Chapter 27
Human Development and Pregnancy
By Boundless
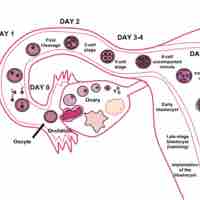
Fertilization occurs when a sperm and an egg have fused together to form a zygote, which begins to divide as it moves towards the uterus.
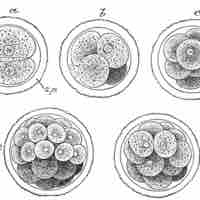
The process of cleavage is the step of embryogenesis where the zygote divides to produce a cluster of cells known as the morula.
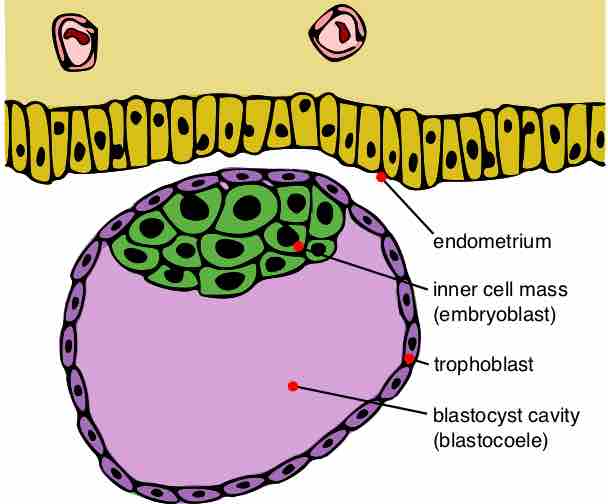
The blastocyst forms early in embryonic development and has two layers that form the embryo and placenta.
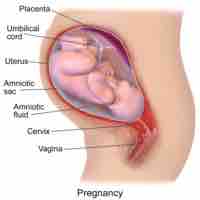
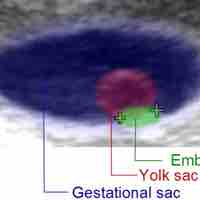
Implantation is the very early stage of pregnancy at which the embryo adheres to the wall of the uterus and begins to form the placenta.
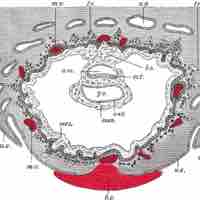
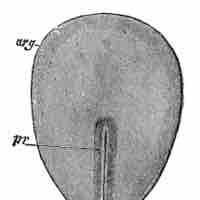
Trophoblasts are the outer layer of cells that provide nutrients to the embryo and form part of the placenta.
The floor of the amniotic cavity is formed by the embryonic disc.
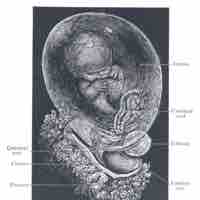
The amnion contains the fluid that cushions and protects the fetus.
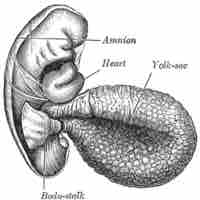
The yolk sac is vascularized and contributes nutrients to the embryo.
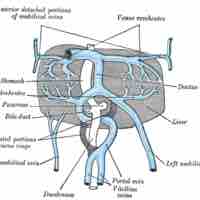
The sinusoids are capillaries that develop after implantation to allow the exchange of gas and nutrients with the mother.
The extra-embryonic coelom is a cavity that contains the chorion. It is located between Heuser's membrane and the trophoblast.
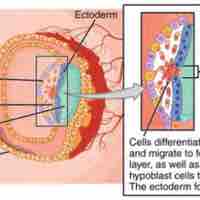
During gastrulation, the embryo develops three germ layers (endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm) that differentiate into distinct tissues.
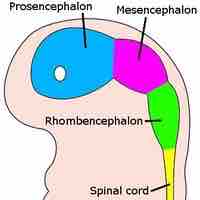
Following gastrulation, the neurulation process develops the neural tube in the ectoderm, above the notochord of the mesoderm.
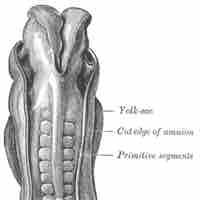
Somites develop from the paraxial mesoderm and participate in the facilitation of multiple developmental processes.
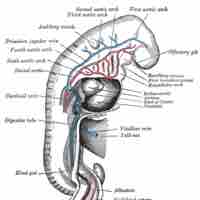
The circulatory system develops initially via vasculogenesis, with the arterial and venous systems developing from distinct embryonic areas.
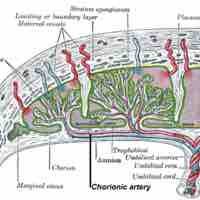
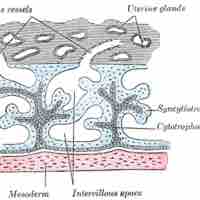
In the placenta, chorionic villi develop to maximize surface-area contact with the maternal blood for nutrient and gas exchange.
Prodromal labor, which includes the latent phase of labor, marks the initial stages of parturition.
Vaginal delivery childbirth has three distinct phases: dilation of the cervix, delivery of the infant, and delivery of the placenta.
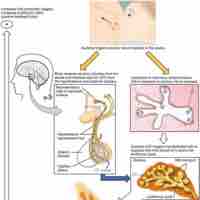
Post birth, an infant's physiology must adapt to breathing independently, changes in blood flow and energy access, and a cold environment.
At the end of the 10th week of gestation, the fetal period begins.
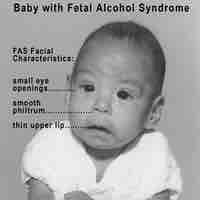
A teratogen is a compound that permanently deforms the function or structure of a developing embryo or fetus.
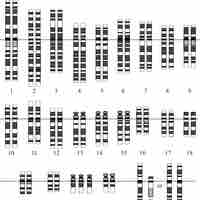
Prenatal diagnosis is a way to screen a fetus for diseases and/or conditions that may increase its morbidity and/or mortality.

Women undergo many physical changes during pregnancy due to hormonal fluctuations and the need to accommodate a growing fetus.
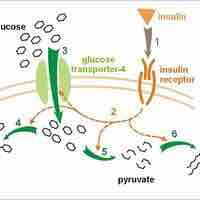
Protein and carbohydrate metabolism are affected during pregnancy and maternal insulin resistance can lead to gestational diabetes.

Maternal physiological changes in pregnancy are entirely normal and serve as adaptations to better accommodate embryonic/fetal development.

In the absence of complications, pregnant women should continue aerobic and strength training exercise for the duration of gestation.