A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used not only in the natural sciences (such as physics, biology, earth science, meteorology) and engineering disciplines (e.g. computer science, artificial intelligence), but also in the social sciences (such as economics, psychology, sociology and political science); physicists, engineers, statisticians, operations research analysts and economists use mathematical models most extensively. A model may help to explain a system and to study the effects of different components, and to make predictions about behavior.
Mathematical models can take many forms, including but not limited to dynamical systems, statistical models, differential equations, or game theoretic models. These and other types of models can overlap, with a given model involving a variety of abstract structures. In general, mathematical models may include logical models, as far as logic is taken as a part of mathematics. In many cases, the quality of a scientific field depends on how well the mathematical models developed on the theoretical side agree with results of repeatable experiments. Lack of agreement between theoretical mathematical models and experimental measurements often leads to important advances as better theories are developed.
For example, a simple model of population growth is the Malthusian growth model. This is essentially exponential growth based on a constant rate of compound interest:
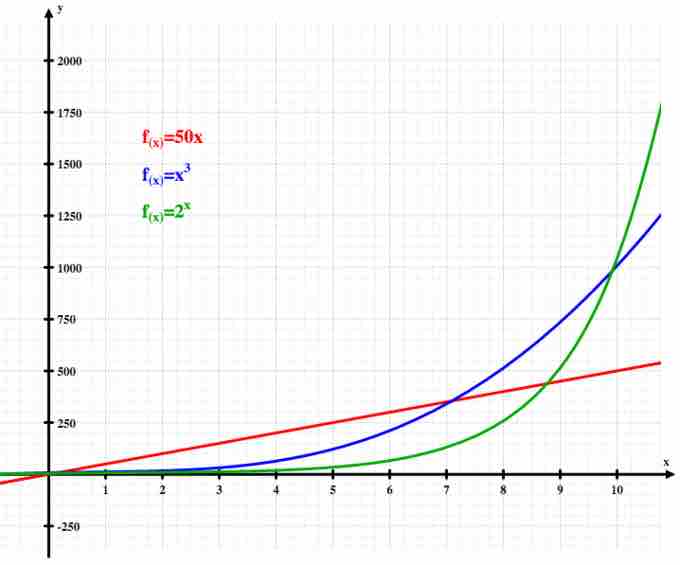
Exponential Growth
The graph illustrates how exponential growth (green) surpasses both linear (red) and cubic (blue) growth.
A slightly more realistic and largely used population growth model is the logistic function that may be defined by the formula:
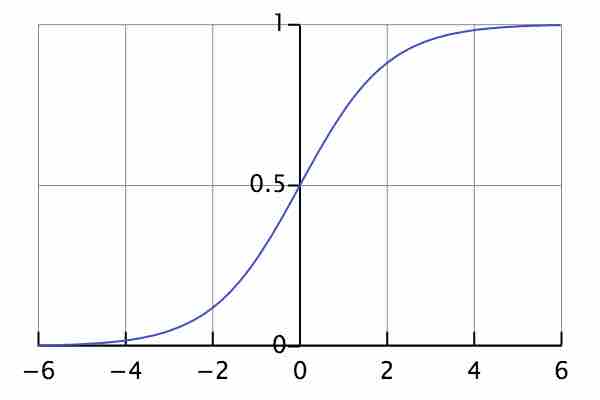
Logistic Curve
The standard logistic curve.
Another example is a model of a particle in a potential-field. In this model we consider a particle as being a point of mass which describes a trajectory in space which is modeled by a function giving its coordinates in space as a function of time. The potential field is given by a function
Even many everyday activities carried out without a thought are uses of mathematical models. A geographical map projection of a region of the earth onto a small, plane surface is a model which can be used for many purposes such as planning travel.