Calculus has widely used in physics and engineering. In this atom, we will learn that instantaneous velocity can be obtained from a position-time curve of a moving object by calculating derivatives of the curve.
Velocity is defined as rate of change of displacement. The average velocity
What will happen when we reduce the time interval Δt\Delta t and let it approach 0? The average velocity becomes instantaneous velocity at time t. Suppose an object is at positions
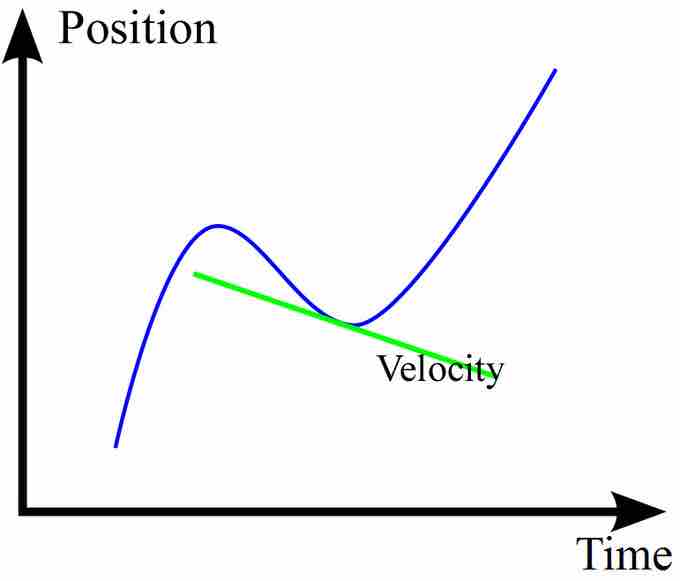
Instantaneous Velocity
The green line shows the tangential line of the position-time curve at a particular time. Its slope is the velocity at that point.
On the other hand, the equation for an object's position can be obtained mathematically by evaluating the definite integral of the equation for its velocity beginning from some initial period time