The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) is a forum for 21 Pacific Rim countries (formally Member Economies) that seeks to promote free trade and economic cooperation throughout the Asia-Pacific region. Established in 1989 in response to the growing interdependence of Asia-Pacific economies and the advent of regional economic blocs (such as the European Union) in other parts of the world, APEC works to raise living standards and education levels through sustainable economic growth and to foster a sense of community and an appreciation of shared interests among Asia-Pacific countries.
Member countries are: Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, China, Hong Kong (Hong Kong, China), Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Mexico, Malaysia, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Peru, Philippines, Russia, Singapore, Taiwan (Chinese Taipei), Thailand, United States, and Vietnam.
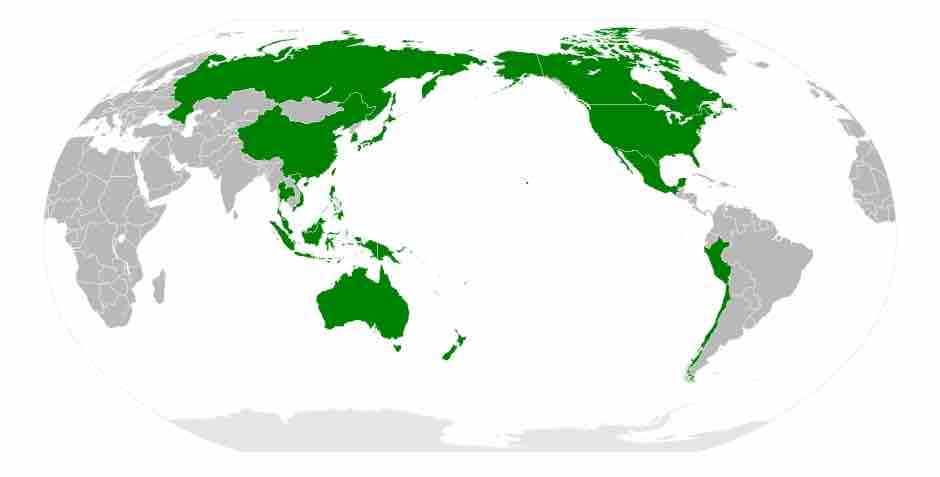
APEC member countries
APEC's member countries border both the east and the west of the Pacific Ocean.
During the meeting in 1994 in Bogor, Indonesia, APEC leaders adopted the Bogor Goals that aim for free and open trade and investment in the Asia-Pacific by 2010, for industrialized economies and by 2020, for developing economies. In 1995, APEC established a business advisory body named the APEC Business Advisory Council (ABAC), composed of three business executives from each member economy. To meet the Bogor Goals, APEC carries out work in three main areas:
- Trade and investment liberalization
- Business facilitation
- Economic and technical cooperation
APEC is considering the prospects and options for a Free Trade Area of the Asia-Pacific (FTAAP), which would include all APEC member economies. Since 2006, the APEC Business Advisory Council, promoting the theory that a free trade area has the best chance of converging the member nations and ensuring stable economic growth under free trade, has lobbied for the creation of a high-level task force to study and develop a plan for a free trade area. The proposal for a FTAAP arose due to the lack of progress in the Doha round of World Trade Organization negotiations, and as a way to overcome the "spaghetti bowl" effect created by overlapping and conflicting elements of the umpteen free trade agreements. There are approximately 60 free trade agreements, with an additional 117 in the process of negotiation in Southeast Asia and the Asia-Pacific region.