Chapter 10
Operations Management
By Boundless

Operations management is the management of processes that transform inputs into goods and services that add value for the customer.
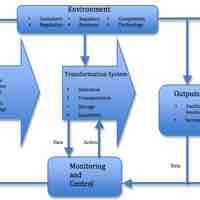
Operations management transforms inputs (labor, capital) into outputs (goods and services) that provide added value to customers.

Services operations often encounter different opportunities and challenges than tangible goods, and thus require unique operational considerations.
Quality management adopts a number of management principles that can be used to guide organizations towards improved performance.

Total quality management (TQM) is an integrative philosophy of management for continuously improving the quality of products and processes.

Companies ensure the quality of products and services by adhering to ISO standards and performing quality audits to ensure compliance.

Reducing waste by more efficient manufacturing is a key goal of management, with supply chain sustainability seen as a key component.
Productivity, or the efficiency of production, is important because it can drive increases in output and improvements in living standards.
New ways of developing and using software have led to higher efficiency and productivity through greater interaction between users.

Productivity improving technologies lower traditional factors of production of land, labor capital, materials, and energy.
Purchasing is the formal process of buying goods and services.
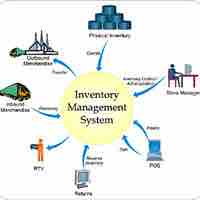
Inventory management is primarily concerned with specifying the shape and percentage of stocked goods to reduce costs and improve sales.
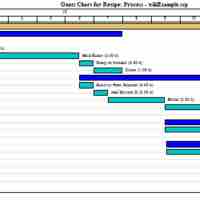
The purpose of scheduling is to minimize production time and costs.
Routing is the process of selecting paths in a network along which to send network traffic.

Outsourcing is the contracting of an existing business process to an external, independent organization.
Logistics plans, implements, and controls the forward and reverse flow and storage of goods between the point of origin and consumption.

Quality control is a process that evaluates output against a standard and takes corrective action when output doesn't meet that standard.
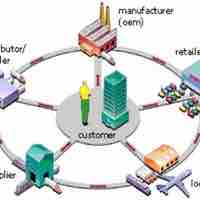
Investment in information technology has made supply chains faster, cheaper, and more reliable.

Organizations put a lot of time and money into new products and thus deploy various methods in an attempt to mitigate the risks.

Designing effective operations is critical, and can have both short-term and long-term impacts on an organization's longevity.

Capacity planning revolves around answering the question "How much? " in both long-term and short-term situations.

Facility layout decisions are based on criteria aimed at creating an effective and efficient workflow and high standard production.

An organization's location choice impacts its efficiency and effectiveness, so it is important for it to properly weigh the various factors.
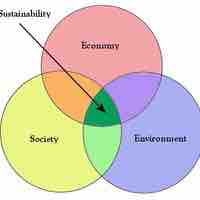
Sustainability initiatives consider every dimension of how a business operates in the social, cultural, and economic environment.