Direct Banking
A direct bank is a bank without any branch network. It offers its financial services by:
- Telephone banking
- Online banking
- Automated teller machines (often through interbank network alliances)
- Mail banking
- Or mobile banking
By eliminating the costs associated with bank branches, direct banks may offer higher interest rates and lower service charges on their products than their traditional competitors. Direct banks were originally based on providing banking services via telephone. One of the world's first fully functional direct banks was First Direct, which launched in the United Kingdom on October 1, 1989. First Direct pioneered the concepts of no branches and 24-hour service from a call center.
The commercialization of the Internet in the early 1990s was the biggest driver in the creation of direct banking models. As the Internet became more generally accessible, traditional banks began to realize their potential to deliver services to their customers while reducing long-term operational costs. Upon realizing this, traditional banks began to offer limited online banking services. The initial success of internet banking services provided by traditional banks led to the development of internet-only banks or "virtual banks. " These banks were designed without a traditional banking infrastructure, a cost-saving feature that allowed many of them to offer savings accounts with higher interest rates and loans with lower interest rates than most traditional banks.
One of the first fully functional direct banks in the United States was the Security First Network Bank (SFNB). Based in Atlanta, it was the first direct bank to be insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). Though SFNB did not make much profit in its initial years, it demonstrated that the concept of direct banking could work.
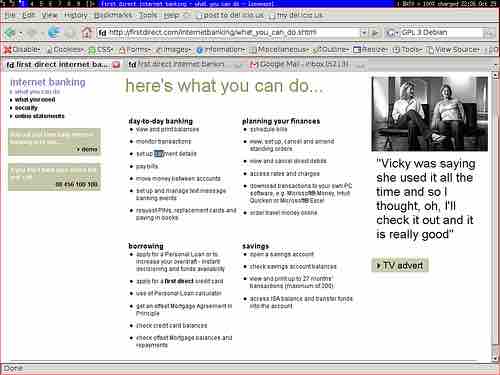
Online Direct Banking
A list of services offered by the First Direct Bank.