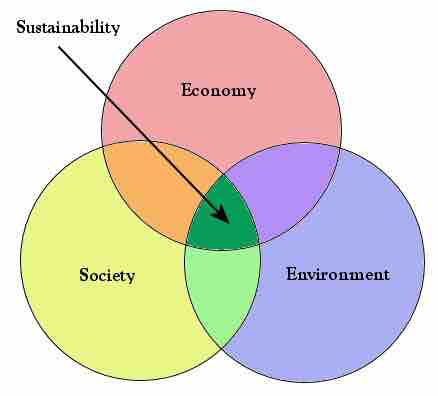
Sustainability, in a general sense, is the capacity to support, maintain, or endure. Since the 1980s, human sustainability has been related to the integration of environmental, economic, and social dimensions towards global stewardship and responsible management of resources .
Sustainability
Sustainability is related to the integration of environmental, economic, and social dimensions towards global stewardship and responsible management of resources.
Corporate sustainability is a business approach that creates long-term consumer and employee value by not only creating a "green" strategy aimed towards the natural environment, but taking into consideration every dimension of how a business operates in the social, cultural, and economic environment. It also involves formulating strategies to build a company that fosters longevity through transparency and proper employee development. Three key principles that should form the foundation of a corporate sustainability initiative are: transparency, employee development, and resource efficiency.
Transparency deals with the idea that having an engaging and open environment within the company, as well as the community, will improve performance and increase profits. An open culture promotes employee involvement in regards to the innovation and creative processes. Reaching out to the community creates a much bigger team and provides evaluation from all angles. Companies are looking inward and realizing changes must be made to fulfill environment needs such as energy efficiency, limiting product waste and toxicity, and designing innovative products.
Employee development involves the idea that people are the most important renewable resource and, therefore, are the strongest asset to any organization. A strong development program could be the underlying factor for a company's success or failure. Employees are the concrete foundation for the company and must be thoroughly analyzed and evaluated to tap into their true motivations and desires. For a company that wants to reach its greatest potential, employees must work towards improvement rather than perfection. Programs should be implemented that reward star performers, foster the creative learning process, and provide comprehensive training and evaluating.
Resource efficiency refers to that fact that companies must adapt to a rapidly changing environment by being prepared to change and implement new creative ideas related to sustainability. Companies should not throw away old products and materials, but rather be prepared with upgraded technology that can transform the product. New solutions that improve recycling and waste redirecting can ultimately reduce costs and increase profits. For example, Wal-Mart Stores Inc. has redirected more than 64% of the waste generated by stores and Sam's Club facilities. In 2009 alone, they recycled more than 1.3 million pounds of aluminum, 120 million pounds of plastics, 11.6 million pounds of mixed paper, and 4.6 billion pounds of cardboard. On an annual basis, they expect to save around $20 million and prevent 38 million pounds of waste being sent to landfills.
Essential Principles of a Sustainability Initiative
- Triple top-line value production: This establishes three simultaneous requirements of sustainable business activities: 1) financial benefits for the company, 2) natural world betterment, and 3) social advantages for employees and members of the local community—with each of these three components recognized as equal in status.
- Nature-based knowledge and technology: This biomimicry-based principal involves the conscious emulation of natural-world genius in terms of growing our food, harnessing our energy, construction, conducting business, healing ourselves, processing information, and designing our communities.
- Products of service and products of consumption: Products of service are durable goods routinely leased by the customer that are made of technical materials and are returned to the manufacturer and re-processed into a new generation of products when they are worn out. Products of consumption are shorter lived items made only of biodegradable materials. This principal requires that we manufacture only these two types of products and necessitates the gradual but continual reductions of products of service and their replacement with products of consumption as technological advancements allow.
- Solar, wind, geothermal, and ocean energy: This principal advocates employing only sustainable energy technology—solar, wind, ocean, and geothermal—that can meet our energy needs indefinitely without negative effects for life on Earth.
- Local-based organizations and economies: This principle calls for durable, beautiful, and healthy communities with locally-owned and operated businesses and locally-managed non-profit organizations, along with regional corporations and shareholders working together in a dense web of partnerships and collaborations.
- Continuous improvement process: This principle suggests that operational processes inside successful organizations include provisions for constant advancements and upgrade as the company does its business.