Introduction
Article One of the United States Constitution describes the powers of Congress, which is the legislative branch of the federal government. More importantly, it establishes limits on the powers of Congress as well as the states. Section Eight gives Congress certain broad enumerated powers. Among these are the power to lay and collect taxes and provide for the common defense and general welfare of the United States; to borrow money on the credit of the United States; and to regulate interstate, foreign, and Indian commerce. As stated in the Constitution, "The Congress shall have power to lay and collect taxes, duties, imposts and excises, to pay the debts and provide for the common defense and general welfare of the United States; but all duties, imposts, and excises shall be uniform throughout the United States. "
United States Armed Forces
The U.S. Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. They consist of the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, Air Force, and Coast Guard. The United States has a strong tradition of civilian control of the military. The President is the overall head of the military. The President helps form military policy with the United States Department of Defense. This department is a federal executive department, acting as the principal organ by which military policy is carried out. The United States has the largest defense budget in the world . As of 2011, the United States spends about 160 billion to fund Overseas Contingency Operations. Combined, the United States constitutes roughly 43 percent of the world's military expenditures.
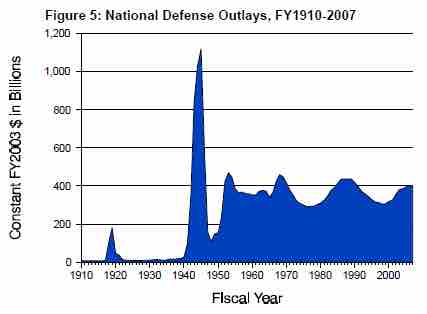
U.S. Defense Spending (1910 - 2007)
The United States has the largest defense budget in the world.
The U.S. military is one of the largest militaries in terms of the number of personnel. It draws its manpower from a large pool of paid volunteers. However, conscription has been used in the past in various times of both war and peace. It has not been used since 1972 . Historically, defense-related spending in the United States is at its highest inflation-adjusted level since World War II. As of September 2010, 1,430,895 people were on active duty in the military, with an additional 848,000 people in the seven reserve components. The United States military is the second largest in the world, after the People's Liberation Army of China. The U.S. has troops deployed around the globe.
United States National Security Council
The White House National Security Council is the principal forum used by the President of the United States for considering national security and foreign policy matters with his senior national security advisors and Cabinet officials. The Security Council is part of the Executive Office of the President of the United States . Since its inception under Harry S. Truman, the function of the Council has been to advise and assist the President on national security and foreign policies. The Council also serves as the president's principal arm for coordinating these policies among various government agencies. The U.S. Council also has counterparts in the national security councils of many other nations.
The National Security Council is chaired by the President. Its regular attendees (both statutory and non-statutory) are the Vice President (statutory), the Secretary of State (statutory), the Secretary of Treasury (non-statutory), the Secretary of Defense (statutory), and the National Security Advisor (non-statutory).