Chapter 6
Elasticity and its Implications
By Boundless
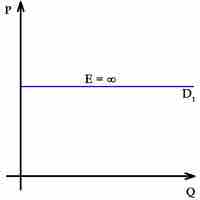
The price elasticity of demand (PED) measures the change in demand for a good in response to a change in price.

The price elasticity of demand (PED) is calculated by dividing the percentage change in quantity demanded by the percentage change in price.
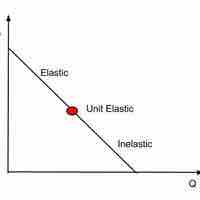
The price elasticity of demand (PED) explains how much changes in price affect changes in quantity demanded.
A good's price elasticity of demand is largely determined by the availability of substitute goods.
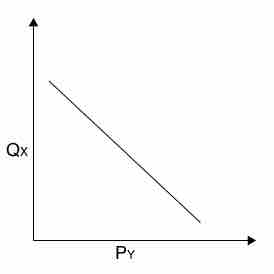
The cross-price elasticity of demand measures the change in demand for one good in response to a change in price of another good.
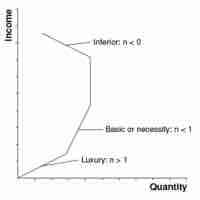
The income elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of the demand for a good or service to a change in income.
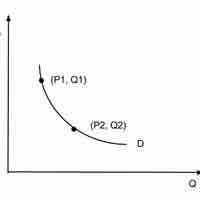
The basic elasticity formula has shortcomings which can be minimized by using the midpoint method or calculating the point elasticity.
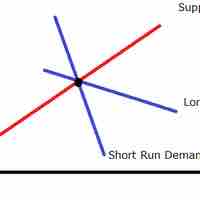
The price elasticity of supply is the measure of the responsiveness in quantity supplied to a change in price for a specific good.
The price elasticity of supply is the measure of the responsiveness of the quantity supplied of a particular good to a change in price.
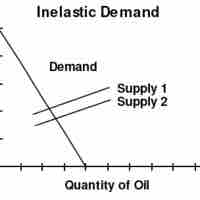
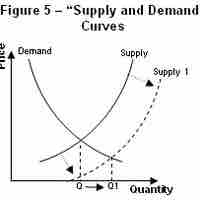
In economics, elasticity refers to how the supply and demand of a product changes in relation to a change in the price.