Enterobacteria phage λ (lambda phage, coliphage λ) is a bacterial virus, or bacteriophage, that infects the bacterial species Escherichia coli. This virus is temperate and may reside within the genome of its host through lysogeny.
Lambda phage consists of a virus particle including a head (also known as a capsid), tail and tail fibers. The head contains the phage's double-stranded circular DNA genome. The phage particle recognizes and binds to its host, E. coli, causing DNA in the head of the phage to be ejected through the tail into the cytoplasm of the bacterial cell. Usually, a "lytic cycle" ensues, where the lambda DNA is replicated many times and the genes for head, tail and lysis proteins are expressed. This leads to assembly of multiple new phage particles within the cell and subsequent cell lysis, releasing the cell contents, including virions that have been assembled, into the environment. However, under certain conditions, the phage DNA may integrate itself into the host cell chromosome in the lysogenic pathway. In this state, the λ DNA is called a prophage and stays resident within the host's genome without apparent harm to the host. The host can be termed a lysogen when a prophage is present.
Lambda phage has been of major importance in the study of specialized transduction.
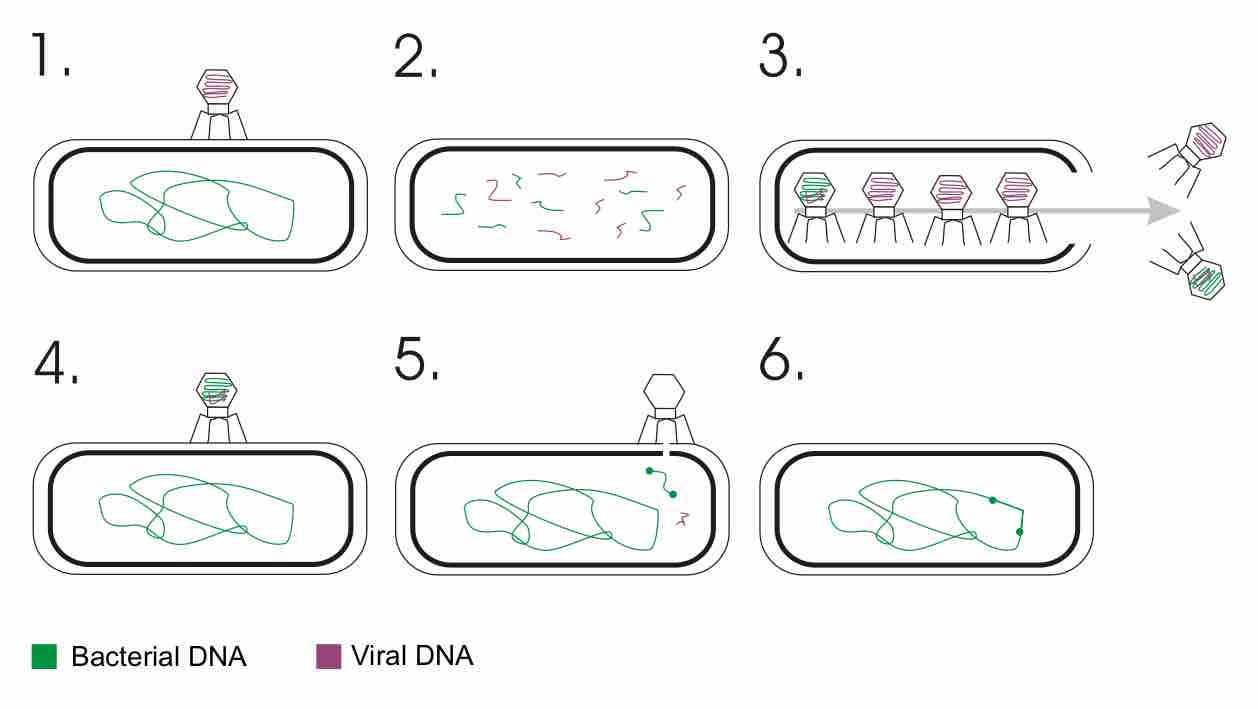
Specialized transduction is the process by which a restricted set of bacterial genes are transferred to another bacterium . The genes that get transferred (donor genes) depend on where the phage genome is located on the chromosome. Specialized transduction occurs when the prophage excises imprecisely from the chromosome so that bacterial genes lying adjacent to the prophage are included in the excised DNA. The excised DNA is then packaged into a new virus particle, which delivers the DNA to a new bacterium where the donor genes can be inserted into the recipient chromosome or remain in the cytoplasm, depending on the nature of the bacteriophage. When the partially encapsulated phage material infects another cell and becomes a "prophage" (is covalently bonded into the infected cell's chromosome), the partially coded prophage DNA is called a "heterogenote. "
Transduction
Transduction is the process by which DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by a virus.It also refers to the process whereby foreign DNA is introduced into another cell via a viral vector.