Immunoblot procedures like protein blotting, or Western blotting, allow individuals to detect specific solubilized proteins from extracts made from cells or tissues, before or after any purification steps.
Immunoblotting Procedures
This analytic technique proceeds in the following steps. Proteins are generally separated by size using sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. After this, they are transferred to a synthetic membrane via dry, semi-dry, or wet blotting methods. In the electric field generated by a power supply, the proteins coated with negatively charged SDS migrate toward the positive electrode. As the proteins migrate out of the gel, they are captured on a membrane. Protein binding to the membrane is an irreversible mechanism. Membranes can be of the nitrocellulose, polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF), or nylon variety. The membrane can then be blocked with serum albumin or milk solution to prevent non-specific antibody binding. This is followed by probing with antibodies specific to the protein being studied on the membrane, a method that is similar to immunohistochemistry, but without a need for fixation. This technique exploits the specificity inherent in antigen-antibody recognition. Detection is typically performed using chromogen or peroxide-linked secondary antibodies to catalyze a chromogenic or chemiluminescent reaction.
Applications of Immunoblotting
Western blotting is a routine molecular biology method that can be used to semi-quantitatively compare protein levels between extracts. The size separation, prior to blotting, allows the protein molecular weight to be gauged, as compared with known molecular weight markers . Immunoblots are most often used in research settings and are usually performed to confirm results from ELISA or other immunoassays. In clinical diagnostic settings, immunoelectrophoresis is applied, which involves the electrophoresis of serum or urine followed by immunodiffusion. The size and position of precipitation bands provides the same type of information about antibody amount as the double immunodiffusion method.
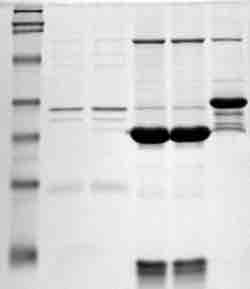
Immunoblot
proteins separated by molecular weight and represented by a dark band on a blot.