Chapter 4
International Business
By Boundless

Competitive advantage is defined as the strategic advantage one business entity has over its rival entities within its competitive industry.

Absolute advantage and balance of trade are two important aspects of international trade that affect countries and organizations.

Nations export products for which they have a competitive advantage in order to import products for which they lack a competitive advantage.
Trade barriers are government-induced restrictions on international trade, which generally decrease overall economic efficiency.

Despite international trading laws and declarations, countries continue to face challenges around ethical trading and business practices.
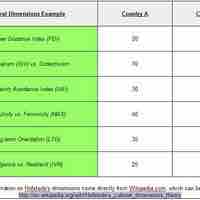
It is typically more difficult to do business in a foreign country than in one's home country due to cultural barriers.
Standards-related trade measures, known in WTO parlance as technical barriers to trade play a critical role in shaping global trade.

Some argue that imports from countries with low wages has put downward pressure on the wages of Americans and therefore we should have trade barriers.

Economists generally agree that trade barriers are detrimental and decrease overall economic efficiency.
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is a multilateral agreement regulating international trade.
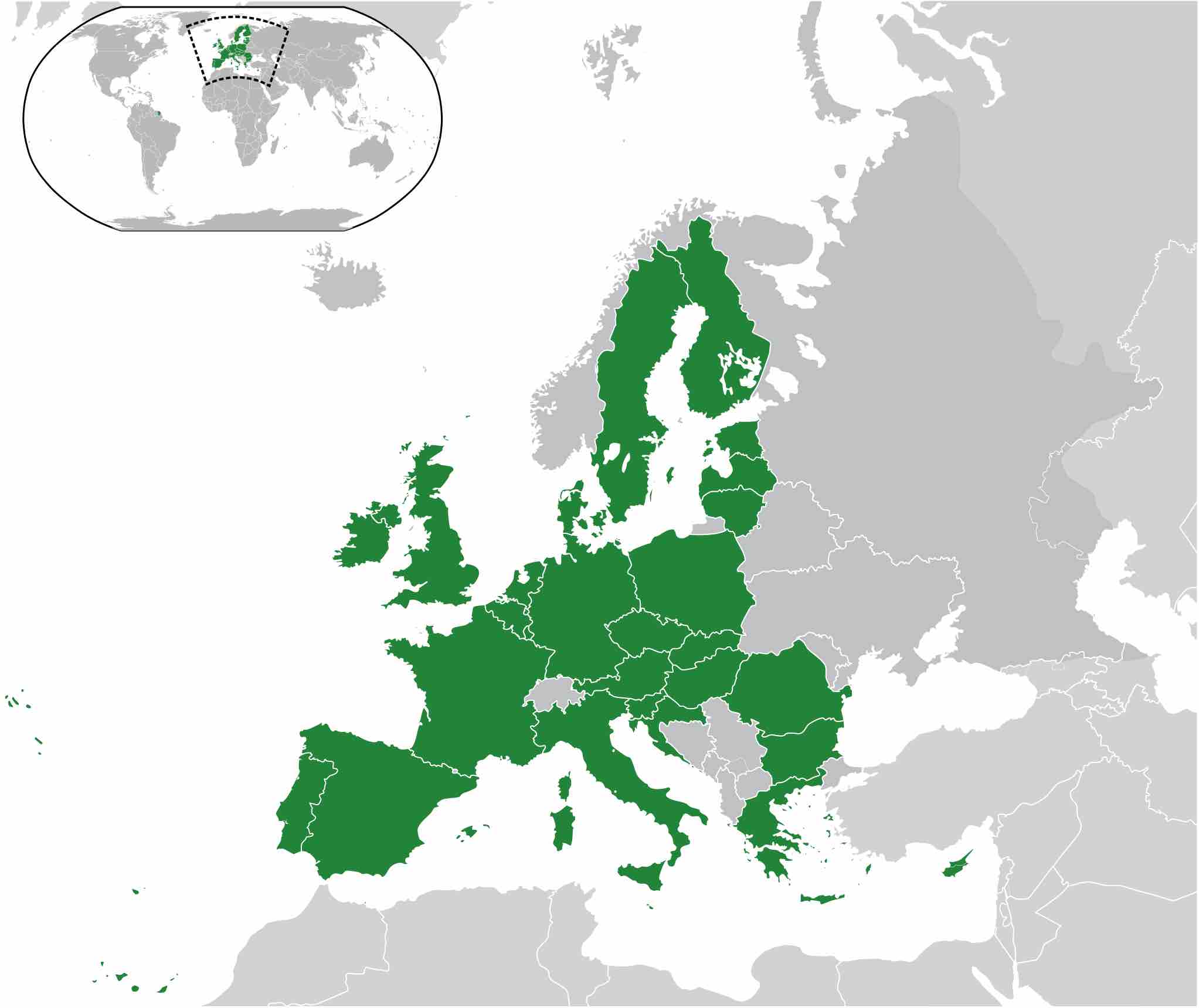
The European Union (EU) is an economic and political union made up of 27 member states that are located primarily in Europe.
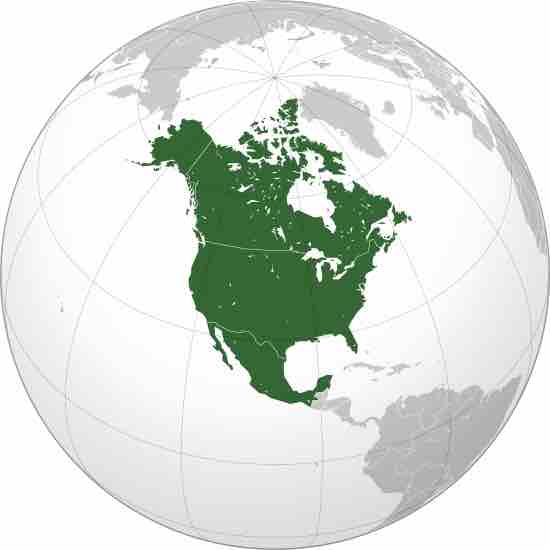
NAFTA is an agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States, creating a trilateral trade bloc in North America.
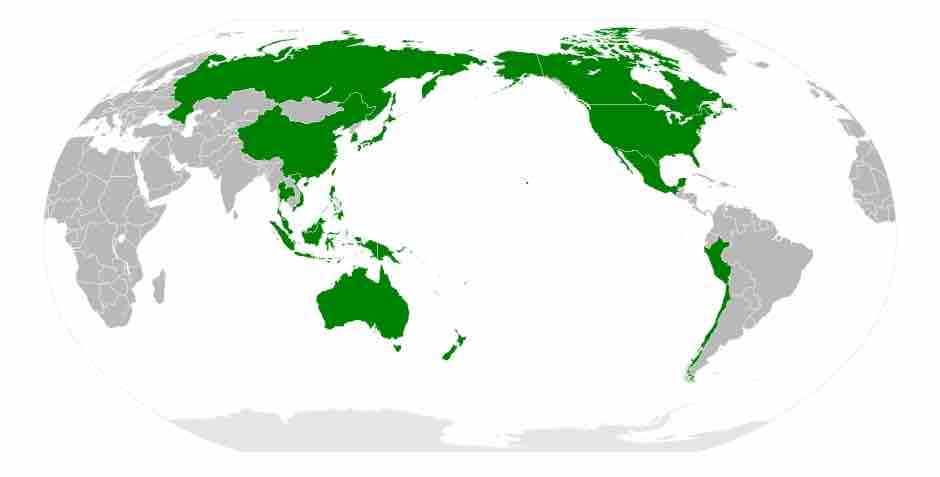
APEC is a forum for 21 Pacific Rim countries that seeks to promote free trade and economic cooperation throughout the Asia-Pacific region.

The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for various programs.

The IMF seeks to promote international economic cooperation, international trade, employment, and exchange rate stability.
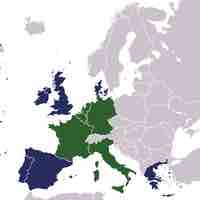
A common market is the first stage towards a single market and may be limited initially to a free trade area.

The Export-Import Bank of the United States (Ex-Im Bank) is the official export credit agency of the United States federal government.
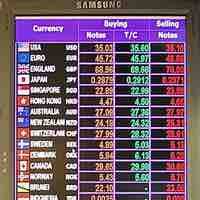
The price of one country's currency in units of another country's currency is known as a foreign currency exchange rate.
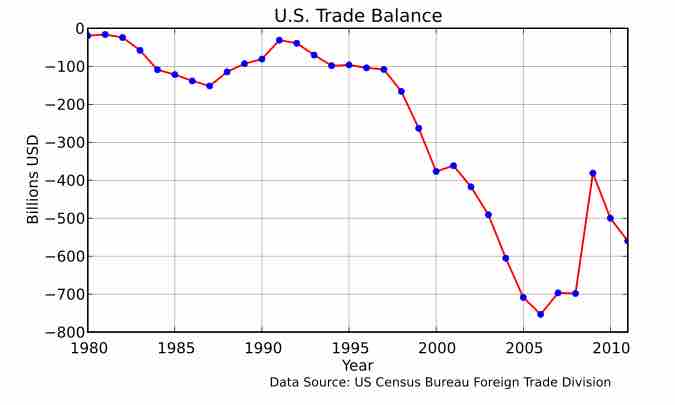
The balance of trade is the difference between the monetary value of exports and imports in an economy over a certain period.
Balance of payments (BOP) accounts are an accounting record of all monetary transactions between a country and the rest of the world.
When considering strategic entry into an international market, licensing is a low-risk and relatively fast foreign market entry tactic.
Franchising enables organizations a low cost and localized strategy to expanding to international markets, while offering local entrepreneurs the opportunity to run an established business.
Exporting is the practice of shipping goods from the domestic country to a foreign country.

Imports are the inflow of goods and services into a country's market for consumption.

In contract manufacturing, a hiring firm makes an agreement with the contract manufacturer to produce and ship the hiring firm's goods.

In a joint venture business model, two or more parties agree to invest time, equity, and effort for the development of a new shared project.

Outsourcing business functions to developing foreign countries has become a popular way for companies to reduce cost.
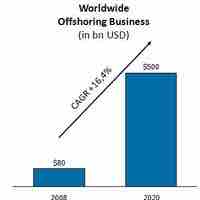
Offshoring entails a company moving a business process from one country to another.

With the advent of improved communication and technology, corporations have been able to expand into multiple countries.

FDI is practiced by companies in order to benefit from cheaper labor costs, tax exemptions, and other privileges in that foreign country.
Countertrade is a system of exchange in which goods and services are used as payment rather than money.