Chapter 19
Lymphatic System
By Boundless
The lymphatic structure is based on that of blood vessels.
The lymphatic system comprises a network of conduits called lymphatic vessels that carry lymph unidirectionally towards the heart.
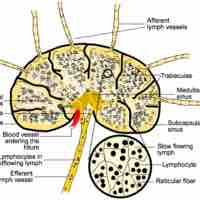
Lymph circulates to the lymph node via afferent lymphatic vessels and drains into the lymph node in the subcapsular sinus.
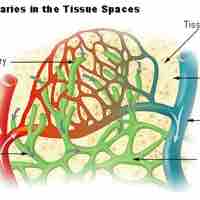
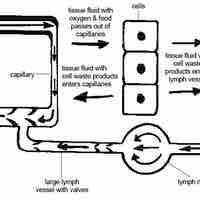
Lymph capillaries are tiny, thin-walled vessels, closed at one end and located in the spaces between cells throughout the body.
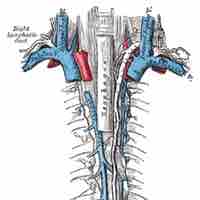
The lymph trunks drain into the lymph ducts, which in turn return lymph to the blood by emptying into the respective subclavian veins.
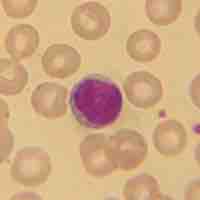
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell in the vertebrate immune system.
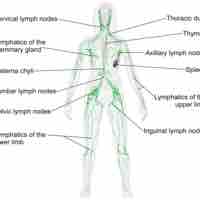
Lymphoid tissue consists of many organs that play a role in the production and maturation of lymphocytes in the immune response.
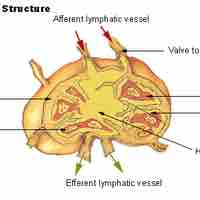
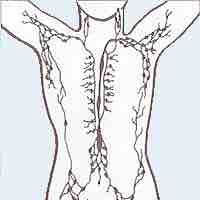
Lymph nodes are small oval-shaped balls of lymphatic tissue distributed widely throughout the body and linked by lymphatic vessels.
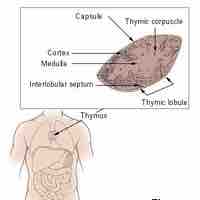
The thymus is a specialized organ that "educates" T cells or T lymphocytes, which are part of the adaptive immune system.
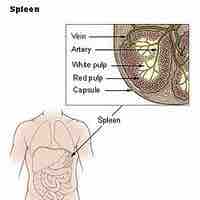
The spleen, similar to a large lymph node, acts primarily as a blood filter in the mononuclear phagocyte system of the immune system.
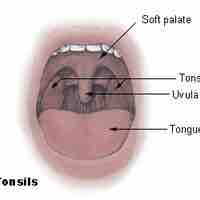
The tonsils are one of the immune system's first lines of defense against ingested or inhaled foreign pathogens.