Chapter 7
Market Failure: Externalities
By Boundless

Market failure occurs when the price mechanism fails to account for all of the costs and benefits necessary to provide and consume a good.
Market failure occurs due to inefficiency in the allocation of goods and services.
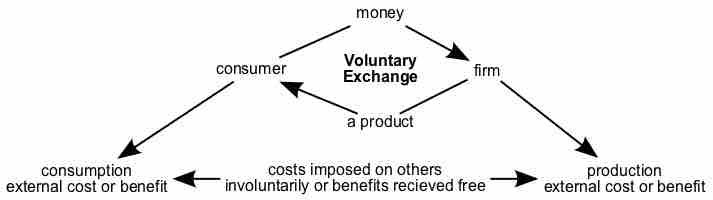
An externality is a cost or benefit that affects an otherwise uninvolved party who did not choose to be subject to the cost or benefit.
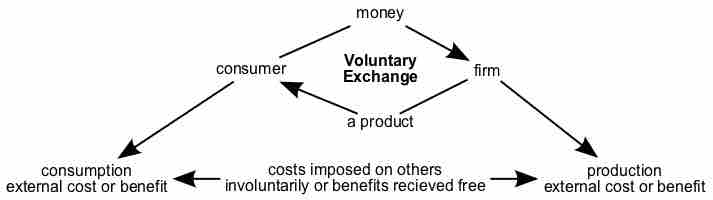
Economic efficiency is the use resources to maximize the production of goods; externalities are imperfections that limit efficiency.

Negative externalities are costs caused by an activity that affect an otherwise uninvolved party who did not choose to incur that cost.
Positive externalities are benefits caused by activities that affect an otherwise uninvolved party who did not choose to incur that benefit.

The government can respond to externalities through command-and-control policies or market-based policies.
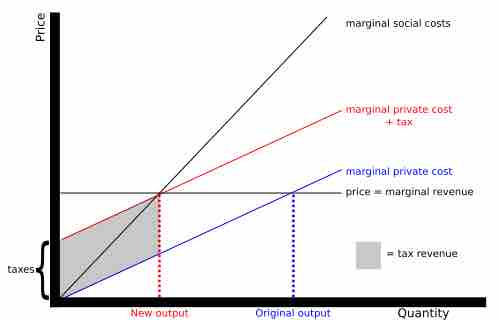
Corrective taxes incentivize economic actors to reduce the production of goods or services generating negative externalities.

Tradable permits are a market-based approach allowing the government to limit negative externalities produced by a group of firms.
