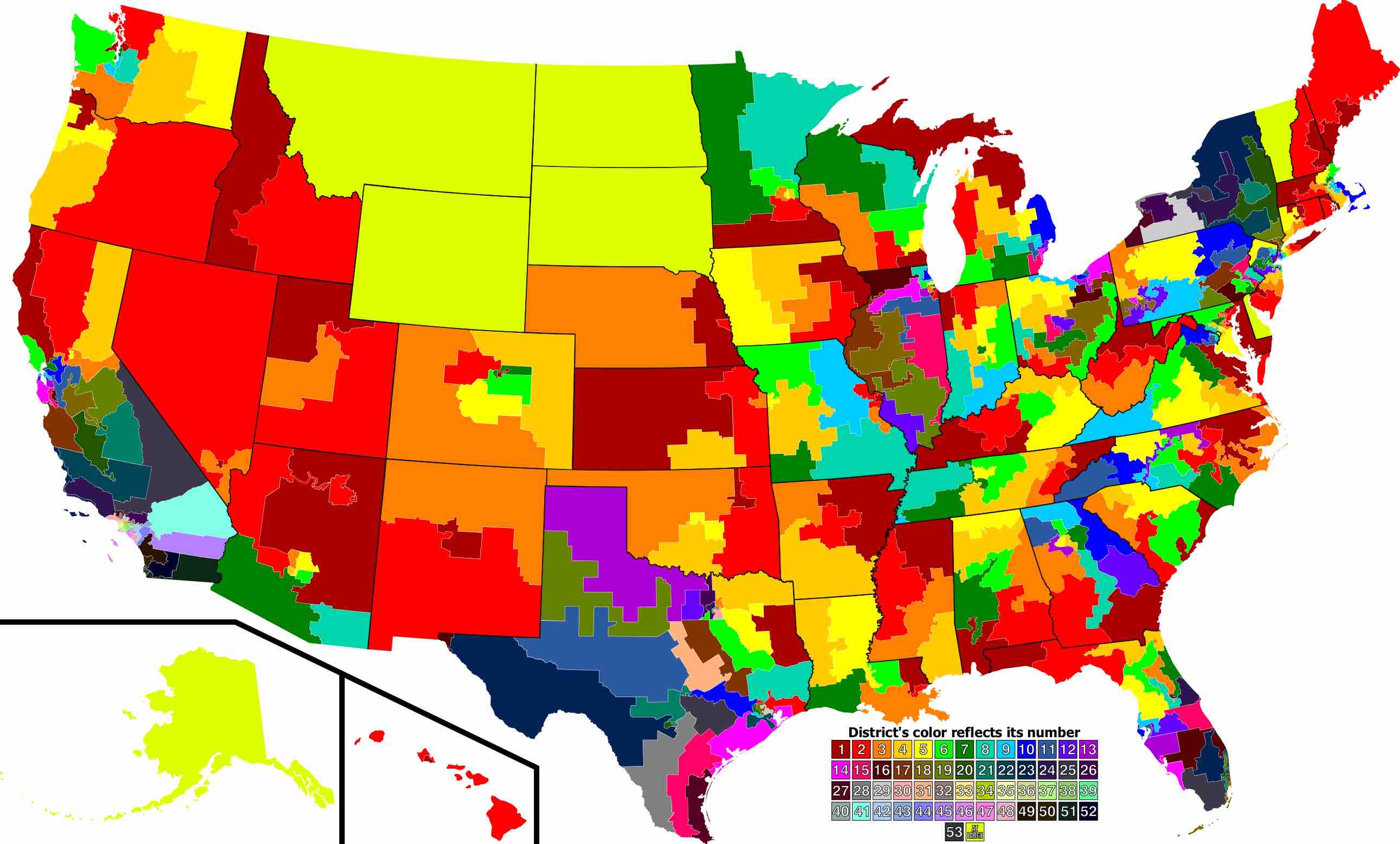
The quantity and boundaries of the 435 districts are determined after each census gauges the population shifts in each state.

A bill is introduced by a member of the legislature, read through, debated, and then passed to become a law.
Deliberation is a process of thoughtfully weighing options, usually prior to voting, emphasizing the use of logic and reason.

Debate is contention in argument and a method of interactive representational argument, and often occurs in Congress.

A conference committee is a committee of Congress appointed by the House and Senate to resolve disagreements on a particular bill.

The Ineligibility Clause prevents the President from being a member of Congress and cannot directly introduce legislative proposals.
Each year, the President of the United States submits his budget request to Congress.

The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) performs key tasks in preparing the presidential budget request that is submitted to Congress.
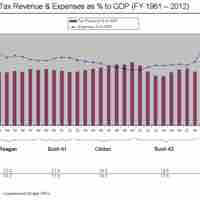
Budget proposals during election years are usually politicized to gain votes and increase constituency support.

The budget resolution serves as a blueprint for the actual appropriations process and provides Congress with some control over the process.

Authorizations and appropriations functions are separate in principle, but this separation is often imperfect in reality.

Congressional oversight is the review, monitoring, and supervision of federal agencies, programs, activities, and policy implementation.

Oversight of various federal agencies is one of Congress' enumerated powers.

Advice and consent is a power of the Senate to be consulted on and approve treaties signed by the president.

Impeachment is an expressed power that allows for formal charges against a civil officer of government for crimes committed in office.

Senate confirmation is required for certain presidential appointments stated under the Constitution.
Sections 2 and 3 of Article 1 of the Constitution describe the qualifications for membership in the House of Representatives and the Senate.

The incumbent is the existing holder of a political office who normally has a structural advantage over challengers during an election.
Members of the Senate may serve unlimited six-year terms and members of the House may serve unlimited two-year terms.
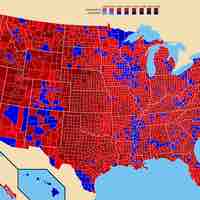
Congressional elections determine the structure and makeup of the House of Representatives and Senate.

Political parties serve to coordinate, assist and provide resources for members of congress and political candidates.
Each member of Congress has a responsibility to their constituents because they decide if a congressional member will be re-elected.

Interest groups attempt to influence Members of Congress in a variety of ways, such as lobbying and financing campaigns using PACs.

Though uncommon, a member of Congress switch parties for either ideological or pragmatic reasons.