Stages of Disease
After an infectious agent invades a host (patient), it undergoes a series of phases (stages) that will eventually lead to its multiplication and release from the host.
STAGE 1: INCUBATION PERIOD
This refers to the time elapsed between exposure to a pathogenic organism, and from when symptoms and signs are first apparent. It may be as short as minutes to as long as thirty years in the case of variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease. While the term latency period is used as synonymous, a distinction is sometimes made between incubation period, the period between infection and clinical onset of the disease, and latent period, the time from infection to infectiousness. Whichever is shorter depends on the disease.
A person may be a carrier of a disease, such as Streptococcus in the throat, without exhibiting any symptoms. Depending on the disease, the person may or may not be contagious during the incubation period. During clinical latency, an infection is subclinical. With respect to viral infections, in clinical latency the virus is actively replicating. This is in contrast to viral latency, a form of dormancy in which the virus does not replicate.
STAGE 2: PRODROMAL PERIOD
In this phase, the numbers of the infectious agents start increasing and the immune system starts reacting to them. It is characterized by early symptoms that might indicate the start of a disease before specific symptoms occur. Prodromes may be non-specific symptoms or, in a few instances, may clearly indicate a particular disease. For example fever, malaise, headache and lack of appetite frequently occur in the prodrome of many infective disorders. It also refers to the initial in vivo round of viral replication.
STAGE 3: ACUTE PERIOD
This stage is characterized by active replication or multiplication of the pathogen and its numbers peak exponentially, quite often in a very short period of time. Symptoms are very pronounced, both specific to the organ affected as well as in general due to the strong reaction of the immune system .
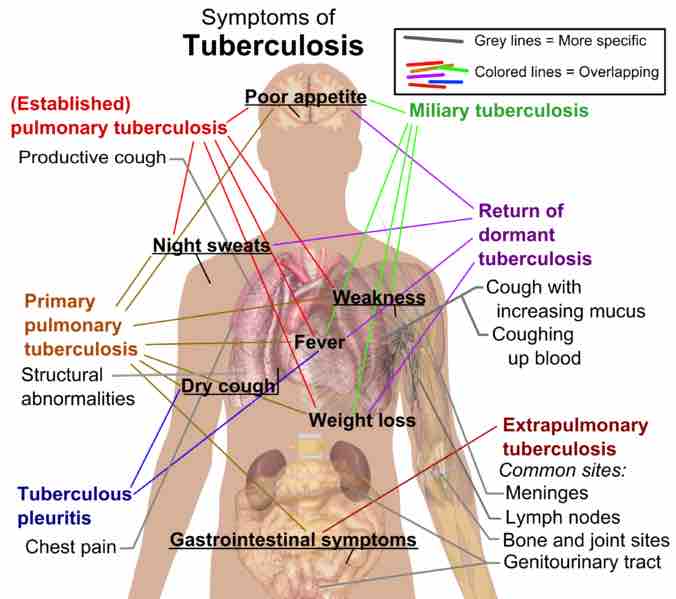
Symptoms of tuberculosis
Some of the symptoms are very specific for the disease while others are more general and can be caused by other pathogens.
Viral infections present with systemic symptoms. This means they involve many different parts of the body or more than one body system at the same time; i.e. a runny nose, sinus congestion, cough, body aches, etc. They can be local at times as in viral conjunctivitis or "pink eye" and herpes. Only a few viral infections are painful, like herpes. The pain of viral infections is often described as itchy or burning.
The classic symptoms of a bacterial infection are localized redness, heat, swelling and pain. One of the hallmarks of a bacterial infection is local pain, pain that is in a specific part of the body. For example, if a cut occurs and is infected with bacteria, pain occurs at the site of the infection. Bacterial throat pain is often characterized by more pain on one side of the throat. An ear infection is more likely to be diagnosed as bacterial if the pain occurs in only one ear.
After the pathogen reaches its peak in newly-produced cells or particles (for viruses), the numbers begin to fall sharply. Symptoms are still present but they are not as strong as in the acute illness phase.
STAGE 4: CONVALESCENCE PERIOD
The patient recovers gradually and returns to normal, but may continue to be a source of infection even if feeling better. In this sense, "recovery" can be considered a synonymous term.