Chapter 3
Britain and the Settling of the Colonies: 1600–1750
By Boundless
The 17th century marked the early beginnings of English rule in the Americas with the establishment of the Thirteen Colonies.
Colonial farmers, planters, and shopkeepers hired servants from Europe who agreed to work for a number of years in exchange for their passage to America.
The Puritans founded Plymouth in order to practice their own brand of Protestantism without interference from England.
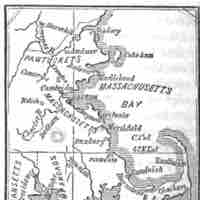
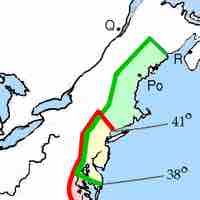
The Massachusetts Bay Colony, founded in the 17th century, included parts of Maine, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Connecticut.

Rhode Island was formed as an English colony by Roger Williams and others fleeing prosecution from Puritans.

Early New England Puritan society was characterized by yeoman farming communities and a growing merchant class.

Unlike most of the Chesapeake or southern colonies which were established to make a profit, New England colonies were largely established for religious reasons.
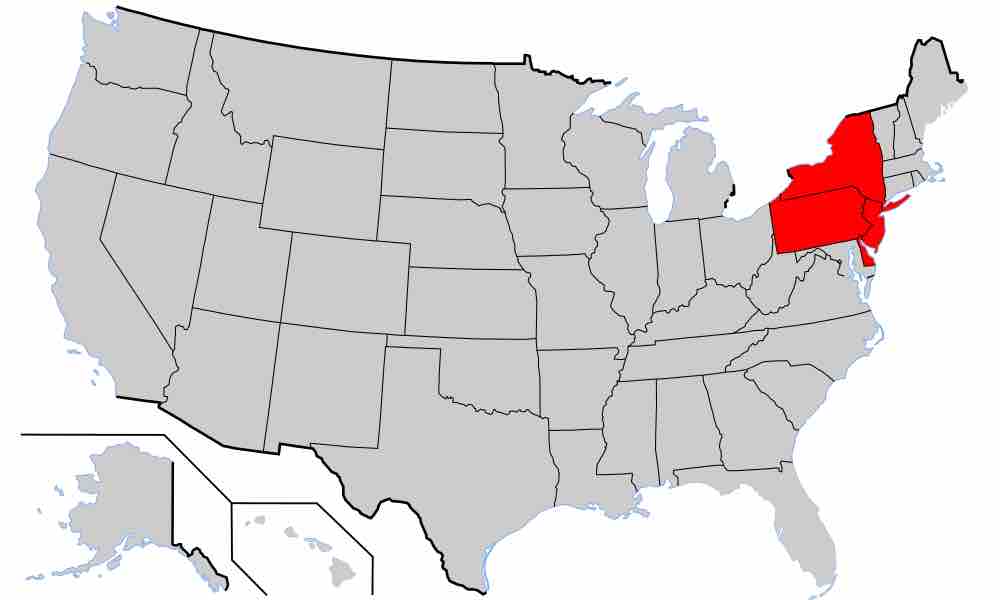
The Middle Colonies later became the states of New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware.
The Dutch colony of New Netherland was taken by the British in the 17th century and later became the colonies of New York and New Jersey.

William Penn founded the Pennsylvania Colony in 1681 and brought over Quaker dissidents from England, Wales, the Netherlands, and France.
The Middle Colonies were more ethnically diverse than elsewhere in British North America and were somewhat more socially tolerant.
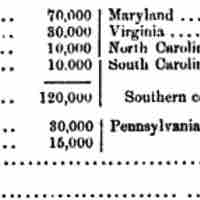
The Southern Colonies, including Maryland, the Carolinas, Virginia, and Georgia were established during the 16th and 17th centuries.

The Virginia Colony became the wealthiest and most populated British colony in North America, largely due to its tobacco crop industry.
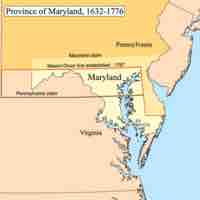
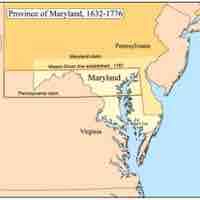
Maryland was established in 1632 as a haven for English Roman Catholics in the New World.
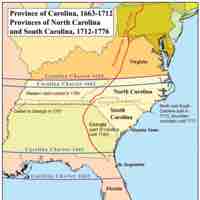
The Carolinas, chartered in 1629, became important southern agricultural colonies.
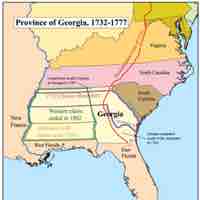
The Province of Georgia was chartered as a proprietary colony in 1733 and was the last of the 13 original British colonies.