Economic policy refers to the actions that governments take in the economic field. It covers the systems for setting interest rates and government budget as well as the labor market, national ownership, and many other areas of government interventions into the economy.
Policy is generally directed to achieve four major goals: stabilizing markets, promoting economic prosperity, ensuring business development, and promoting employment. Sometimes other objectives, like military spending or nationalization, are important.
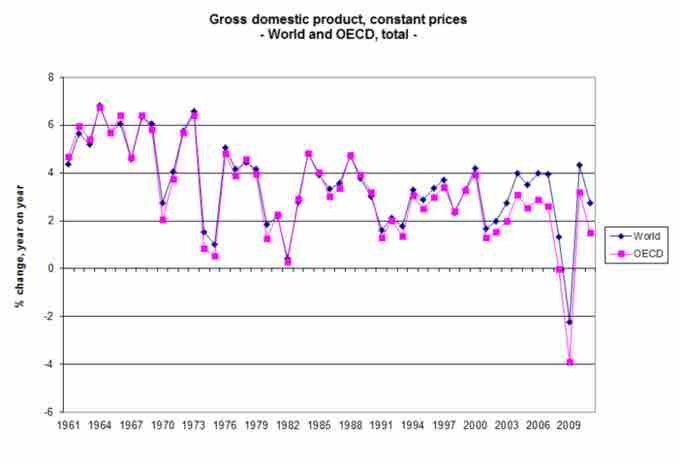
Economic Growth
One of the major goals of economic policy is to promote economic growth. How growth is measured though is another question. The above image Rate of change of Gross domestic product, world and OECD, since 1961, is one representation of economic growth.
To achieve these goals, governments use policy tools which are under the control of the government. These generally include the interest rate and money supply, tax and government spending, tariffs, exchange rates, labor market regulations, and many other aspects of government.
Selecting Tools and Goals
Government and central banks are limited in the number of goals they can achieve in the short term. For instance, there may be pressure on the government to reduce inflation, reduce unemployment, and reduce interest rates while maintaining currency stability. If all of these are selected as goals for the short term, then policy is likely to be incoherent, because a normal consequence of reducing inflation and maintaining currency stability is increasing unemployment and increasing interest rates.
For much of the 20th century, governments adopted discretionary policies such as demand management that were designed to correct the business cycle. These typically used fiscal and monetary policy to adjust inflation, output and unemployment.
However, following the stagflation of the 1970s, policymakers began to be attracted to policy rules.
A discretionary policy is supported because it allows policymakers to respond quickly to events. However, discretionary policy can be subject to dynamic inconsistency: a government may say it intends to raise interest rates indefinitely to bring inflation under control, but then relax its stance later. This makes policy non-credible and ultimately ineffective.
A rule-based policy can be more credible, because it is more transparent and easier to anticipate. Examples of rule-based policies are fixed exchange rates, interest rate rules, the stability and growth pact and the Golden Rule. Some policy rules can be imposed by external bodies, for instance, the Exchange Rate Mechanism for currency.
A compromise between strict discretionary and strict rule-based policy is to grant discretionary power to an independent body. For instance, the Federal Reserve Bank, European Central Bank, Bank of England and Reserve Bank of Australia all set interest rates without government interference, but do not adopt rules.
Another type of non-discretionary policy is a set of policies which are imposed by an international body. This can occur (for example) as a result of intervention by the International Monetary Fund.