Business-to-consumer (B2C) e-commerce, or commerce between companies and consumers, involves customers gathering information; purchasing physical goods (i.e., tangibles such as books or consumer products) or information goods (or goods of electronic material or digitized content, such as software or e-books); and, for information goods, receiving products over an electronic network. It is the second largest and the earliest form of e-commerce. Its origins can be traced to online retailing (or e-tailing). Thus, the more common B2C business models are the online retailing companies such as Amazon.com, Drugstore.com, Beyond.com, Barnes and Noble, and Toys-R-Us. Other B2C examples involving information goods are E-Trade and Travelocity.
The more common applications of this type of e-commerce are in the areas of purchasing products and information, and personal finance management, which pertains to the management of personal investments and finances with the use of online banking tools (e.g., Quicken). Online retailing transactions make up a significant share of the B2C e-commerce market.
B2C e-commerce reduces transactions costs (particularly search costs) by increasing consumer access to information and allowing consumers to find the most competitive price for a product or service. B2C e-commerce also reduces market entry barriers since the cost of putting up and maintaining a website is much cheaper than installing a "brick-and-mortar" structure for a firm. In the case of information goods, B2C e-commerce is even more attractive because it saves firms from factoring in the additional cost of a physical distribution network. Moreover, for countries with a growing and robust Internet population, delivering information goods becomes increasingly feasible.
Another form of e-commerce involving selling to consumers is known as consumer-to-consumer (C2C). It is simply commerce between private individuals or consumers. This type of e-commerce is characterized by the growth of electronic marketplaces and online auctions, particularly in vertical industries where firms/businesses can bid for what they want from among multiple suppliers. It perhaps has the greatest potential for developing new markets.
This type of e-commerce comes in at least three forms:
- Auctions facilitated at a portal, such as eBay, which allows online real-time bidding on items being sold in the Web
- Peer-to-peer systems, such as the Napster model (a protocol for sharing files between users used by chat forums similar to IRC) and other file exchange and later money exchange models
- Classified ads at portal sites such as Craigslist (an interactive, online marketplace where buyers and sellers can negotiate and that features "Buyer Leads & Want Ads")
B2C E-Commerce
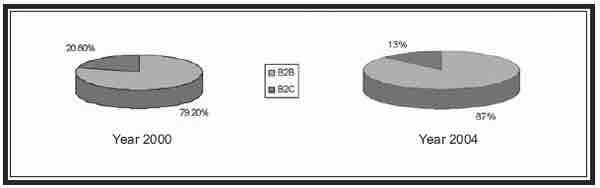
B2C e-commerce makes up a smaller portion of the market share of e-commerce compared to B2B, and appears to be shrinking in comparison.