How Economies Can Benefit From Socialism
Socialist economics entails the following:
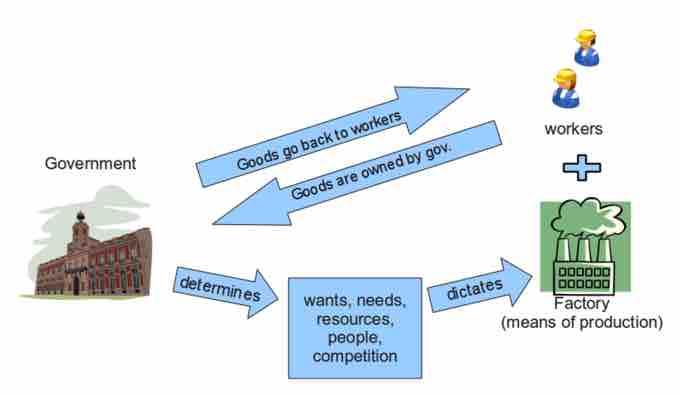
Socialism
A graphical illustration of socialism.
- Nationalization of key industries, such as mining, oil, steel, energy and transportation. A common model includes a sector being taken over by the state, followed by one or more publicly owned corporations arranging its day-to-day running. Advantages of nationalization include: the ability of the state to direct investment in key industries, distribute state profits from nationalized industries for the overall national good, direct producers to social rather than market goals, and better control the industries both by and for the workers. Additionally, nationalization enables the benefits and burdens of publicly funded research and development to be extended to the wider populace.
- Redistribution of wealth, through tax and spending policies that aim to reduce economic inequalities. Social democracies typically employ various forms of progressive taxation regarding wage and business income, wealth, inheritance, capital gains and property. On the spending side, a set of social policies typically provides free access to public services such as education, health care and child care. Additionally, subsidized access to housing, food, pharmaceutical goods, water supply, waste management and electricity is common.
- Social security schemes in which workers contribute to a mandatory public insurance program. The insurance typically includes monetary provisions for retirement pensions and survivor benefits, permanent and temporary disabilities, unemployment and parental leave. Unlike private insurance, governmental schemes are based on public statutes rather than contracts; therefore, contributions and benefits may change in time, and are based on solidarity among participants. Its funding is done on an ongoing basis, without direct relationship to future liabilities.
- Minimum wages, employment protection and trade union recognition rights for the benefit of workers. These policies aim to guarantee living wages and help produce full employment. While a number of different models of trade union protection have evolved throughout the world over time, they all guarantee the right of workers to form unions, negotiate benefits and participate in strikes. Germany, for instance, appointed union representatives at high levels in all corporations, and as a result, endured much less industrial strife than the UK, whose laws encouraged strikes rather than negotiation.
The benefits of socialism also include the following:
- In theory, based on public benefits, socialism has the greatest goal of common wealth;
- Since the government controls almost all of society's functions, it can make better use of resources, labors and lands;
- Socialism reduces disparity in wealth, not only in different areas, but also in all societal ranks and classes. Those who suffer from illnesses or are too old to work are still provided for and valued in by the government, assuming that the government is more compassionate that the individual's family;
- Excess or insufficient production can be avoided;
- Prices can be controlled in a proper extent;
- Socialism can tackle unemployment to a great extent.