Sexual Orientation
Sexual orientation describes an enduring pattern of attraction—emotional, romantic, sexual, or some combination of these—to the opposite sex, the same sex, both, or neither. The varying forms of these attractions are generally divided into the following categories:
- heterosexuality, or attraction to members of the opposite biological sex
- homosexuality, or attraction to members of the same biological sex
- bisexuality, or attraction to members of both biological sexes
- asexuality, or attraction to neither biological sex.
Some individuals have tried to trouble these categories of sexual orientation by not describing themselves as hetero-, homo-, bi-, or asexual and preferring the umbrella term "queer. " Part of the opposition to the gender binary is that it creates heteronormative assumptions that mark heterosexuality as normal and homosexuality deviant merely because it is the opposite of heterosexuality.
Significantly, sexual orientation does not only refer to one's sexual practices, but also includes a psychological component, like the direction of an individual's erotic desire. Sexual identity and sexual behavior are closely related to sexual orientation, but they are distinguishable. Sexual identity refers to an individual's conception of their own sexuality, while sexual behavior limits one's understanding of sexuality to behaviors performed. People may or may not express their sexual orientation in their behaviors.
Development of Sexual Orientation
The primary tension in conversations about sexual orientation addresses whether sexual orientation is static or fluid, whether one is born with an immutable sexual orientation, or whether one develops sexual orientation. Each interpretation of sexuality manages our understanding of what sexual orientation means in different ways, particularly when combined with political debates about homosexuality. Organizations that subscribe to the static interpretation of sexual orientation fall on both sides of the political divide. Some organizations are socially and politically conservative, advancing the view that sexuality, left untreated, is static. These organizations tend to pathologize non-heterosexual orientations, or conceive of them as an illness that must be corrected through medical or therapeutic means. Some of these institutions offer sexual reorientation therapies in which individuals who are attracted to members of the opposite sex but do not want to have those attractions can try to become solely attracted to members of the opposite biological sex. Many of these programs are religiously motivated; 79% of men who said that they had changed their sexual orientation said that they had done so for religious reasons, while 93% indicated that religion was "extremely" or "very" important to them.
Sexual Reorientation
A significant amount of professional and academic doubt exists about the efficacy of these reorientation programs. No major mental health professional organization has sanctioned efforts to change sexual orientation and virtually all of them have adopted policy statements cautioning the profession. These include the American Psychiatric Association, the American Psychological Association, the American Counseling Association, the National Association of Social Workers in the USA, and the Royal College of Psychiatrists. According to the American Psychological Association and the Royal College of Psychiatrists' Gay and Lesbian Mental Health Special Interest Group, there is no sound scientific evidence that sexual orientation can be changed.
Though they obviously disagree with the conceit that homosexuality needs to be treated, many major gay rights advocacy groups mirror the underlying assumption that homosexuality is a static sexual orientation. The idea that sexual orientation is not a choice, but that rather one is born with an assigned orientation, is pervasive in popular conceptions of sexual orientation. This idea runs up against studies that demonstrate how widely sexual orientation varies in light of cultural and historical circumstances, indicating that one's environment and cultural context play significant roles in determining one's sexual orientation.
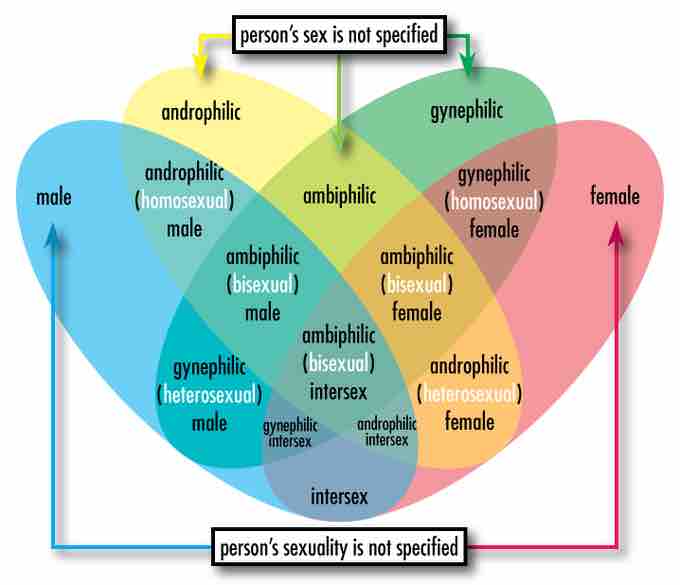
Sex and Sexuality
Venn diagram depicting the relationships between assigned sex and sexual orientation. Androphilia and gynephilia are preferred terms for some populations, because homosexual and heterosexual assign a sex to the person being described.