Chapter 13
Organized Labor Relations
By Boundless
A union is an organization of workers who have come together to achieve work related goals, such as higher pay and better conditions.
The union movement began in the early 19th century and paved the way for the establishment of the modern labor organizations.
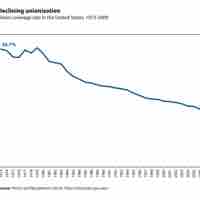
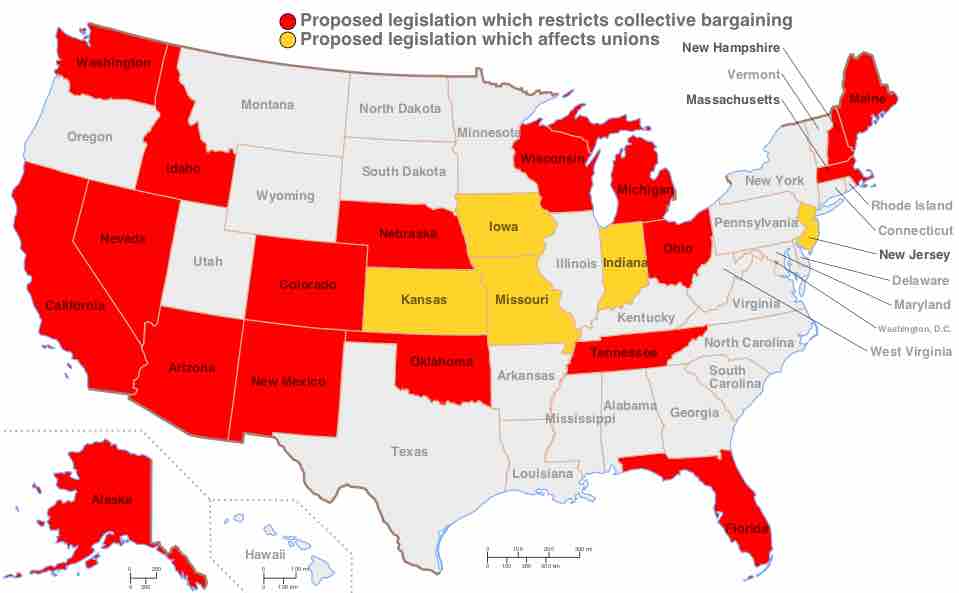
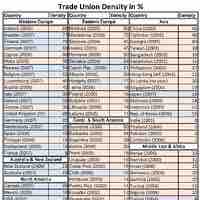
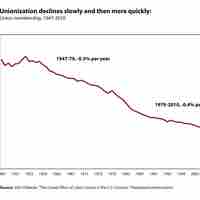
Labor unions have lost power in the United States over the years and, today, union membership varies by sector.

The Norris–LaGuardia Act removed certain legal and judicial barriers against the activities of organized labor in the United States.

The National Labor Relations Act limits employers' relations to workers who create labor unions and collectively act in support of demands.
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) established a national minimum wage, "time-and-a-half" for overtime in certain jobs, and etc.

The Labor Management Relations Act (Taft-Hartley Amendment) is a U.S federal law that monitors the activities and power of labor unions.

The Landrum-Griffin Act of 1959 is a U.S. labor law regulating labor unions' internal affairs and officials' relationships with employers.

By considering internal and external equity, a company can work toward a fair base pay system, attracting and retaining the best employees.

Job design is the allocation of specific work tasks to individuals and groups, in line with the company's general direction and strategy.
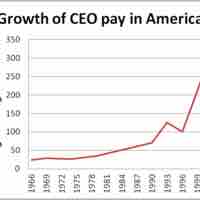
Levels of executive pay have been controversial in recent times, with only tenuous links between executive pay and company performance.

Sexual harassment is bullying or coercion of a sexual nature, or unwelcome/inappropriate promises of rewards in exchange for sexual favors.

Explaining why drug testing is necessary and following proven process guidelines will go a long way toward appeasing workers.

Conflict in the workplace arises when there is a non-acceptance of the differences which exist between people at work.

Different participation systems can be implemented to authentically get employee input and to capitalize on the benefits.

Strike action, also called a labor strike, is a work stoppage caused by the mass refusal of employees to work.

Union boycotts are a form of industrial action by a trade union in support of a strike initiated by workers in another, separate enterprise.

Employers are generally motivated to prevent, mitigate the impact of, and undermine strikes when they occur by using a variety of tactics.

Labor trends include a declining union movement in the US, public sector unions, women leaders, and international unions.