Chapter 1
Introduction to Business
By Boundless
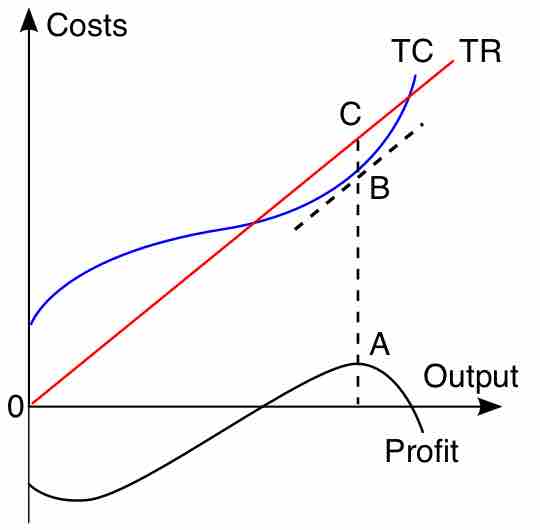
The primary purpose of a business is to maximize profits for its owners or stakeholders while maintaining corporate social responsibility.
Organization helps businesses achieve focus and success in reaching their goals.
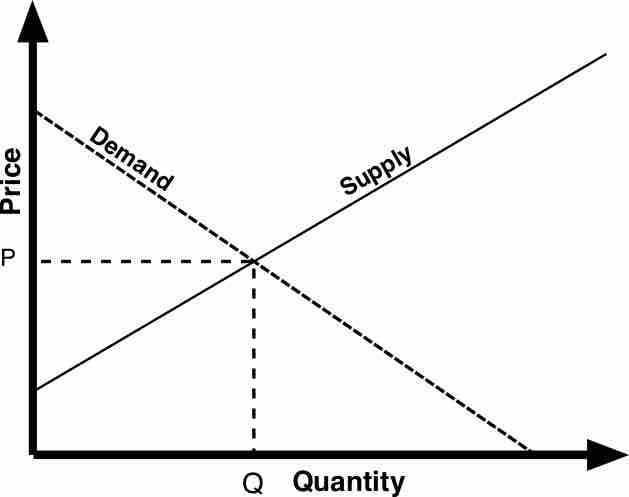
In today's business environment, ascertaining market needs is vital for a firm's future viability, and even existence, as a going concern.

Profit is equal to a firm's revenue minus its expenses, while value is the present value of the firm's current and future profits.
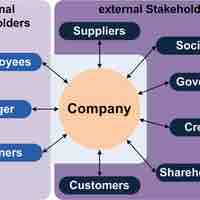
A stakeholder is any group or individual who can affect or who is affected by achievement of a group's objectives.

Nonprofits play a vital role in society by focusing resources and providing services to community needs without regard to profit.

Despite recent economic woes, America's economy remains the world's largest and most diverse.
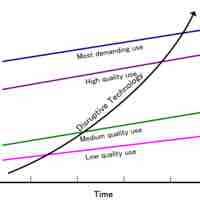
The constant evolution of technology offers both considerable opportunity and risk to businesses across all industries.

Current competition can be examined through market dominance, mergers and acquisitions, public sector regulation, and intellectual property.
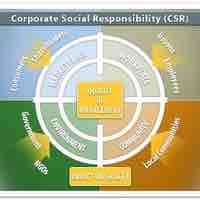
Businesses must consider their social environment, since their actions have repercussions that echo throughout society.
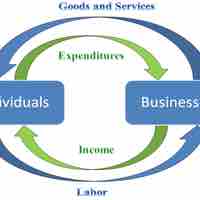
Global business is changing and evolving quickly due to demographic and technological trends.
During the second agricultural revolution, U.S. agricultural productivity rose fast, especially due to the development of new technologies.
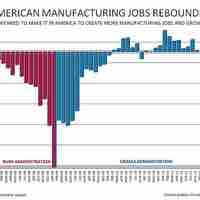
In 2009, the United States was the world's largest manufacturer, with $2.33 trillion in output, more than Germany, France, India, and Brazil combined.

Productivity improving technologies date back to antiquity, and have accelerated greatly of late.
Most of the U.S. economy is classified as services as of 2011 (agriculture 1.2%, industry 22.1%, services 76.7%).

The goals of entrepreneurs are varied and individualized but can include the achievement of independence, financial success, or social change.
In general, small firms have greater flexibility than larger firms and capacity to respond promptly to industry or community developments.
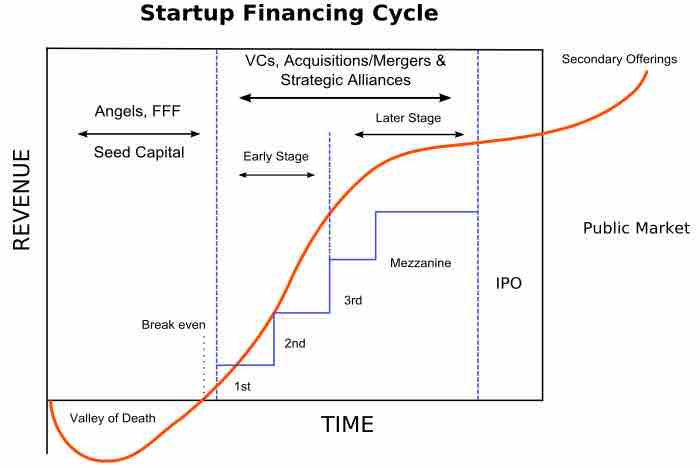
Creativity and entrepreneurship are needed to combine inputs in profitable ways, resulting in large scale economic growth/development.

There are two main ways to learn business topics: problem-based and team-based learning.
The teaching approach of presenting students with a case and putting them in the role of a decision maker is known as the case method.

A business game (also called business simulation game) refers to a simulation game that is used as an educational tool for teaching business.