Personal Finance Defined
Personal finance is the application of the principles of finance to the monetary decisions of an individual or family. It addresses the ways in which individuals or families obtain, budget, save, and spend monetary resources over time, taking into account various financial risks and future life events. When planning personal finances there are many financial products one might consider: such as banking products (checking, savings accounts, credit cards, and consumer loans), investment products (stock market, bonds, and mutual funds), and insurance products (life insurance, health insurance, and disability insurance). One might also consider individual or employer sponsored retirement plans, social security benefits, and income tax management.
Personal Finance Strategies
Here are ways to start saving more:
Have an emergency savings account. This is an account you can tap into if you lose your job or have major, unforeseen expenses. "Emergency savings will help ensure that you don't have to borrow from your retirement nest egg or take out additional loans that would push you into debt," said Luke W. Reynolds, Chief of the FDIC's Community Affairs Outreach Section. A general rule of thumb is to have enough money in this "rainy day" fund equal to at least two months of living expenses. If your employment outlook is especially uncertain, consider setting aside enough to cover six or more months of anticipated expenses.
Also, keep your emergency savings in an account that will be fairly liquid — such as a bank savings account, money market account, or a short-term certificate of deposit (CD) — so you can withdraw the money relatively quickly, if necessary. "You should probably also keep your emergency money in a deposit account, where your funds are protected by federal deposit insurance, as opposed to stocks or stock or bond mutual funds that can lose value in a volatile market," said Mary Bass, an FDIC Senior Community Affairs Specialist. Try to save money for long-term goals, such as your retirement. If your employer matches a portion of your payroll contributions to a tax-advantaged retirement savings plan, "not participating means you are passing up free money and perhaps losing out on a valuable tax break," added Reynolds.
Pay yourself first. That means each month, before you're tempted to spend money, commit to putting a good bit of it into a savings account. You can write out a check to be deposited into your savings account, but it's much easier to arrange with your bank to automatically transfer a certain amount from your paycheck or your checking account into your savings. And as you pay your bills, your mortgage and other obligations, take satisfaction in knowing that some of your hard-earned dollars are already saved for you!
Start small. "By consistently saving small amounts, even $25 out of every paycheck, your savings account will grow and you will be motivated to try to save more," said Reynolds. "Even that spare change you put once a month into a bank savings account can add up faster than you think. "
Review your existing accounts and comparison shop for the best deals. Look at what is being offered by your bank and a few competitors. The idea is to make sure the interest rates are competitive and that the fees and features are appropriate for how you use each account. For example, if your money is sitting in a low-rate checking or savings account, consider moving it to a higher-yielding account, perhaps a CD where the earnings can get an extra boost. Turn a debt payment into a deposit. If you pay off a debt, such as the outstanding balance on a credit card, or if you make that last loan payment on your car, put that money to work as part of your savings.
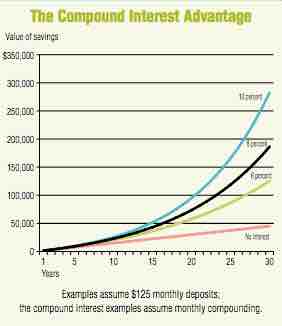
Compound Interest
The chart to the left shows how compound interest at various rates would increase Lynne's savings compared with simply putting the money in a shoebox. This is compound interest that you earn. And as you can see from an investment, compounding has a greater effect after the investment and interest have increased over a longer period.