Chapter 12
Human Resource Management
By Boundless

The National Labor Relations Act establishes the right of most private-sector workers to form unions, bargain with management and strike.

The Labor-Management Relations Act (or the Taft-Hartley Act) is a U.S. federal law that monitors the activities and power of labor unions.
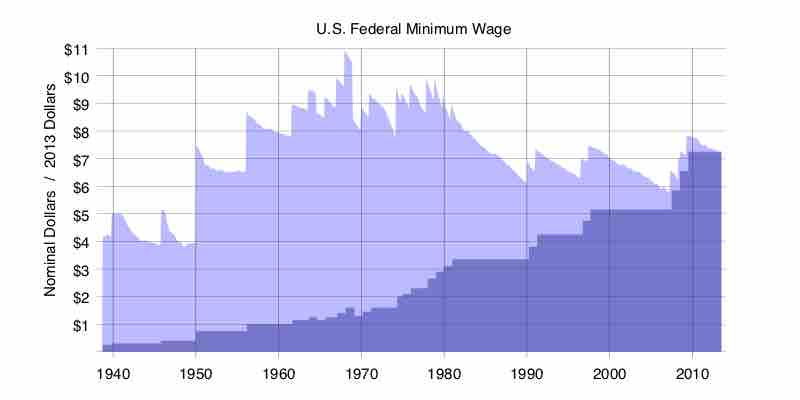
The Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 established a national minimum wage, forbade "oppressive" child labor, and provided for overtime pay in designated occupations.

The Equal Pay Act of 1963 is a U.S. Federal law amending the Fair Labor Standards Act aimed at abolishing wage disparity based on sex.
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 outlawed major forms of discrimination against African Americans and women, including racial segregation.

Under this act both employees and applicants who are 40 years old or over are protected from employment discrimination based on their age.

The goal of the OSHA Act is to make sure employers provide employees a place to work that is free from recognized hazards.

Businesses who voluntarily set up pension and health plans in private industry must adhere to rules ERISA rules that protect employees.
Affirmative action prevents discrimination against employees on the basis of race, religion, gender, or nationality.

The ADA makes it illegal to discriminate against people with disabilities in employment, public transportation, and communications.

The four methods of collecting performance review data: objective production, personnel, judgmental evaluation, and peer or self evaluation.
Organizations derive significant value from empowering employees to help manage their managers.
When a person receives a promotion, they are rewarded for good performance by receiving a higher rank or position in the organization.

Terminations occur in a variety of ways, both voluntary and involuntary, and determine the employee's future relationship with the employer.
When a person retires, they stop working completely or semi-retire by reducing their hours.
An employee leaving one company to join another one is known as attrition.

Compensation is a monetary benefit given to workers in return for services provided by them and it can take a number of different forms.
Organizations can remunerate labor according to different criteria, including hours worked, output produced, or a combination of the two.
Human resource requisites regarding employee compensation include a wide variety of common benefits beyond salary.

Fringe benefits are various indirect benefits, often of a more discretionary nature than standard benefits.

Training is the acquisition of knowledge, skills, and competencies through a conscious skills development program.
Professional development refers to skills and knowledge attained for both personal development and career advancement.
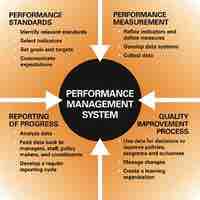
A performance appraisal is done to assess an employee's job performance and productivity on certain preestablished criteria and objectives.

Turnover is the rate at which employees leave an organization.
Human resource departments are responsible for a wide variety of activities across a number of core organizational functions

Human resource development combines training and career development to improve the effectiveness of the individual, group, and organization.

Human resource management is responsible for the attraction, selection, training, assessment, and rewarding of employees.
HR forecasting is the process of ascertaining the net requirements for staff by determining present and future HR needs.
Diversity in an organization should reflect a globalized and multicultural workforce where value is placed on diversity of thought.
Diversity brings substantial potential benefits such as better decision making and problem solving, and greater creativity and innovation.

