Chapter 17
Psychological Disorders
By Boundless

Ideas of "normal" and "abnormal" are largely shaped by social standards and can have profound social ramifications.
The DSM guides the diagnoses of psychological disorders; it has been revised many times and is both praised and criticized.
Focusing on the prevention of mental illness, rather than only on treating existing mental illness, has numerous health and economic benefits.
Intellectual disabilities are neurodevelopmental disorders characterized by significantly impaired intellectual and adaptive functioning.

Autism spectrum disorder is a neuro-developmental disorder characterized by impaired social communication and restricted or repetitive behaviors.
ADHD is a developmental disorder characterized by inattention, distractibility, impulsivity, and hyperactivity.
Specific learning disorder includes difficulties in general academic skills, specifically in the areas of reading, mathematics, or written expression.

Schizophrenia is a disorder of psychosis in which the person’s thoughts, perceptions, and behaviors are out of contact with reality.
The spectrum of psychotic disorders includes schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, delusional disorder, and catatonia.
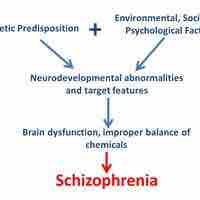
While genetics, environment, neurobiology, and psychosocial stress contribute to schizophrenia, the exact cause of the disease is unknown.
Anxiety disorders involve extreme reactions to anxiety-inducing situations, including excessive worry, uneasiness, apprehension, or fear.
Generalized anxiety disorder is characterized by chronic anxiety that is excessive, uncontrollable, and often irrational.
A panic attack is a sudden period of intense anxiety; if these attacks occur often, they may indicate a panic disorder.
Social anxiety disorder is marked by intense fear and avoidance of social situations in which one might be negatively judged.
Specific phobias involve excessive, distressing, and persistent fear or anxiety about a specific object or situation.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder is characterized by intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors aimed at reducing anxiety.
Other obsessive-compulsive disorders include body dysmorphic disorder, hoarding disorder, trichotillomania, and excoriation disorder.
PTSD is a disorder that develops after exposure to a traumatic event that involves actual or threatened death or serious injury.
Reactive attachment disorder is a childhood condition characterized by markedly disturbed ways of relating socially to others.
The 10 personality disorders mentioned in the DSM-5 involve pervasive and enduring personality styles that differ from cultural expectations and cause distress and/or conflict with others.
Cluster A personality disorders have a likely genetic component and are characterized by personality styles that are odd or eccentric.
Cluster B personality disorders are characterized by personality styles that are impulsive, dramatic, highly emotional, and erratic.
Cluster C personality disorders are characterized by personality styles that are nervous and fearful.


