Glucagon and insulin are peptide hormones secreted by the pancreas that play a key role in maintaining a stable blood glucose level. The blood glucose level is carefully monitored by cells within the pancreas that respond by secreting key hormones.
Glucagon
Glucagon is produced by alpha cells in the pancreas and elevates the concentration of glucose in the blood by promoting gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis. Glucose is stored in the liver in the form of the polysaccharide glycogen, which is a glucan.
Liver cells have glucagon receptors and when glucagon binds to the liver cells they convert glycogen into individual glucose molecules and release them into the bloodstream—this process is known as glycogenolysis. As these stores become depleted, glucagon then encourages the liver and kidney to synthesize additional glucose by gluconeogenesis. Glucagon also turns off glycolysis in the liver, causing glycolytic intermediates to be shuttled to gluconeogenesis that can induce lipolysis to produce glucose from fat.
Insulin
Insulin is produced by beta cells in the pancreas and acts to oppose the functions of glucagon. It's main role is to promote the conversion of circulating glucose into glycogen via glycogenesis in the liver and muscle cells.
Insulin also inhibits gluconeogenesis and promotes the storage of glucose in fat through lipid synthesis and also by inhibiting lipolysis.
In Disease
When control of insulin levels fails, diabetes mellitus can result. As a consequence, insulin is used medically to treat some forms of diabetes mellitus.
Patients with type 1 diabetes depend on external insulin (most commonly injected subcutaneously) for their survival because the hormone is no longer produced internally.
Patients with type 2 diabetes are often insulin resistant and, because of such resistance, they may suffer from a relative insulin deficiency. Some patients with type 2 diabetes may eventually require insulin if other medications fail to control blood glucose levels adequately.
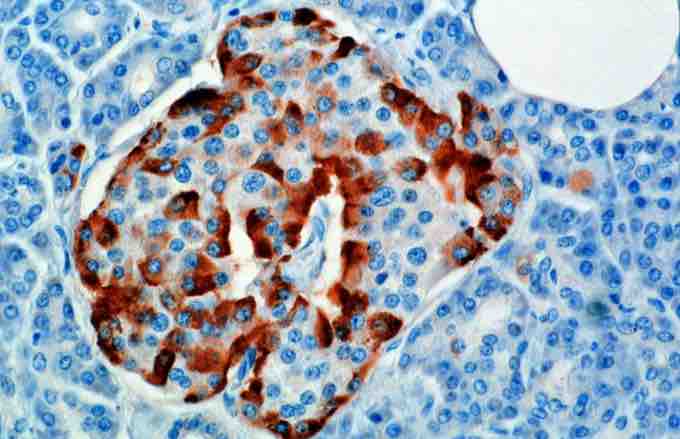
Glucagon staining
This is an image from a microscope stained for glucagon.